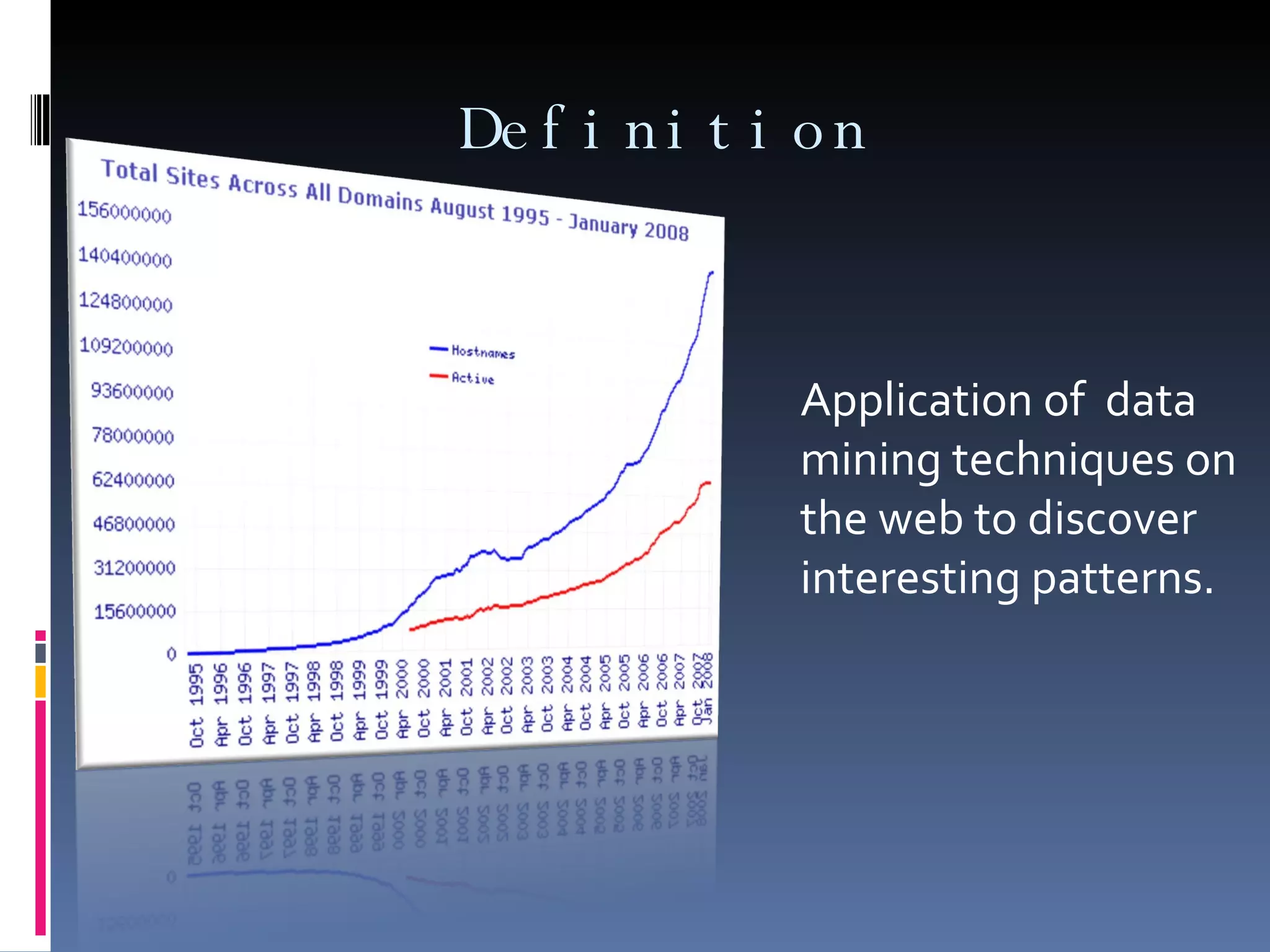
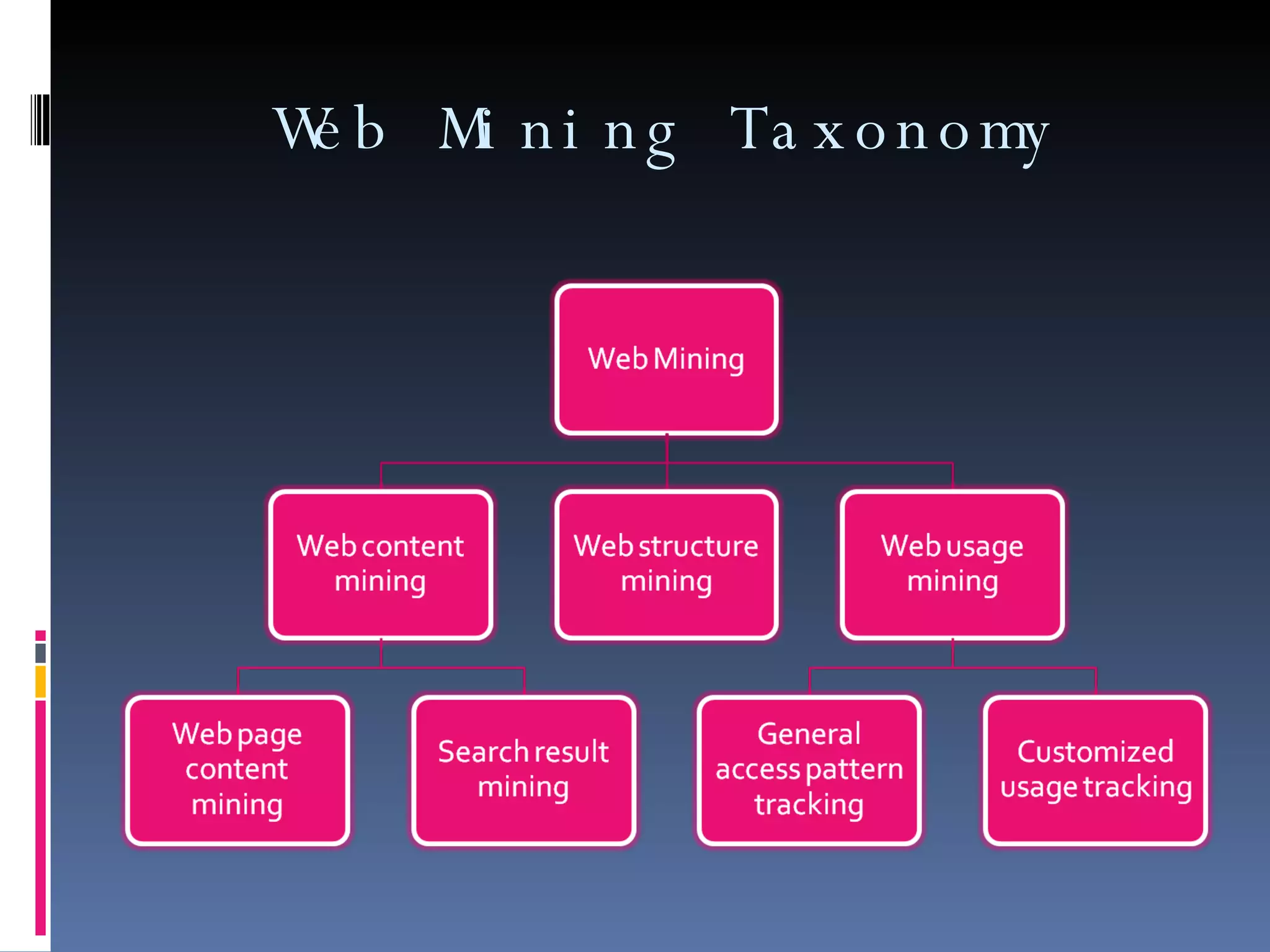
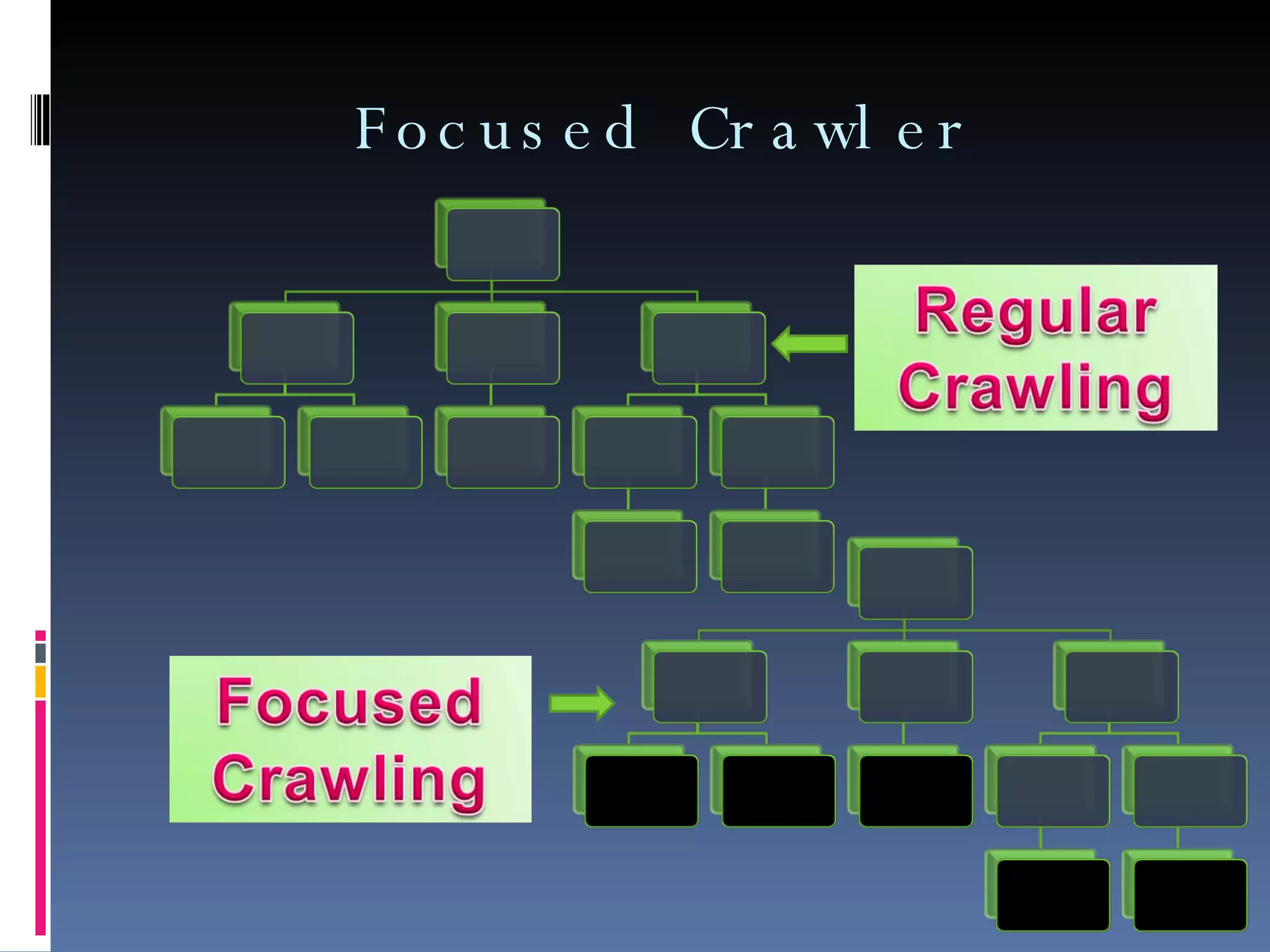
