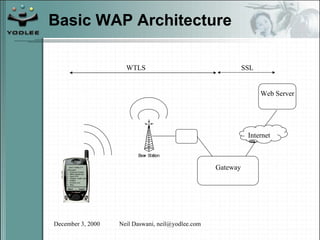
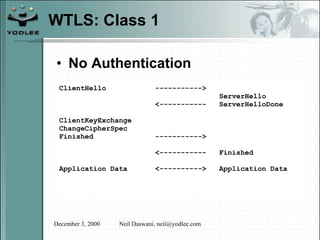
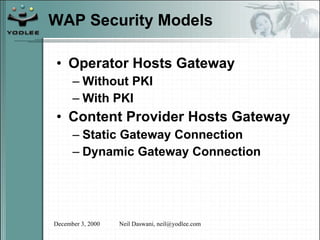
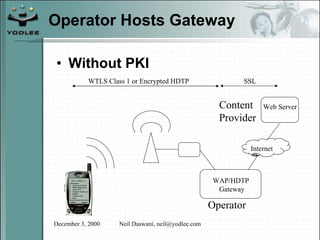
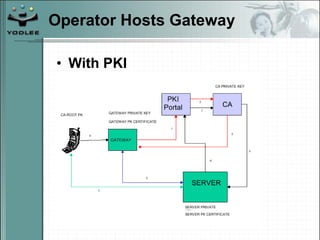
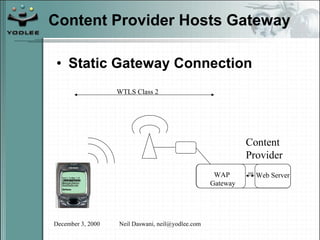
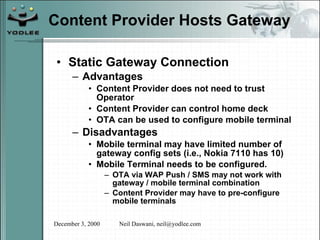
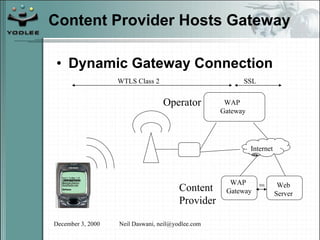
The document discusses security models and architectures for the Wireless Application Protocol (WAP). It describes various approaches for authentication, confidentiality, and authorization between mobile devices, WAP gateways, and content providers. These include using WTLS to provide encryption and authentication between devices and gateways, implementing a Wireless Identity Module (WIM) for secure storage of keys on devices, and controlling access to WAP content through WML and WMLScript.
![A Survey of WAP Security Architecture Neil Daswani [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/wapsecurityarchpresentation-090721044330-phpapp02/75/Wap-Security-Arch-Presentation-1-2048.jpg)