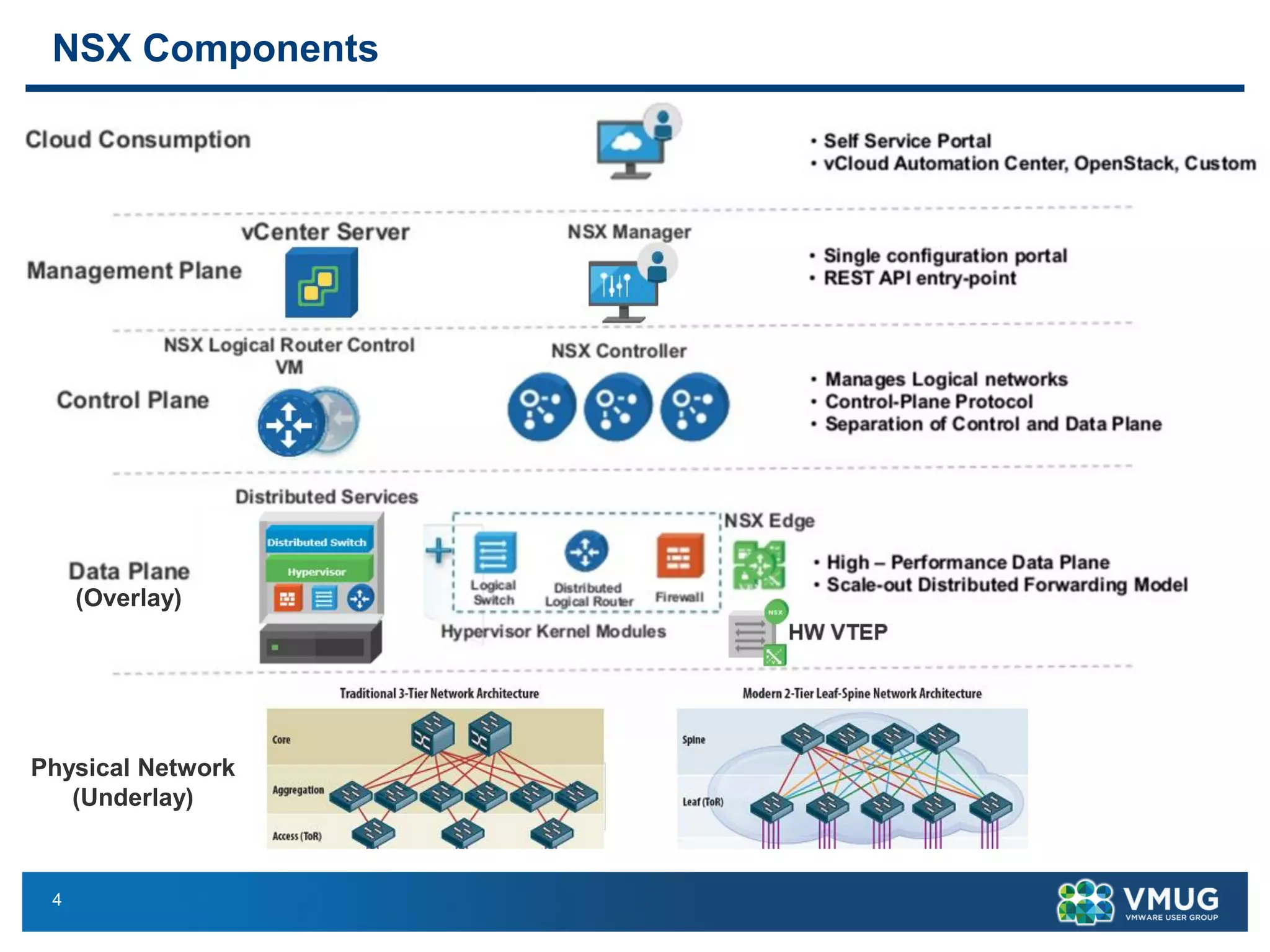
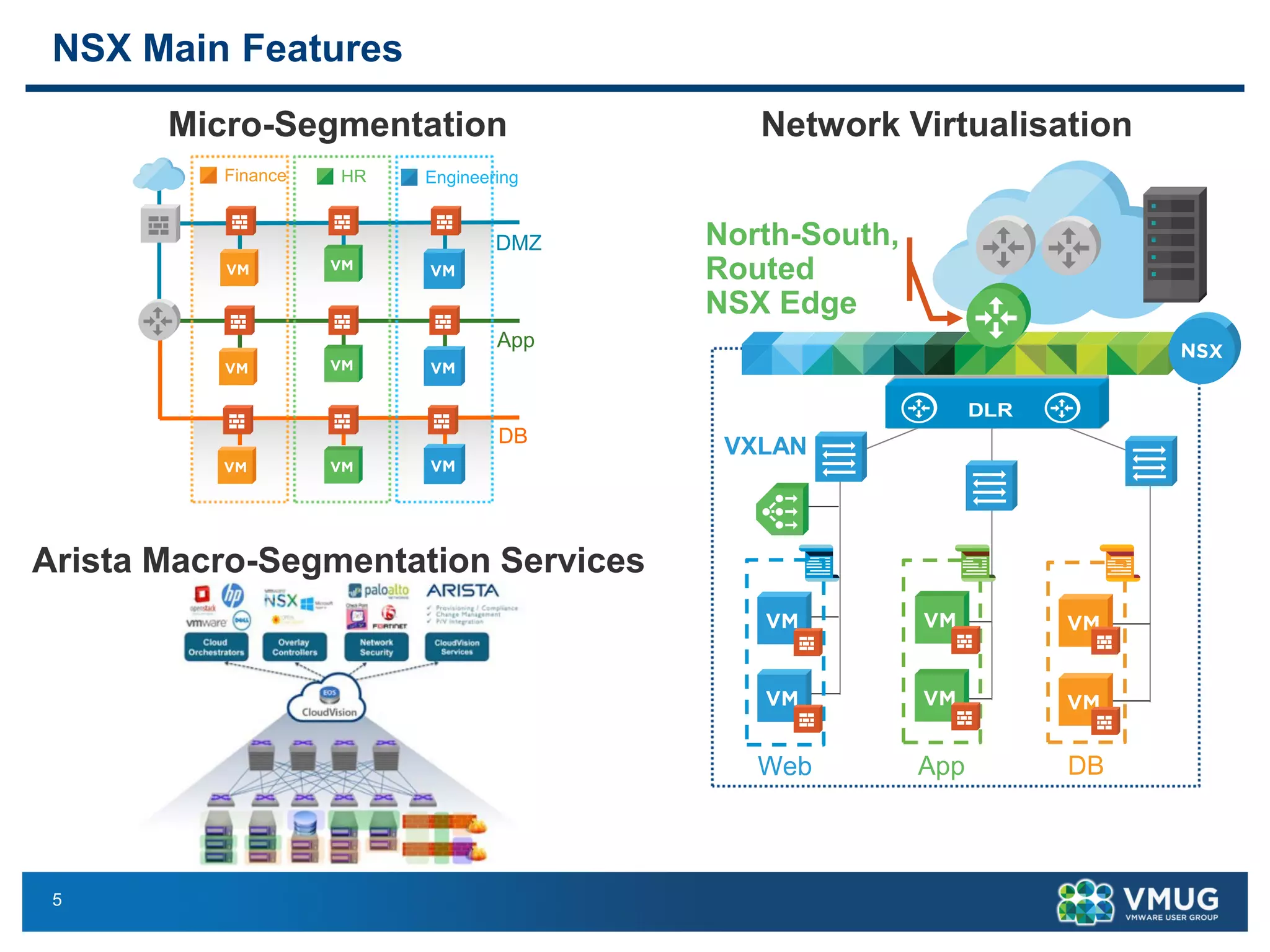
