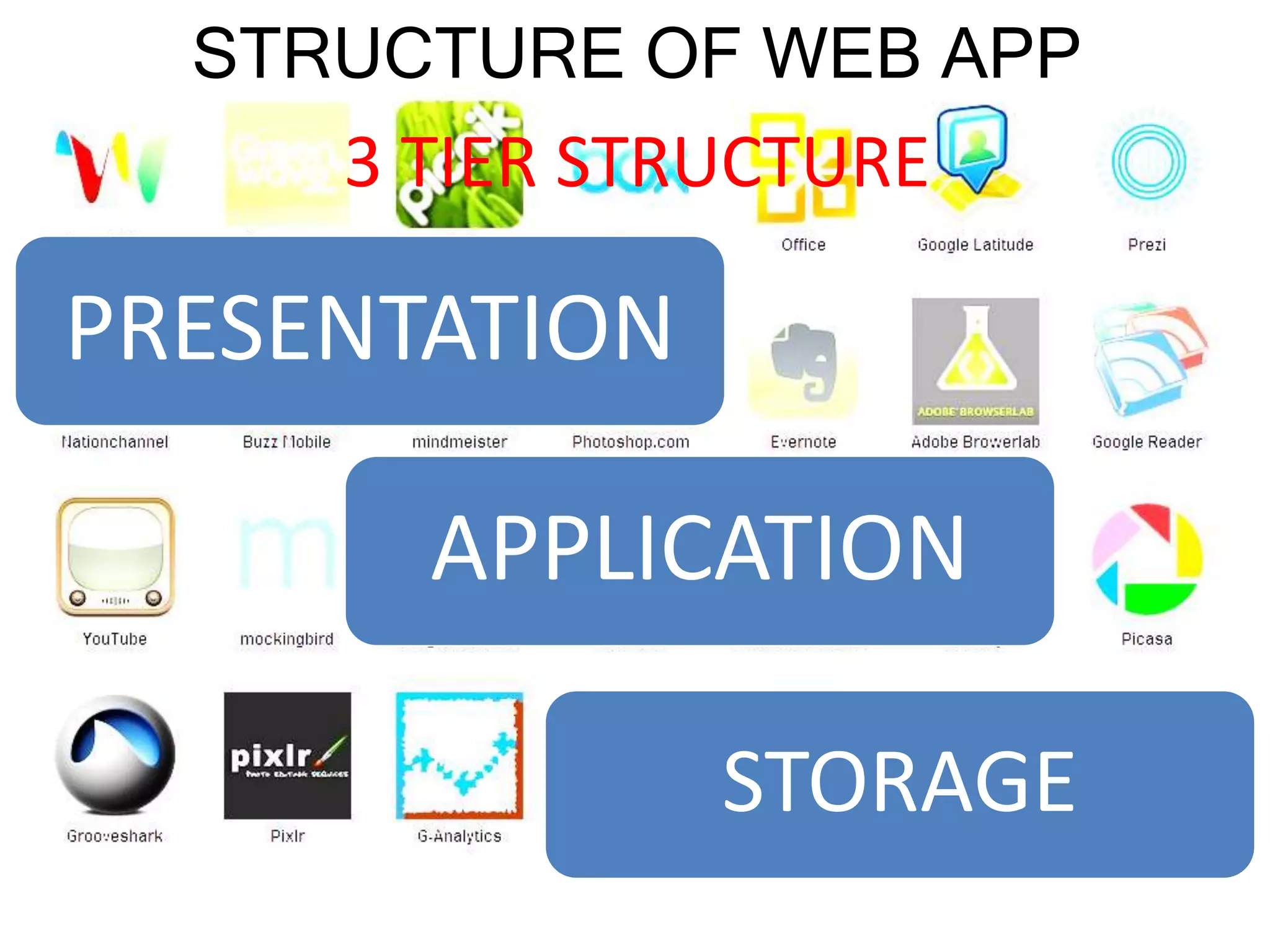
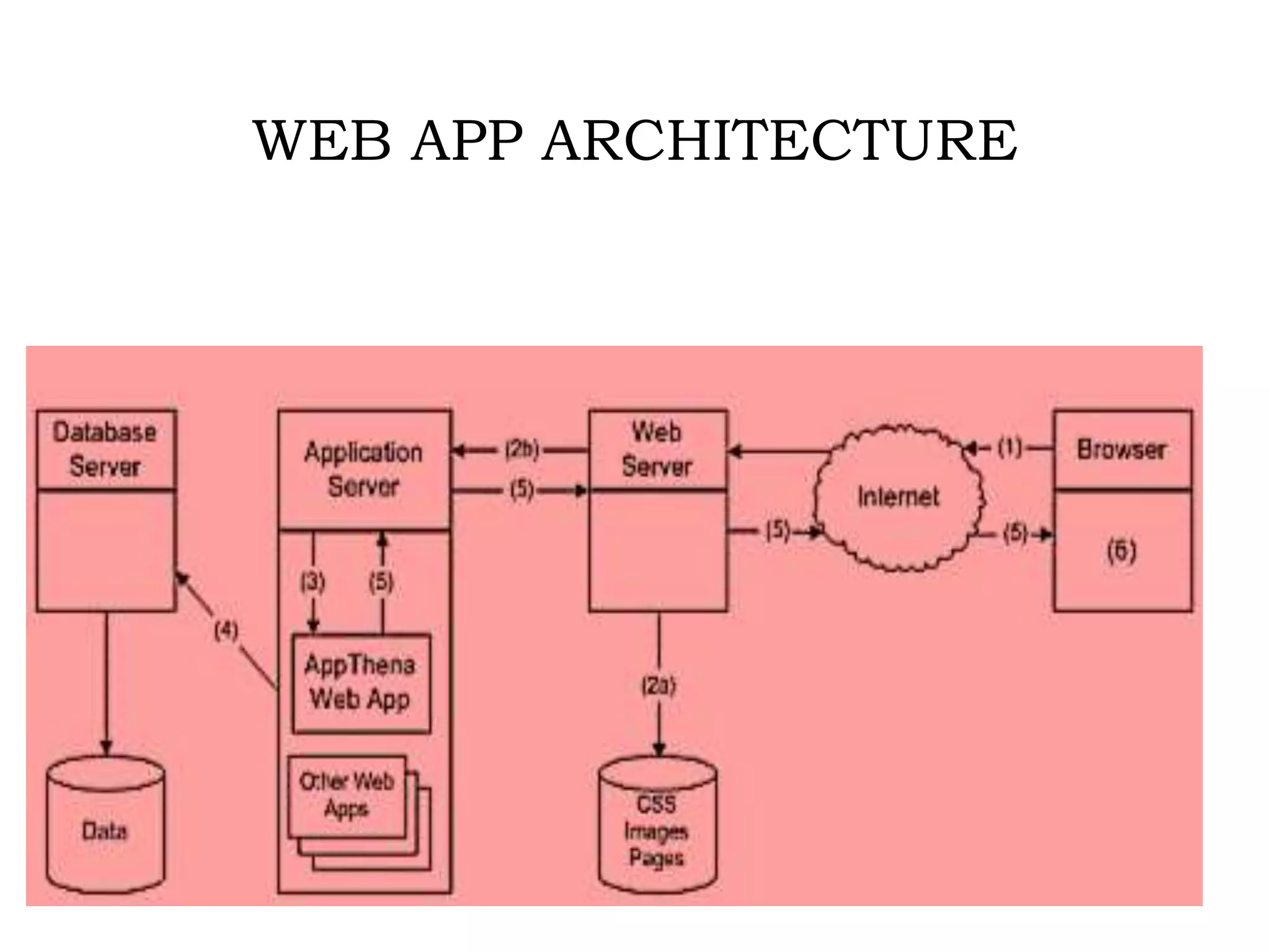
Web applications are client-server software applications where the client interface runs within a web browser. Historically, client-server applications required installing separate client software on each user's device. Web apps avoid this by running entirely within the browser. Common uses of web apps include webmail, ecommerce, auctions, and wikis. They use tools like JavaScript, Flash, Silverlight, and dynamic HTML. Web apps follow a three-tier architecture with the presentation layer in the browser, an application layer using technologies like PHP or Node.js, and a database storage layer. Frameworks like Django and Ruby on Rails simplify development by handling common issues so developers can focus on unique aspects of their applications.