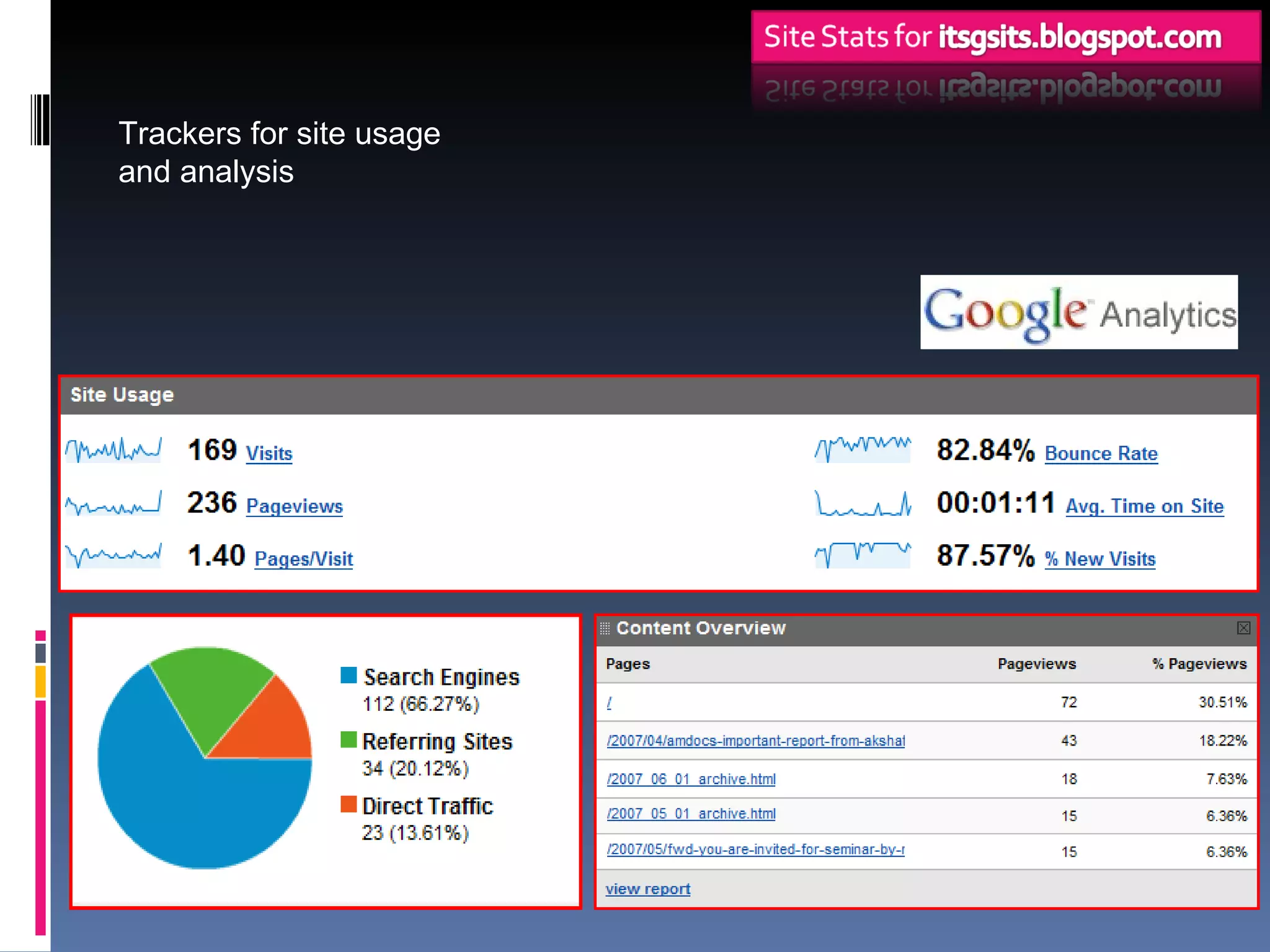
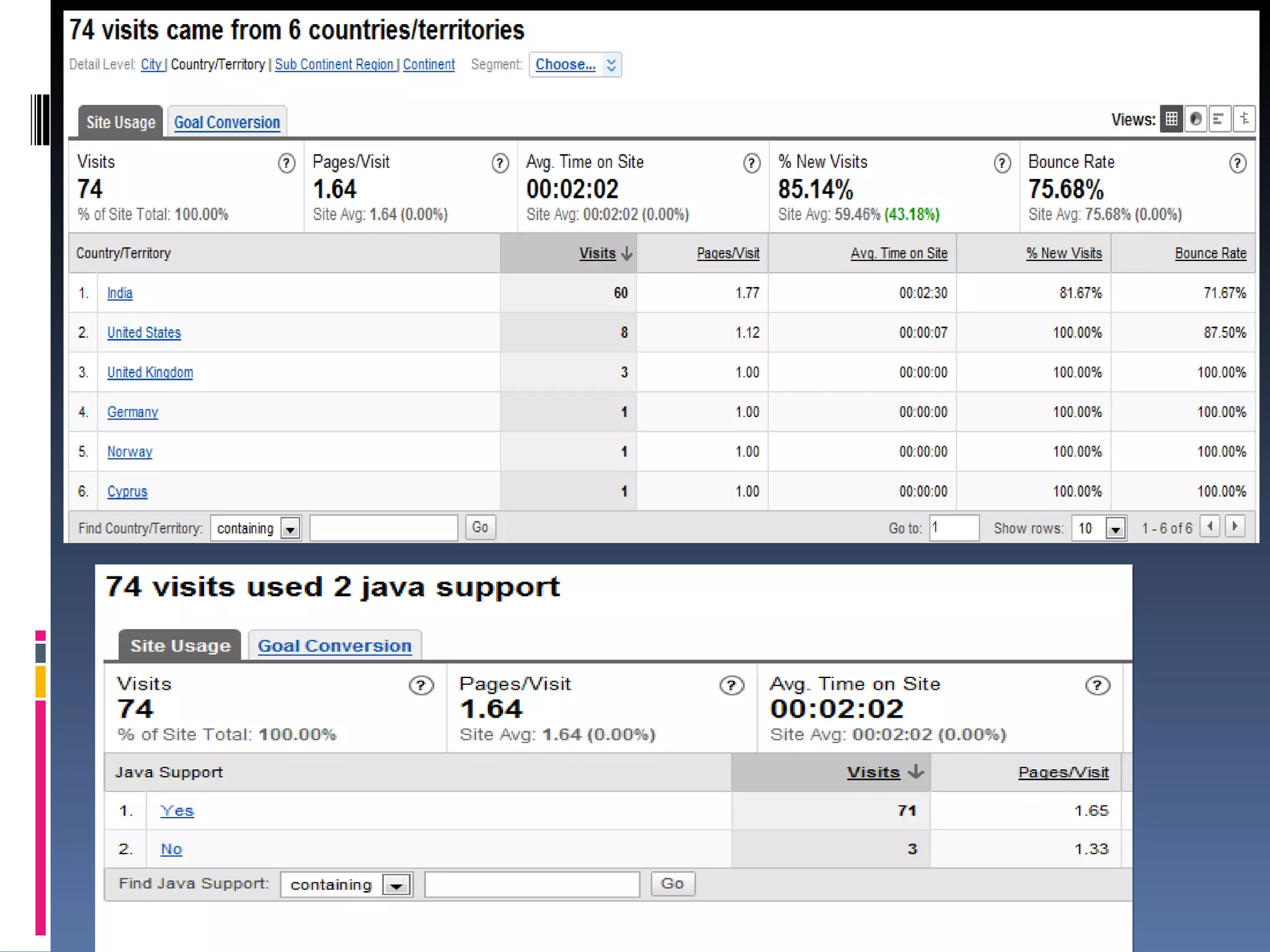
Web mining involves applying data mining techniques to discover patterns from the web. There are three types of web mining: web content mining which analyzes the contents of web pages; web structure mining which examines the hyperlink structure of the web; and web usage mining which refers to mining patterns from web server logs. Web usage mining applies data mining methods to web server logs to discover user browsing patterns and evaluate website usage.