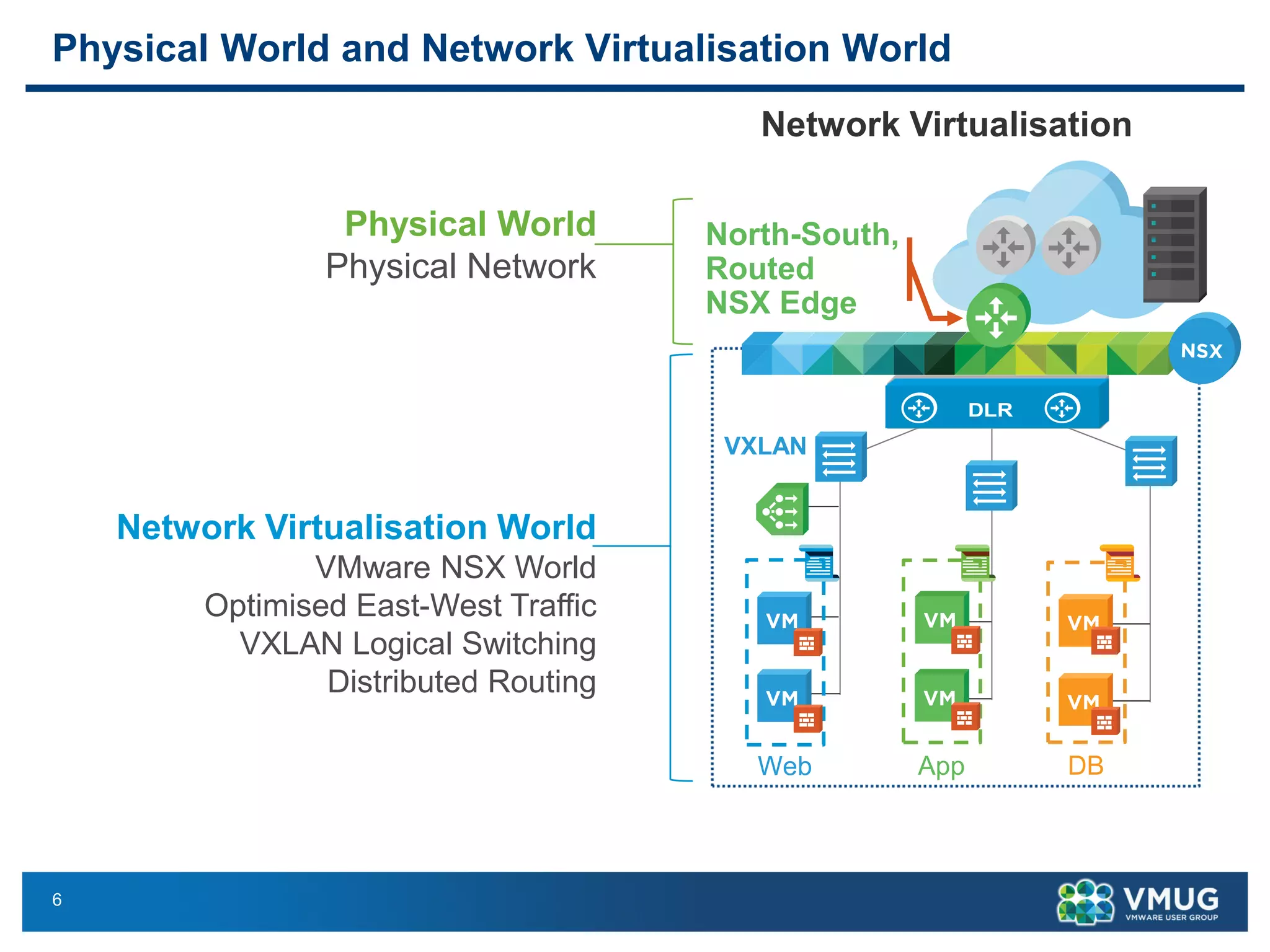
