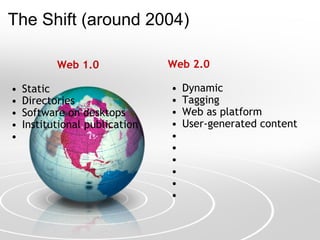
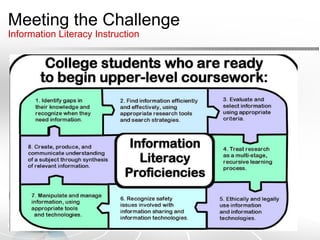
This document discusses how Web 2.0 technologies have shifted education from a static, instructor-centered model to a more dynamic, collaborative model that emphasizes active participation, user-generated content, and knowledge sharing. It introduces the concepts of connectivism and personal learning environments and examines how Web 2.0 impacts education by moving from an individual "sage on the stage" approach to a more collaborative "guide on the side" model. Challenges of digital divides and plagiarism are also addressed.