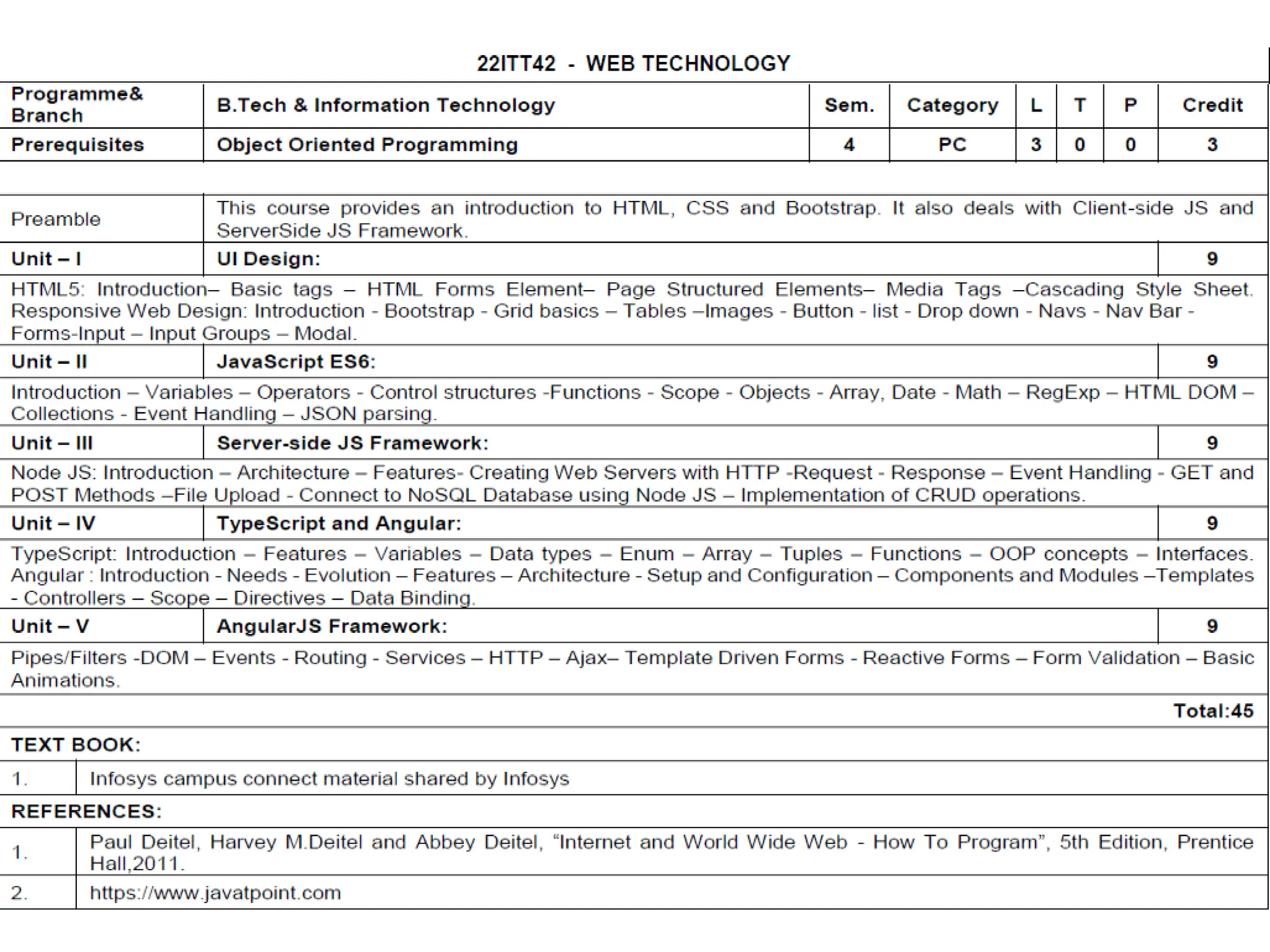
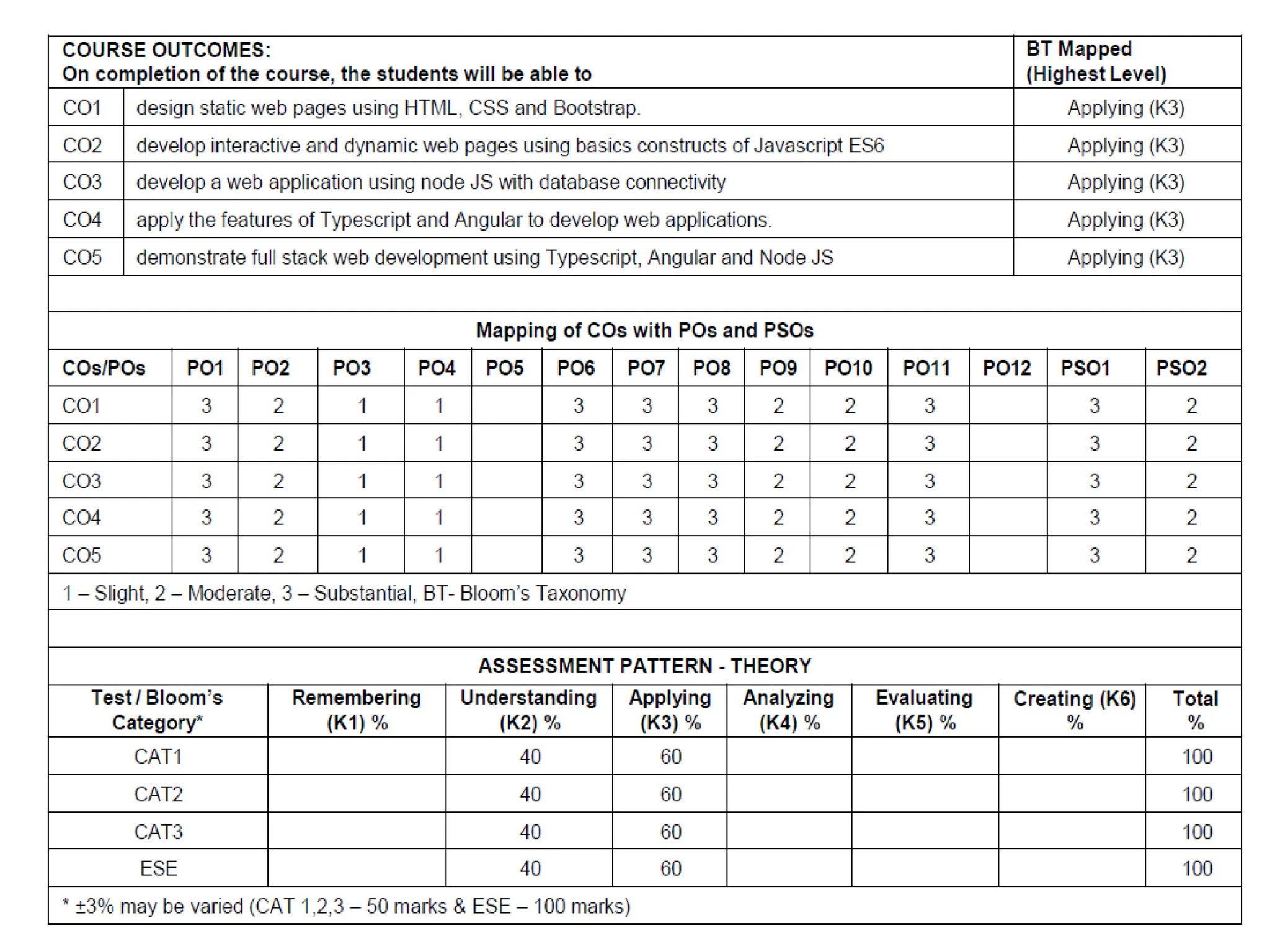
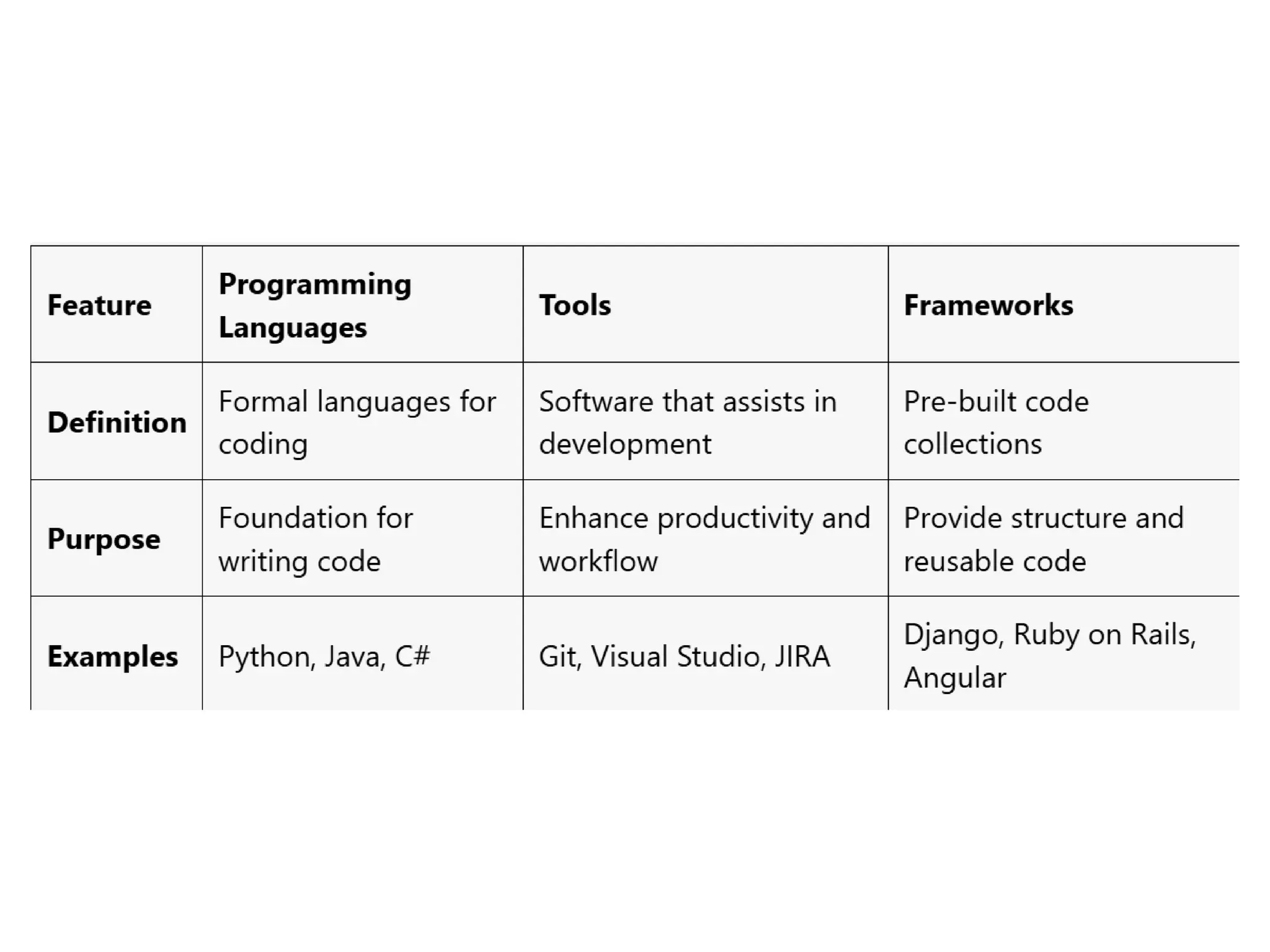