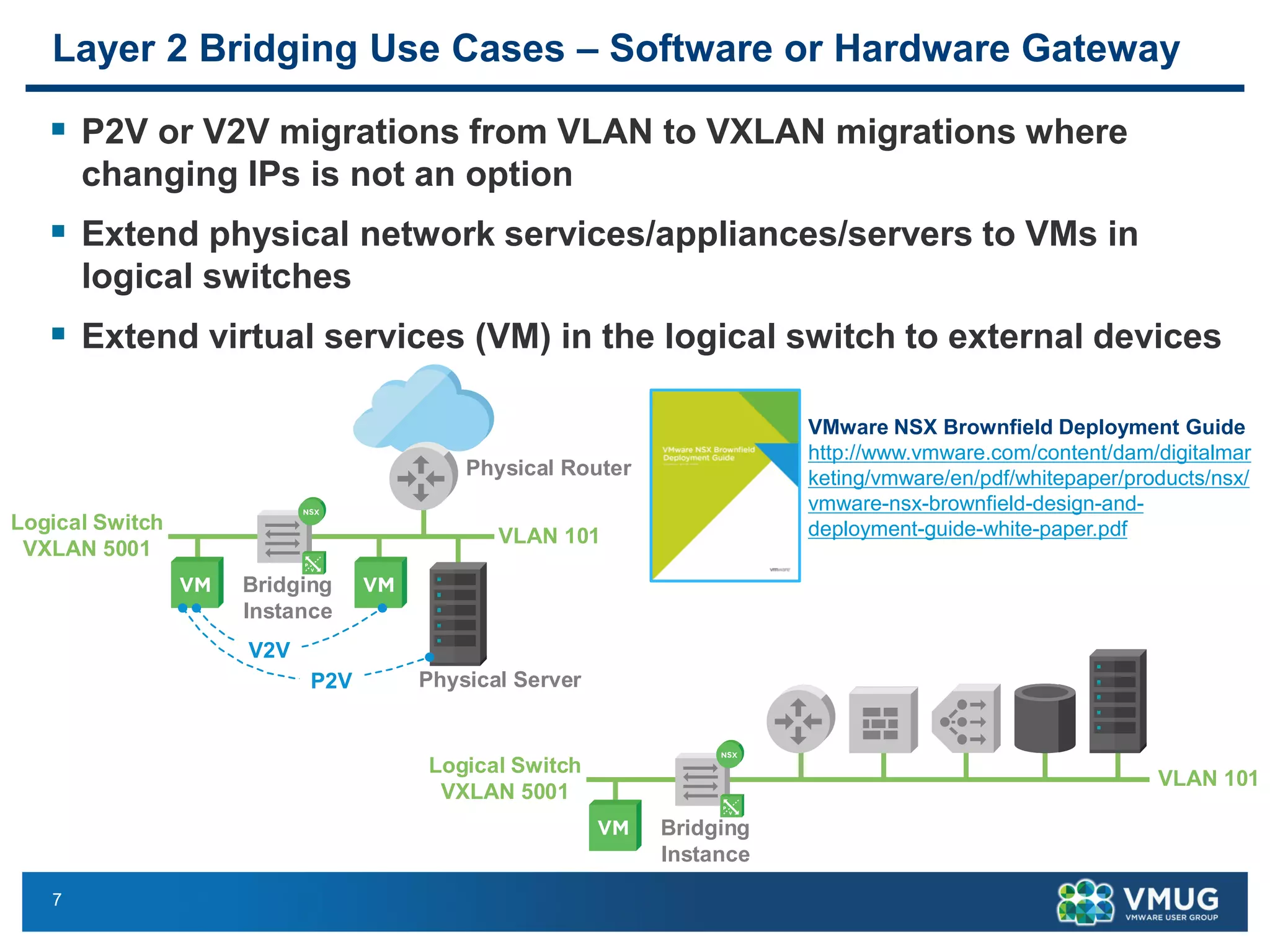
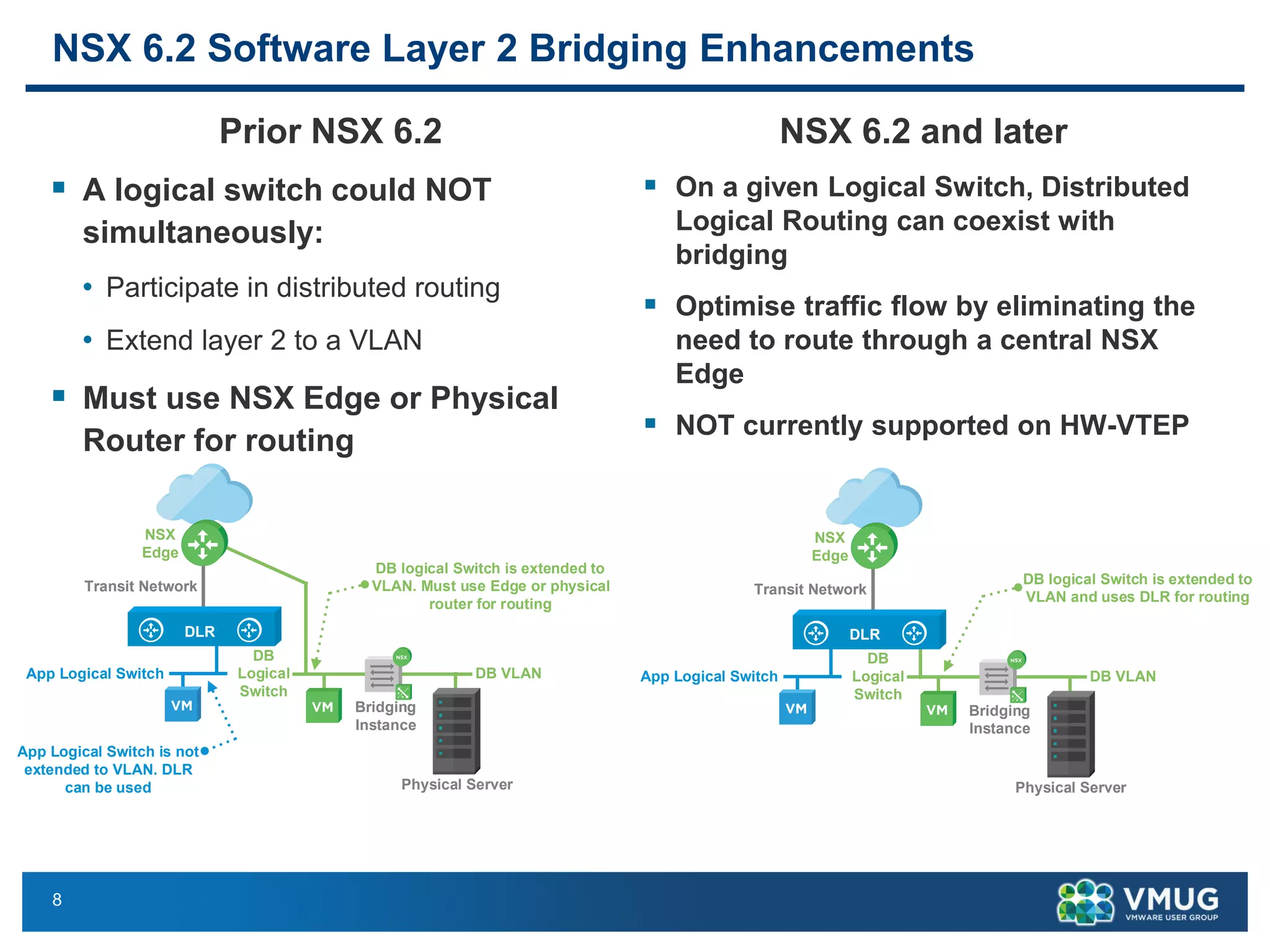
