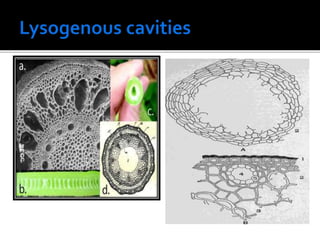
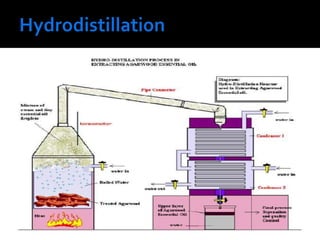
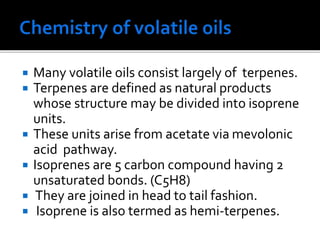
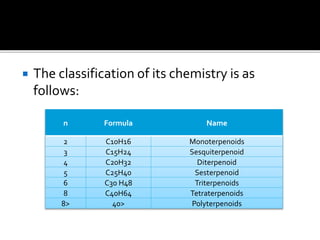
Volatile oils, also known as essential oils, are aromatic oily liquids found in many plants. They are highly volatile and evaporate easily at room temperature. Volatile oils are composed of hydrocarbons and oxidized hydrocarbons derived from terpenes. They are found stored in secretory cells, cavities, or channels located in different parts of plants. Volatile oils have various therapeutic uses and are also used in perfumes, cosmetics, and flavorings due to their strong aromas. They are extracted from plants using various techniques including water and steam distillation, solvent extraction, and enfleurage.