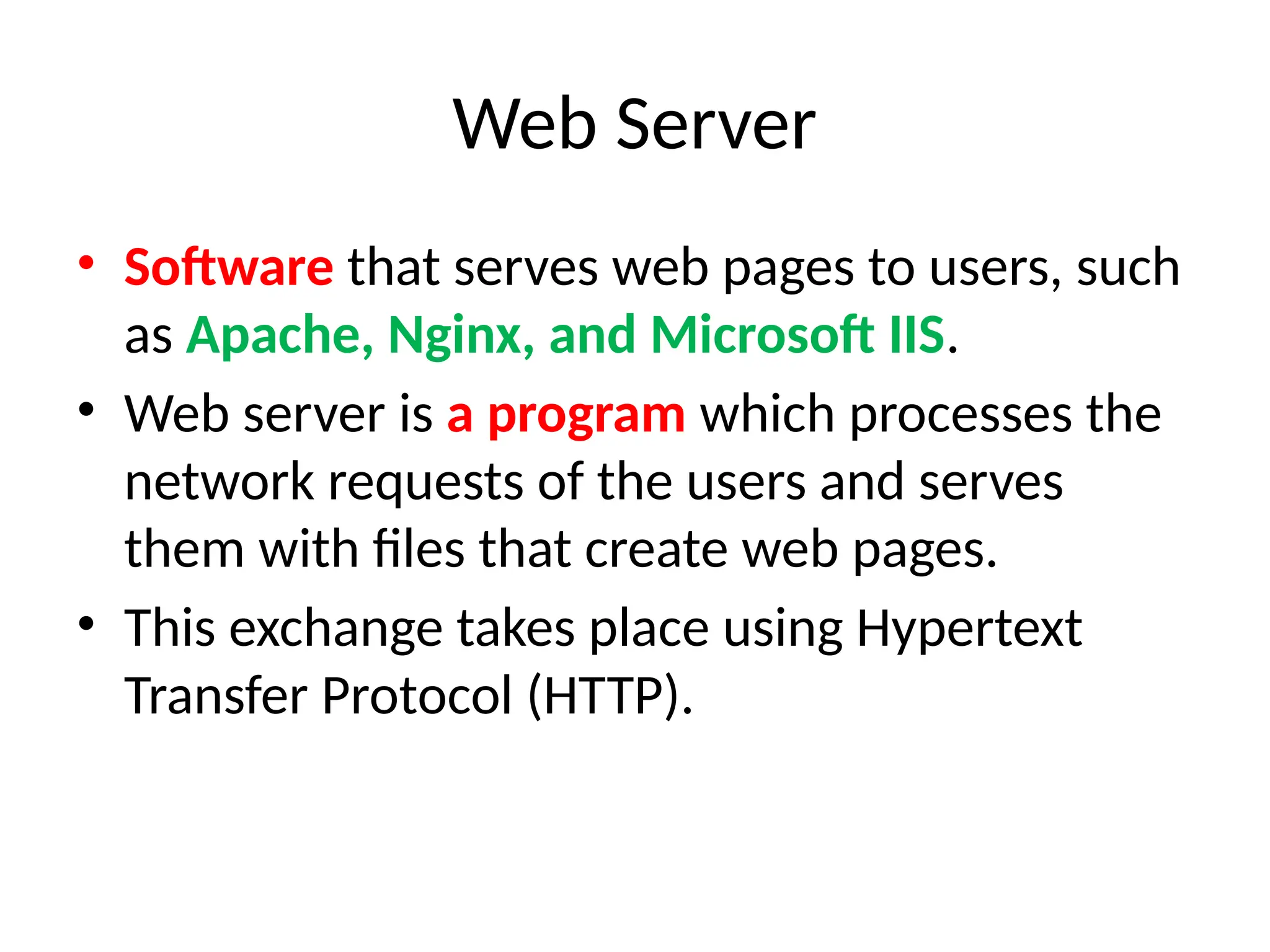
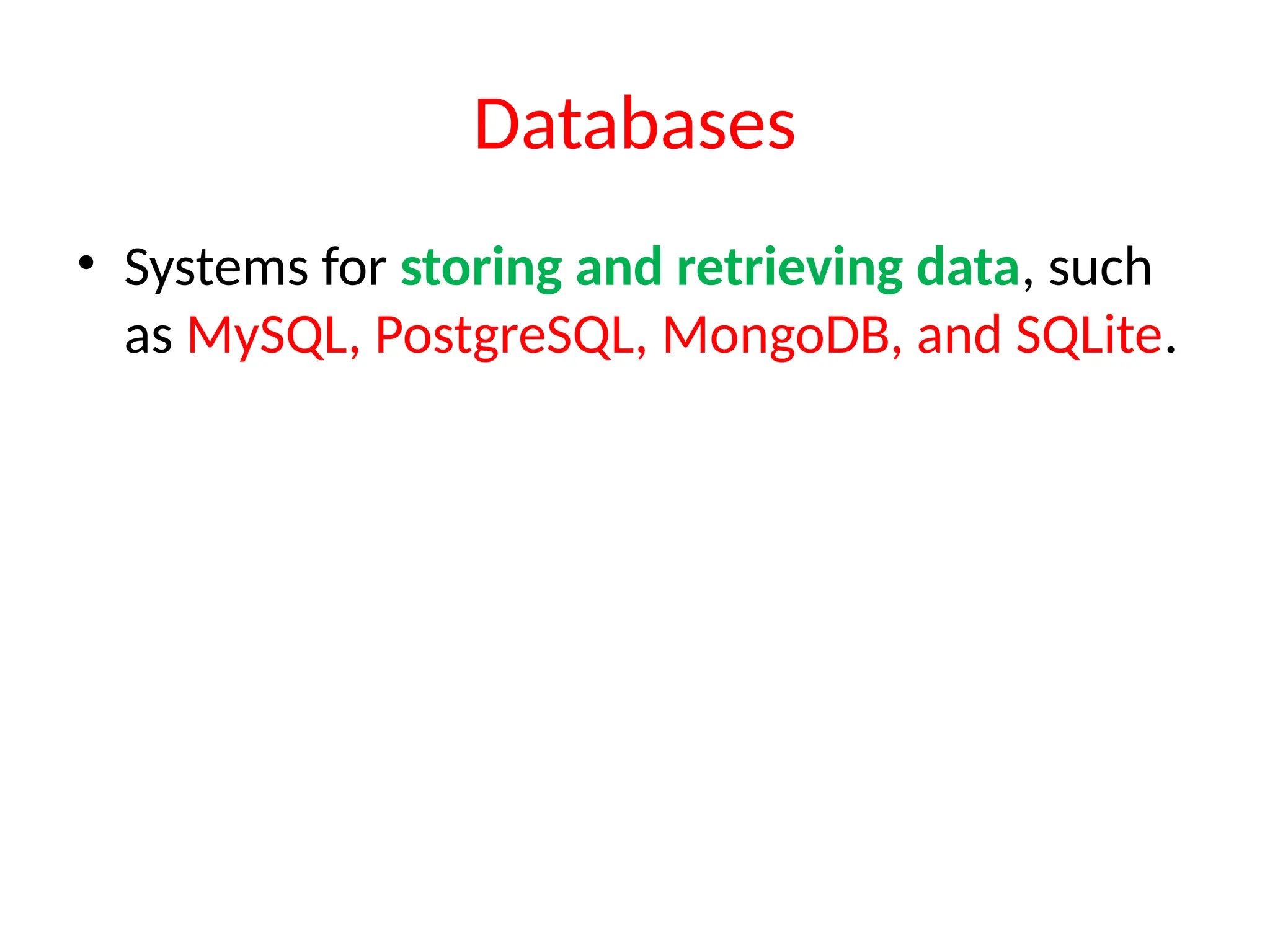
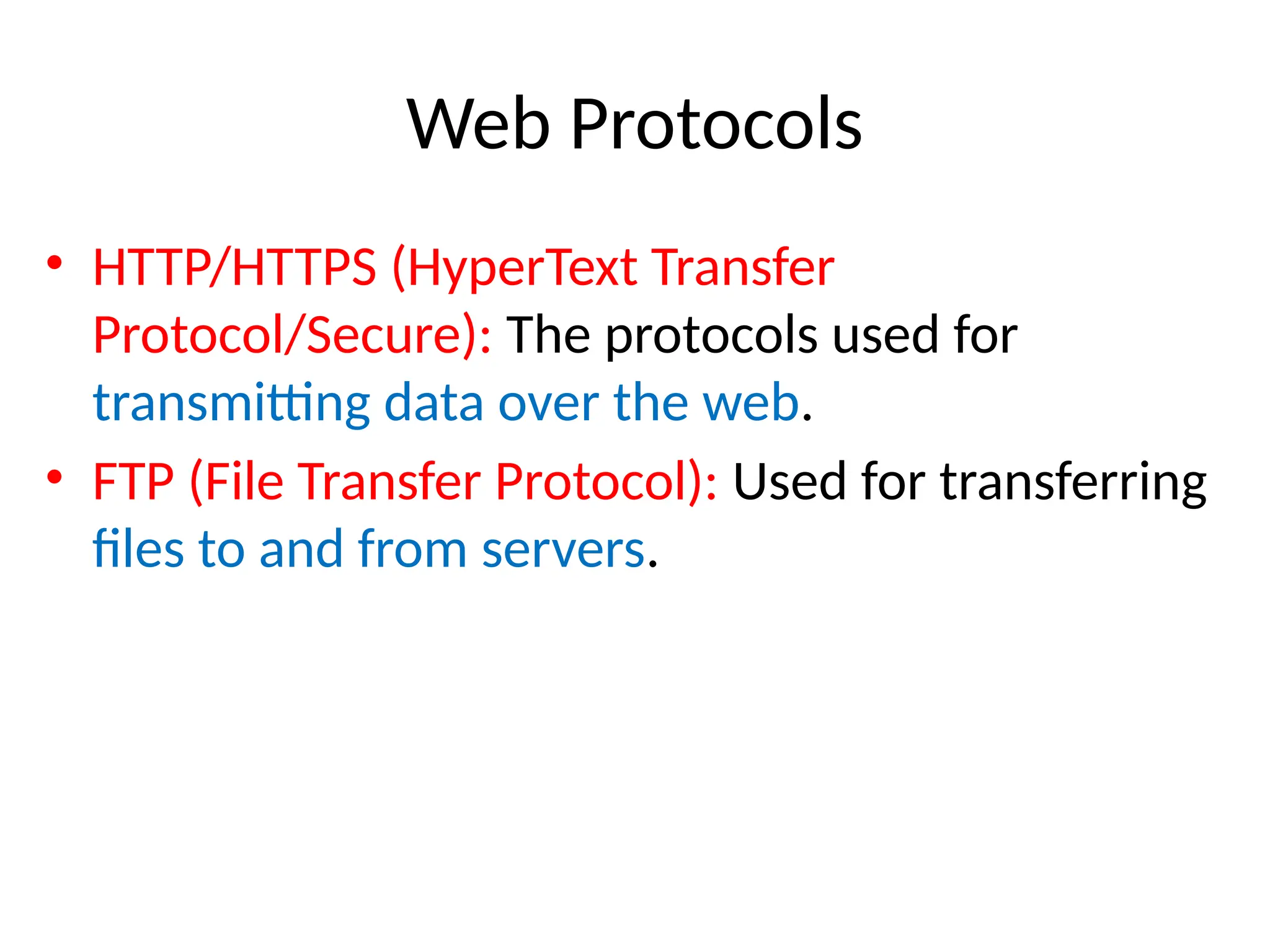