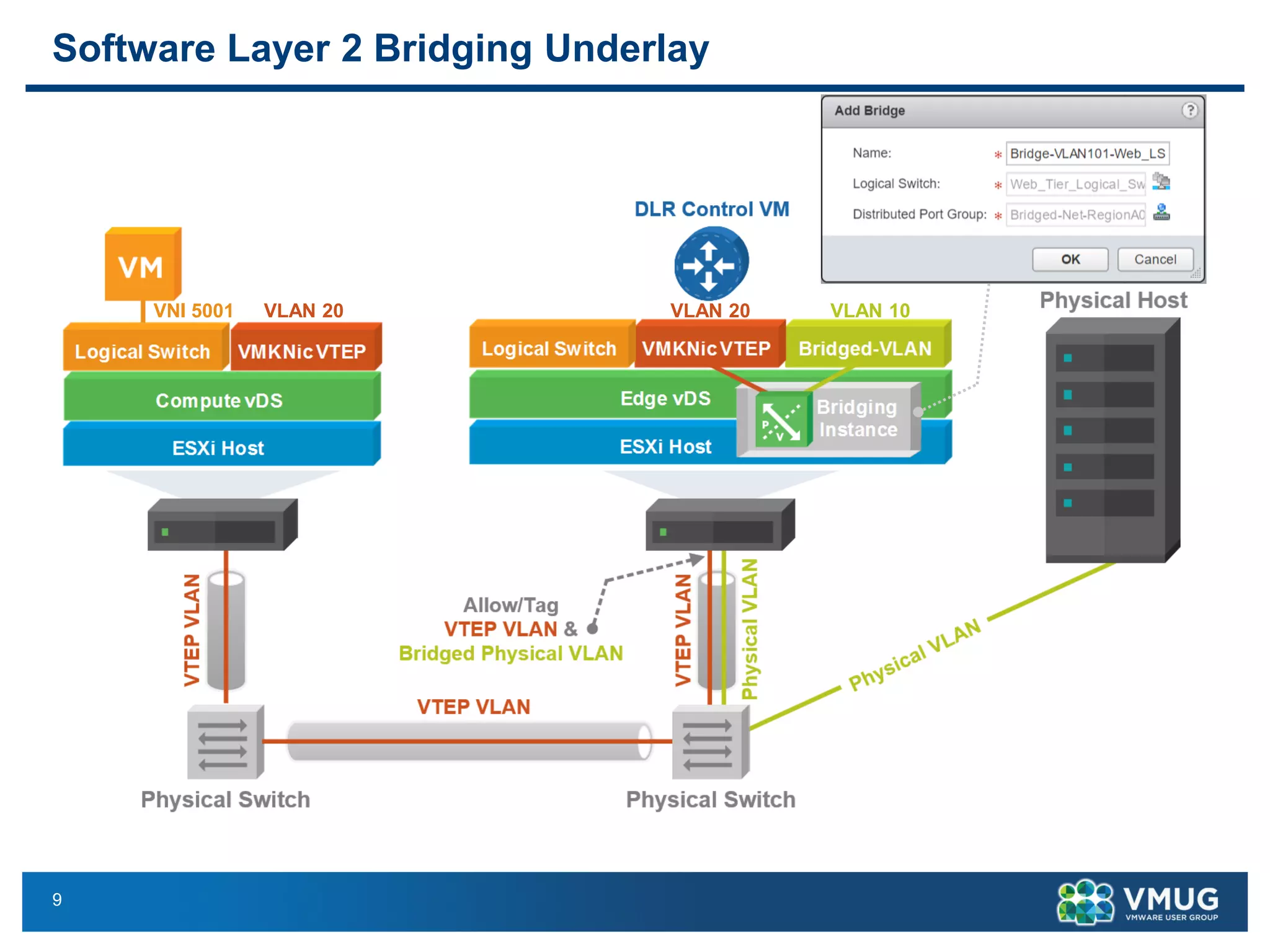
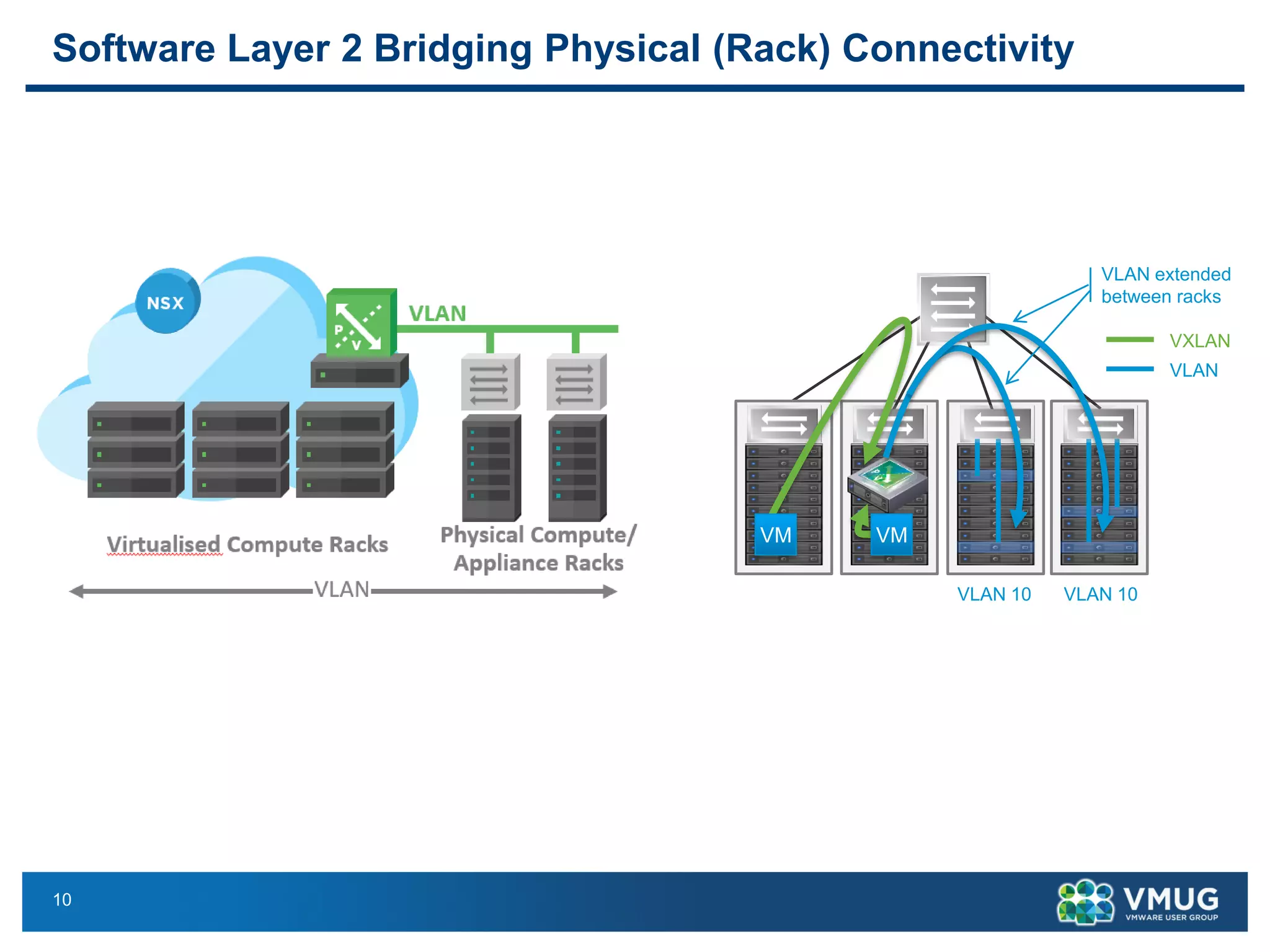
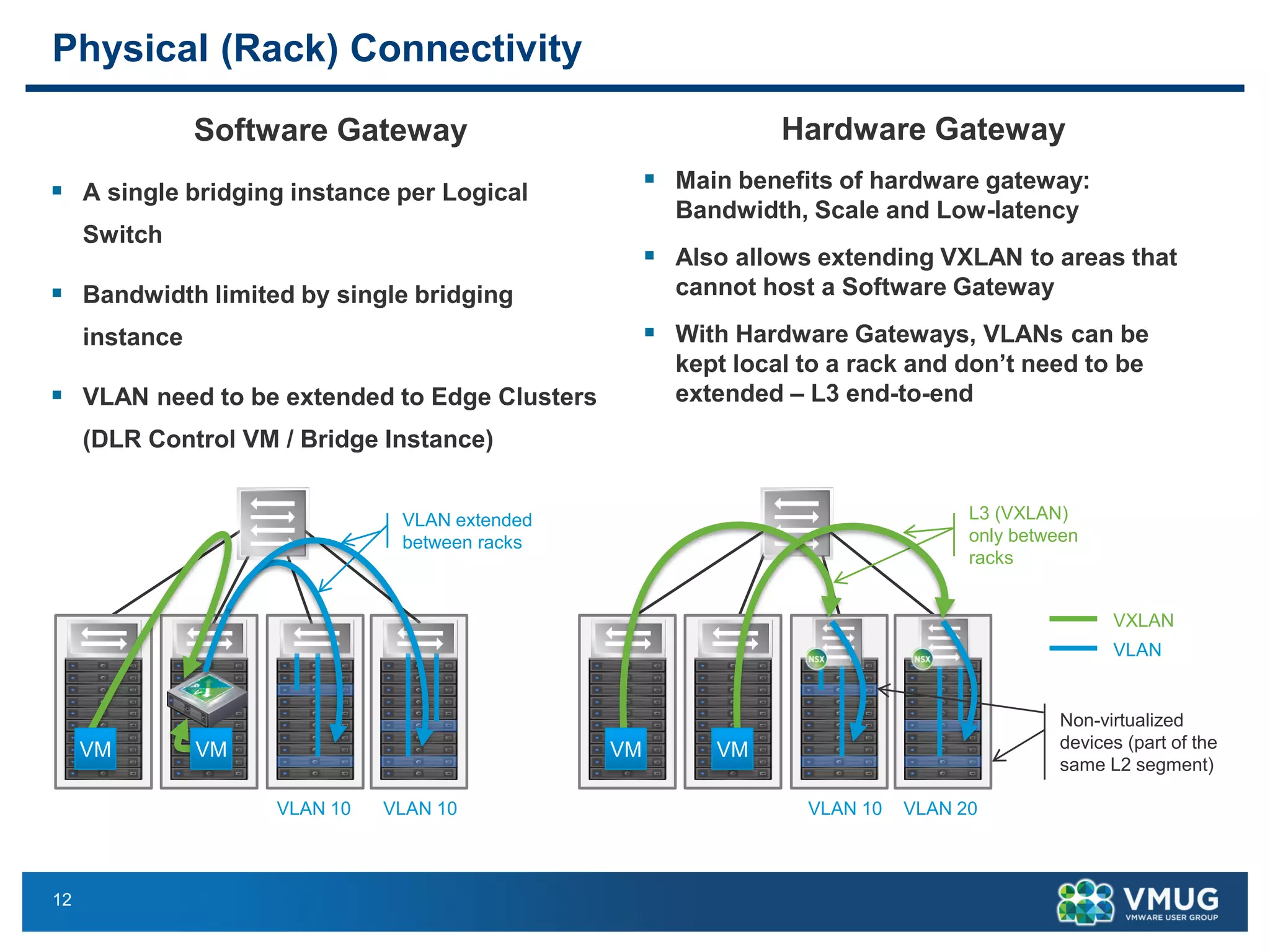