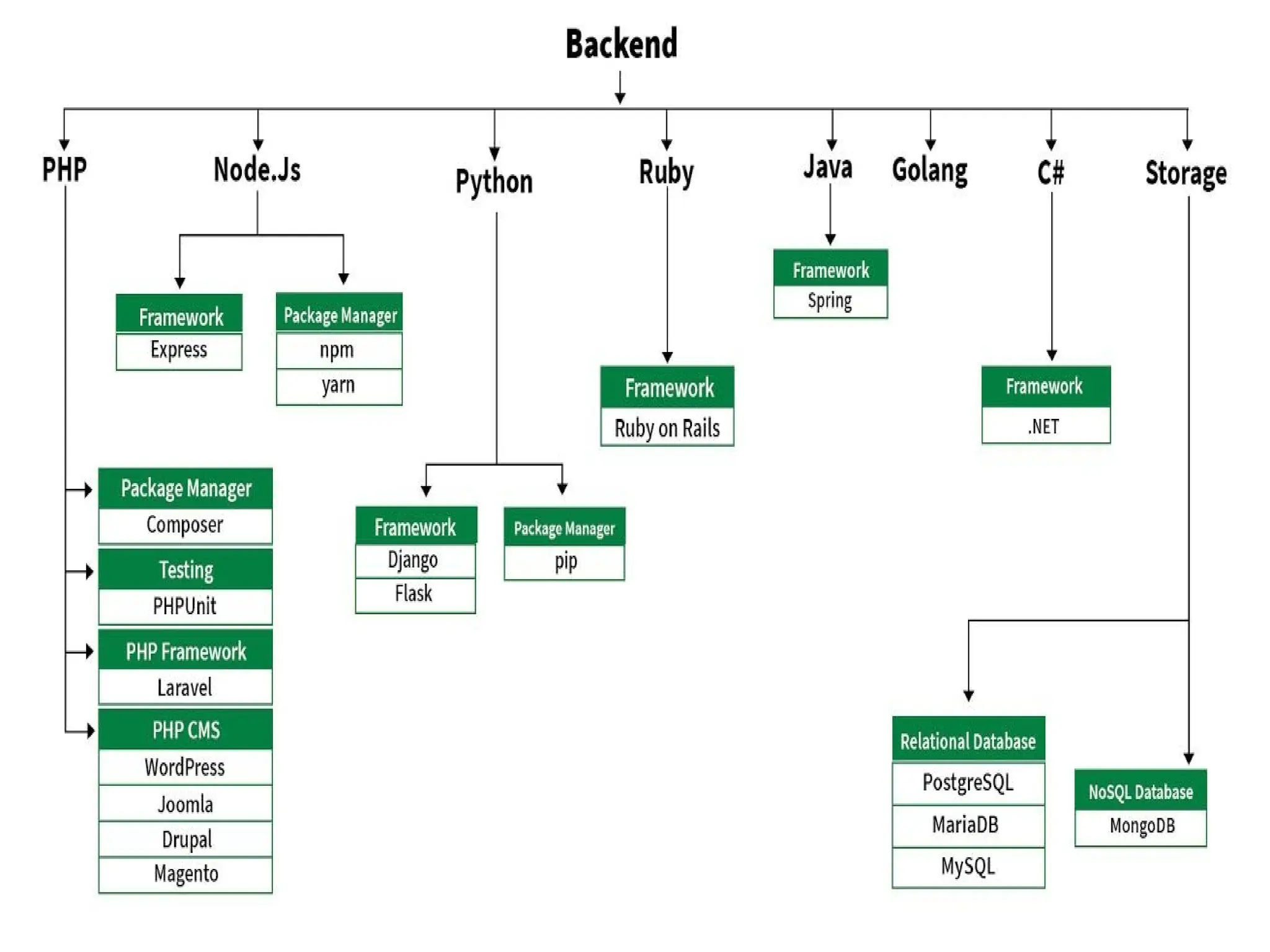
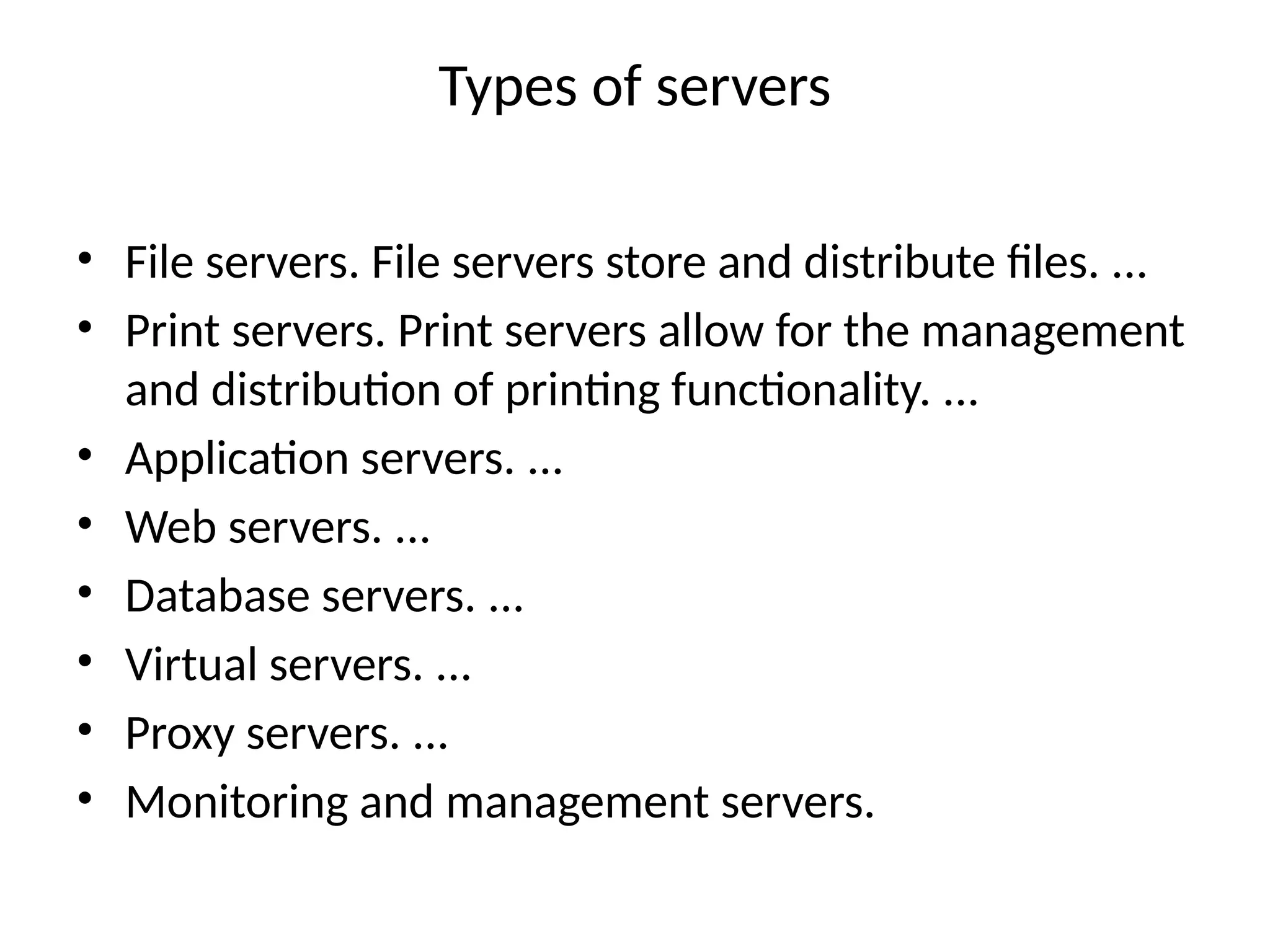