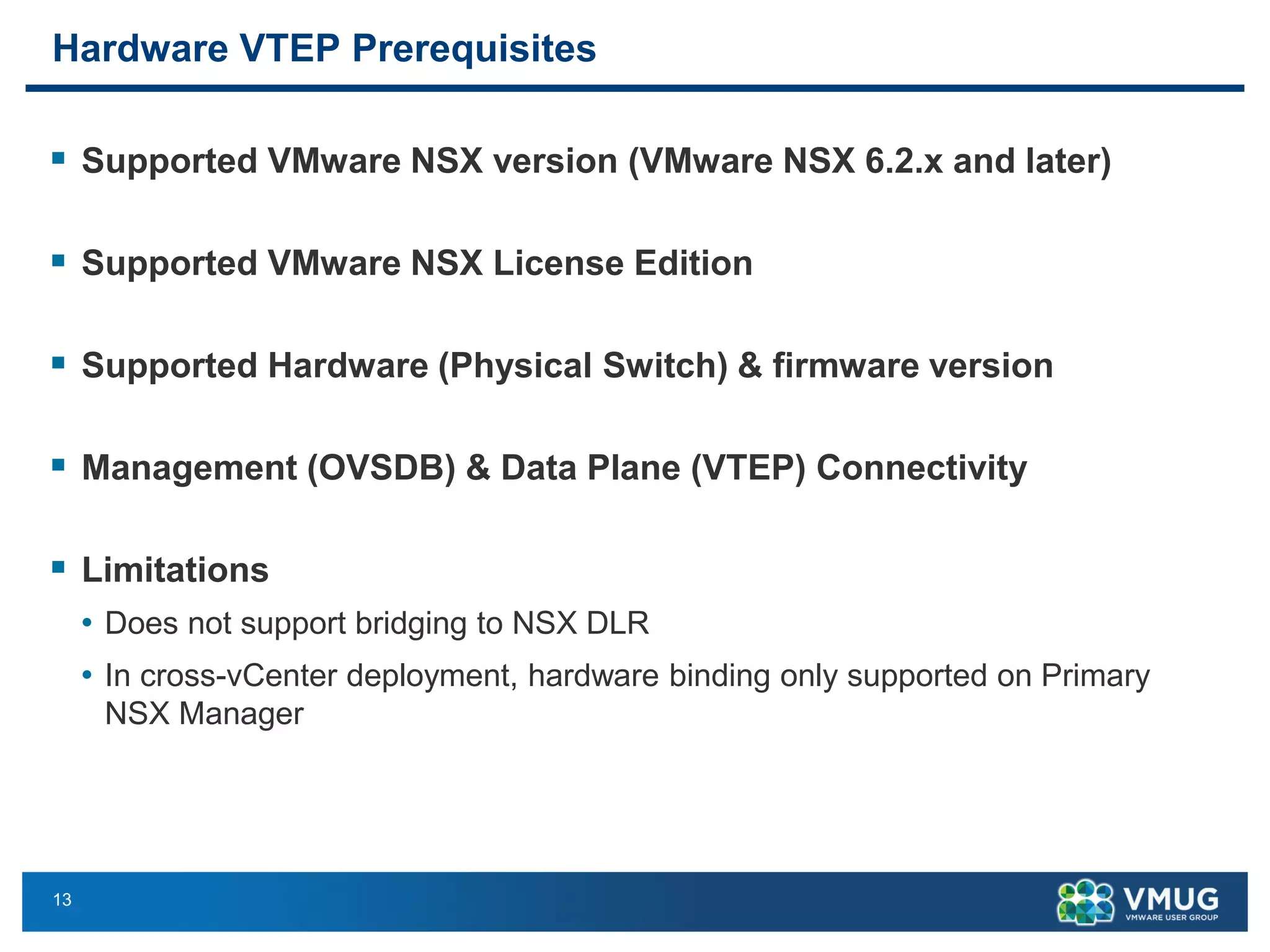
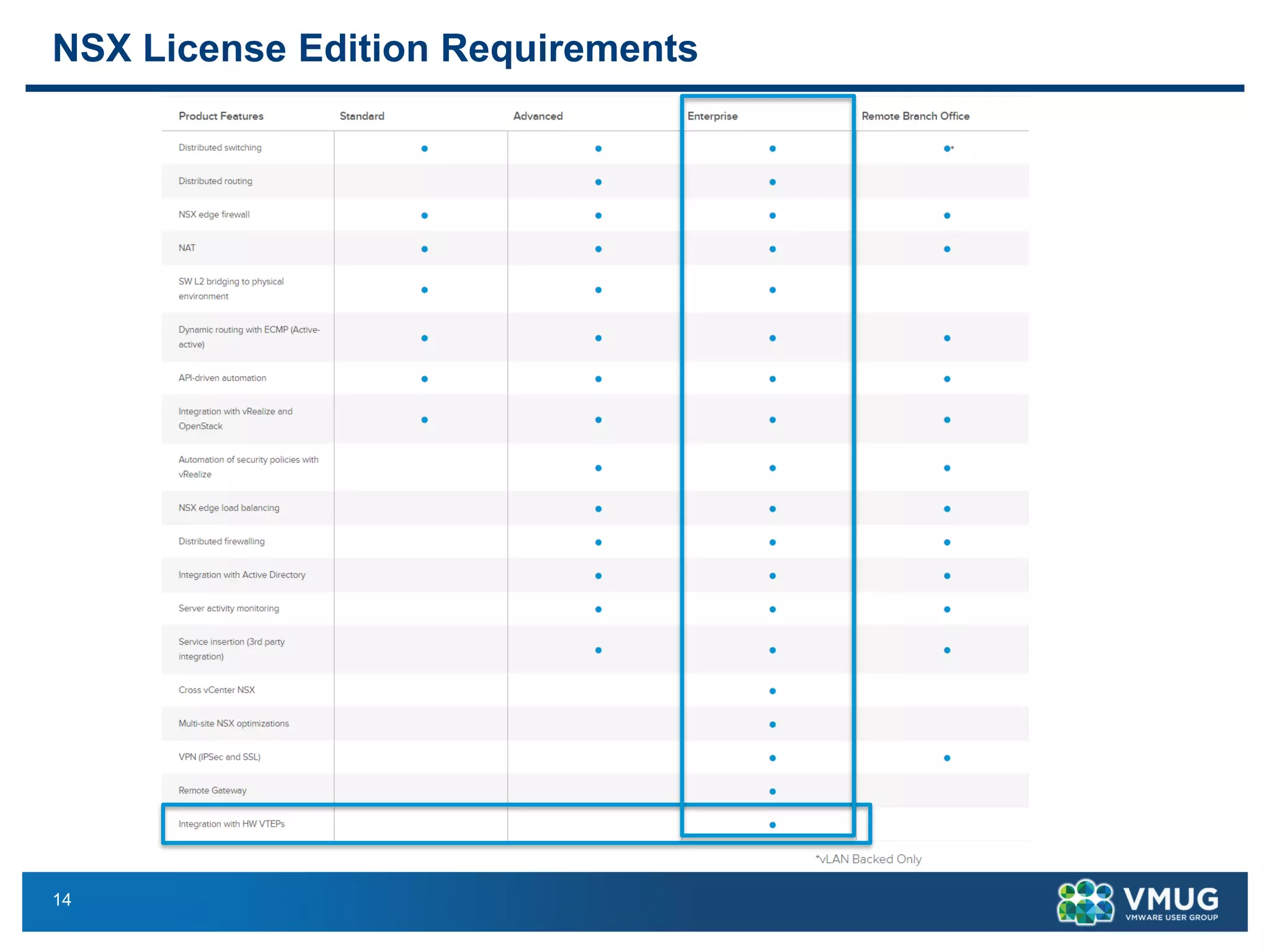
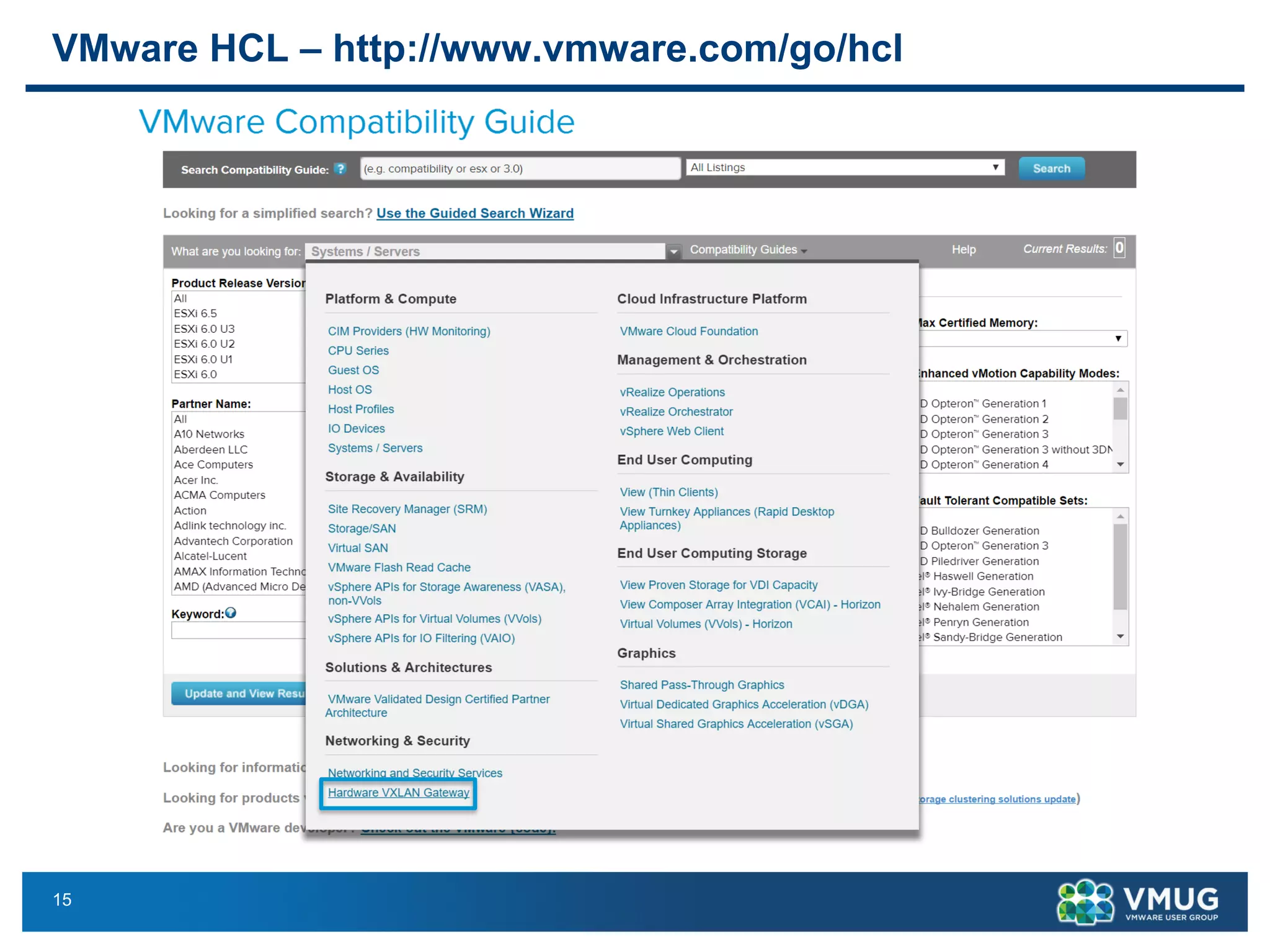