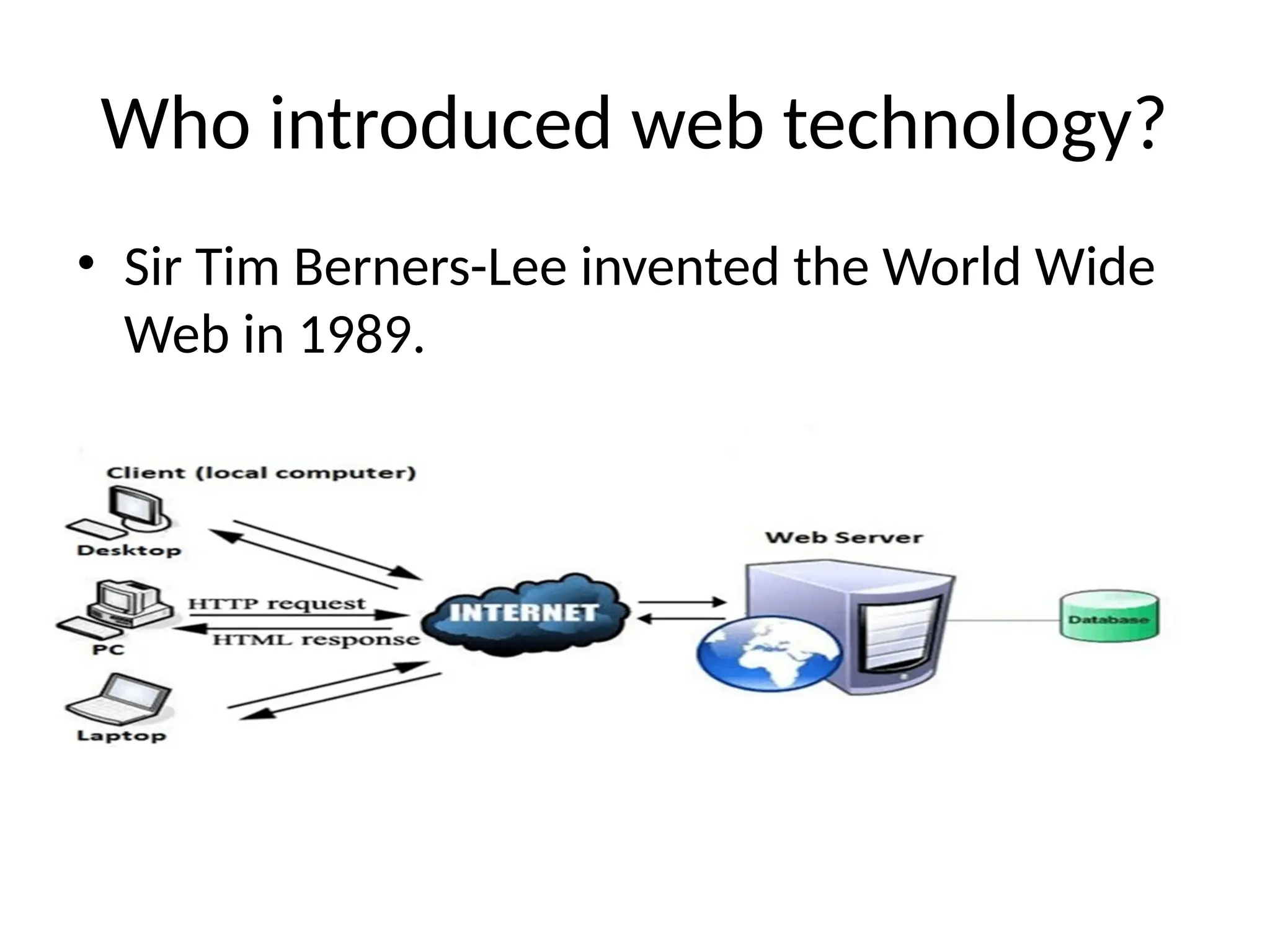
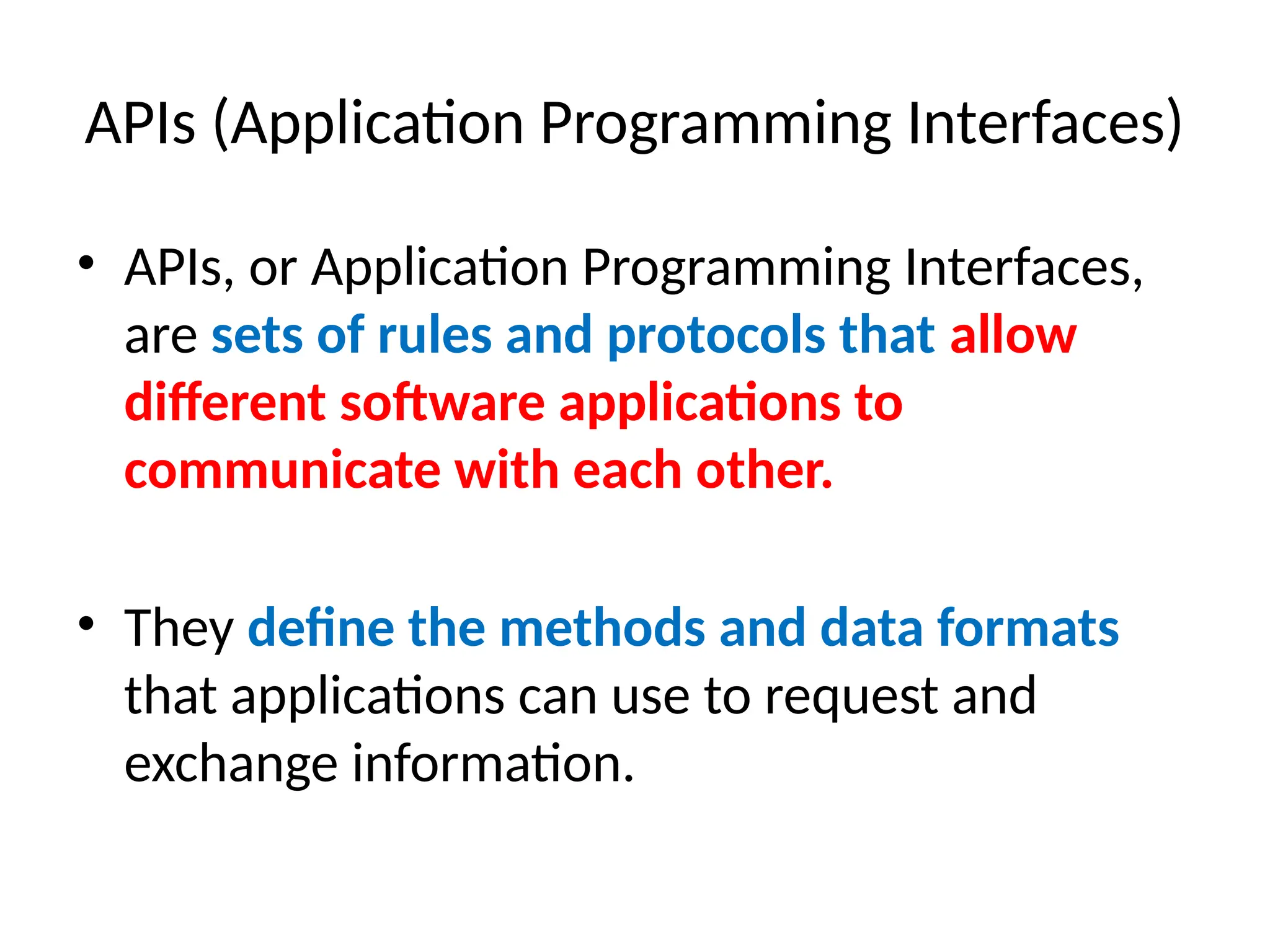
The document provides an overview of web technology, including its definition, components, and development processes. It covers topics such as programming languages (HTML, CSS, JavaScript), tools, frameworks, and the differences between frontend and backend development. Additionally, it explains the role of web servers, browsers, databases, and APIs in creating and managing websites.

































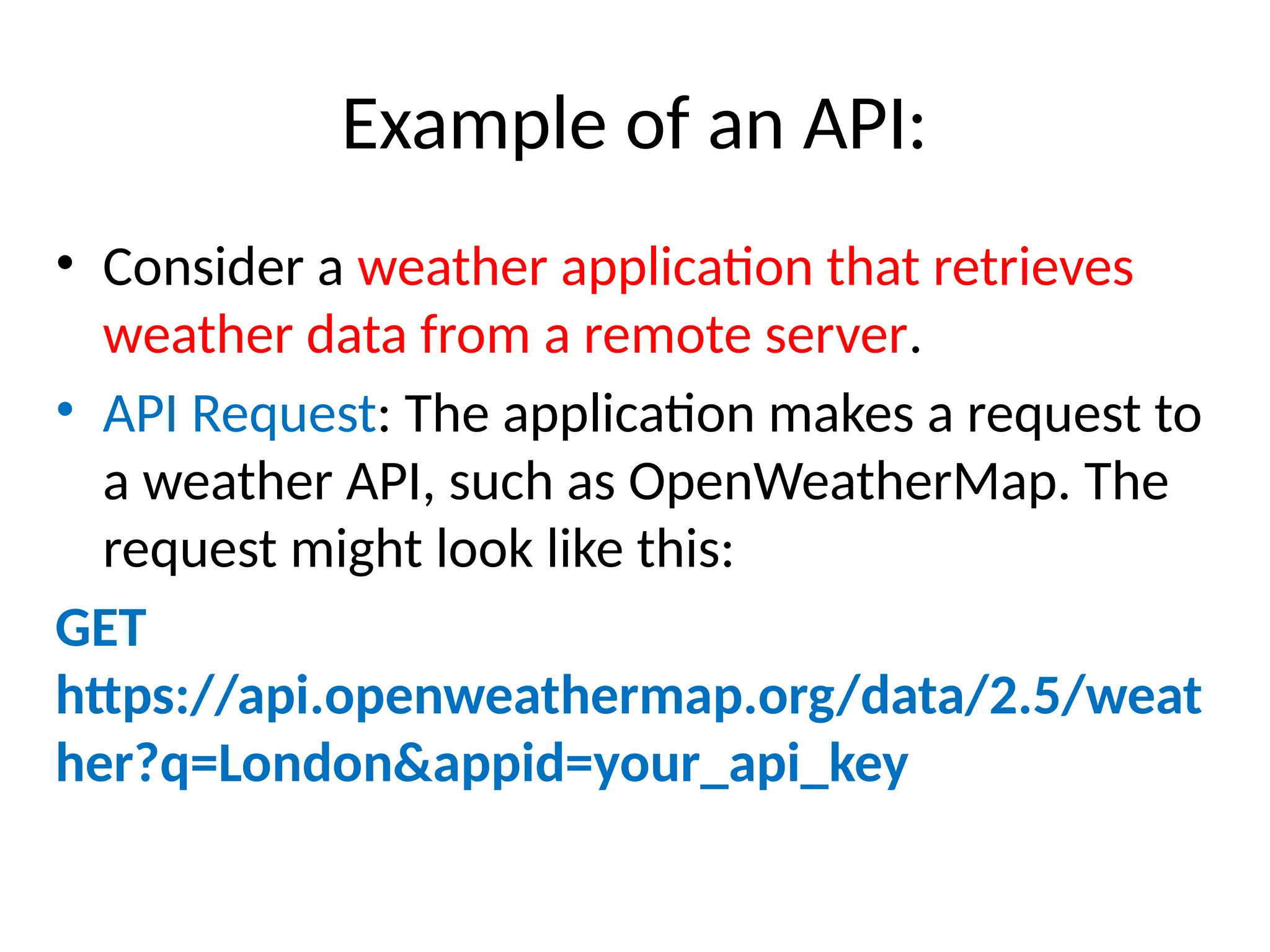
![Response: The API responds with data in a
structured format, typically JSON
{
"weather": [
{
"description": "light rain"
}
],
"main": {
"temp": 280.32,
"pressure": 1012,
"humidity": 81
},
"name": "London"
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/webtechnologyintro-250107111653-a79b8de7/75/Web-Technology-Introduction-framework-pptx-49-2048.jpg)