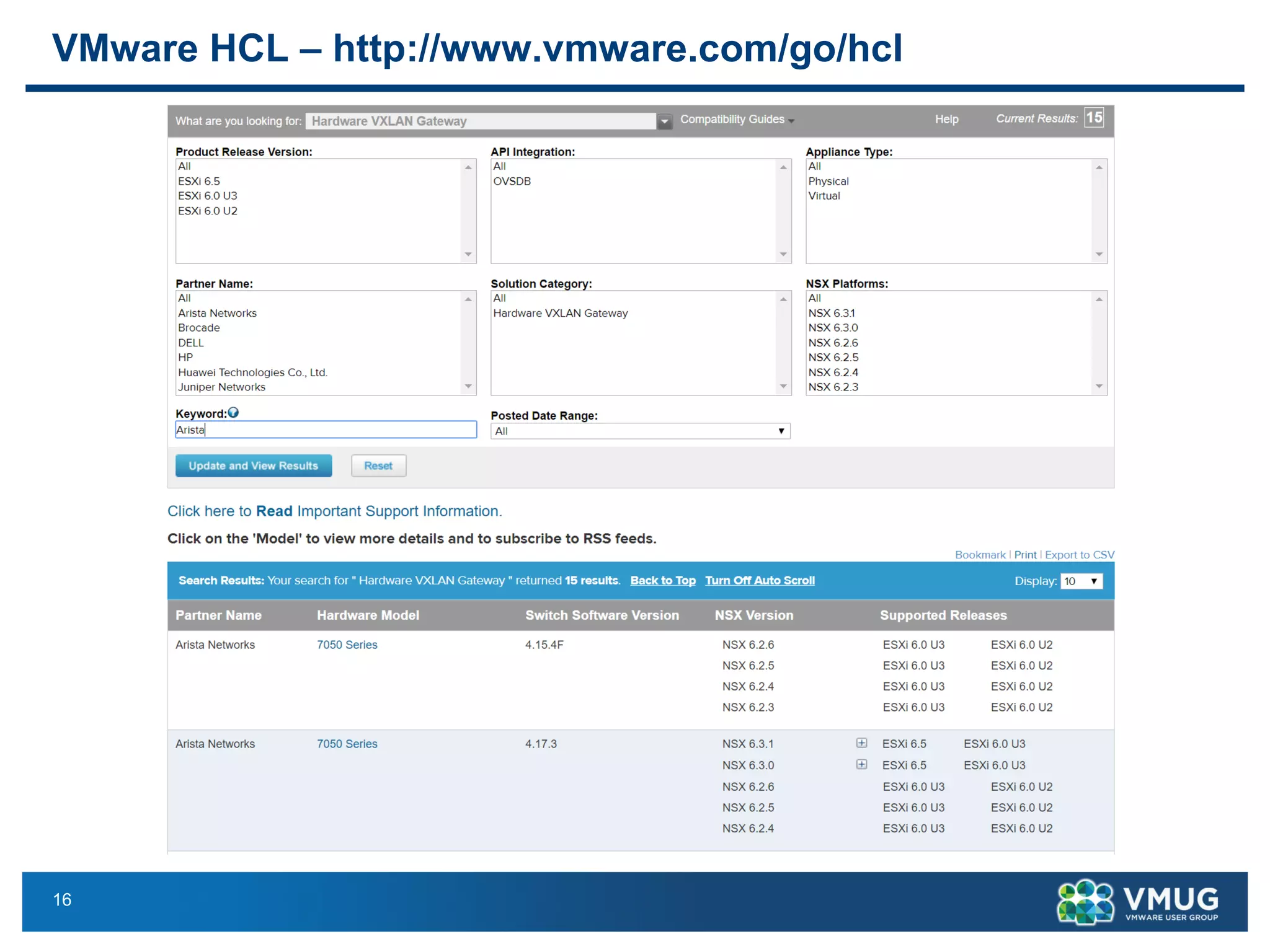
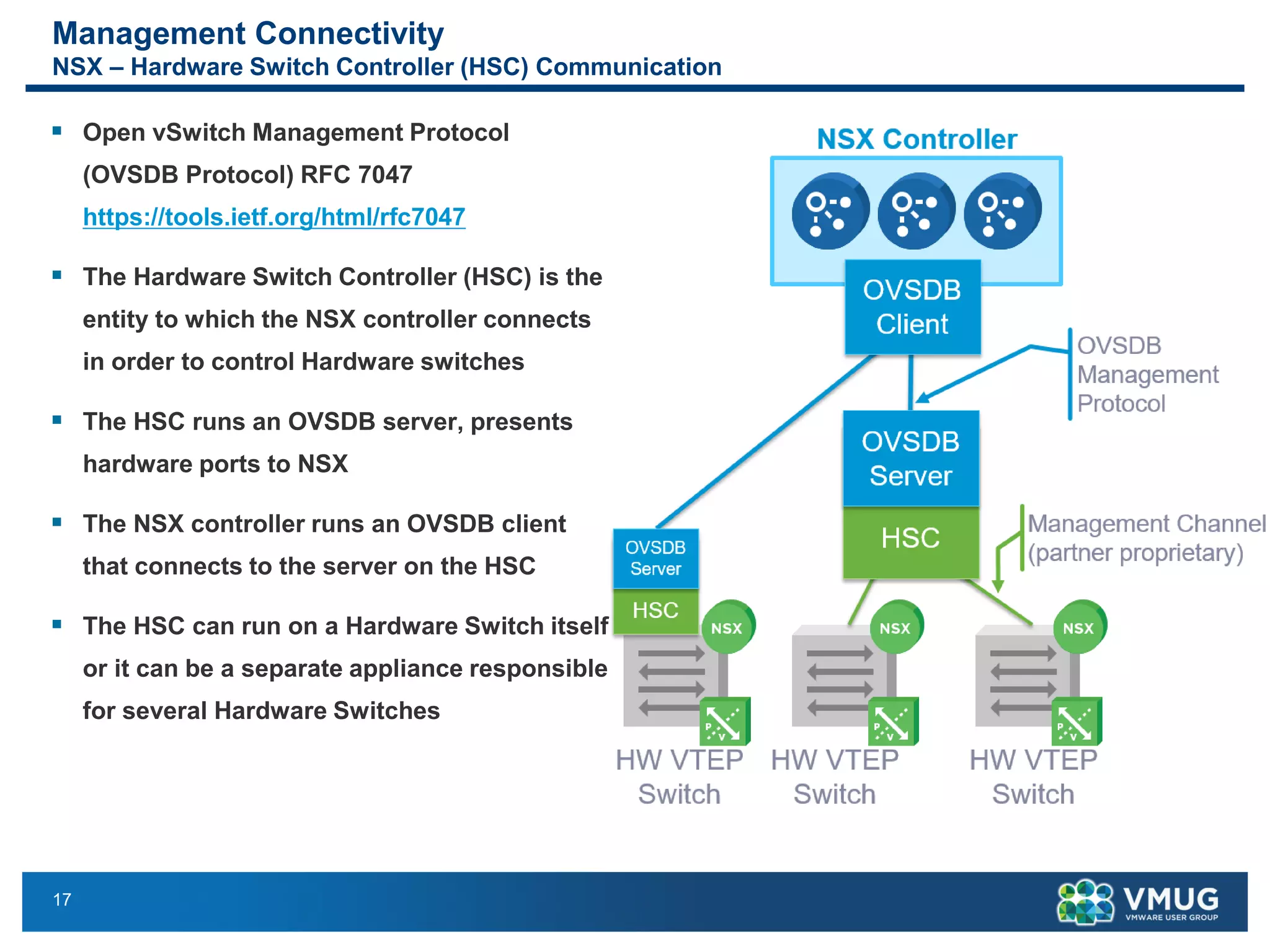
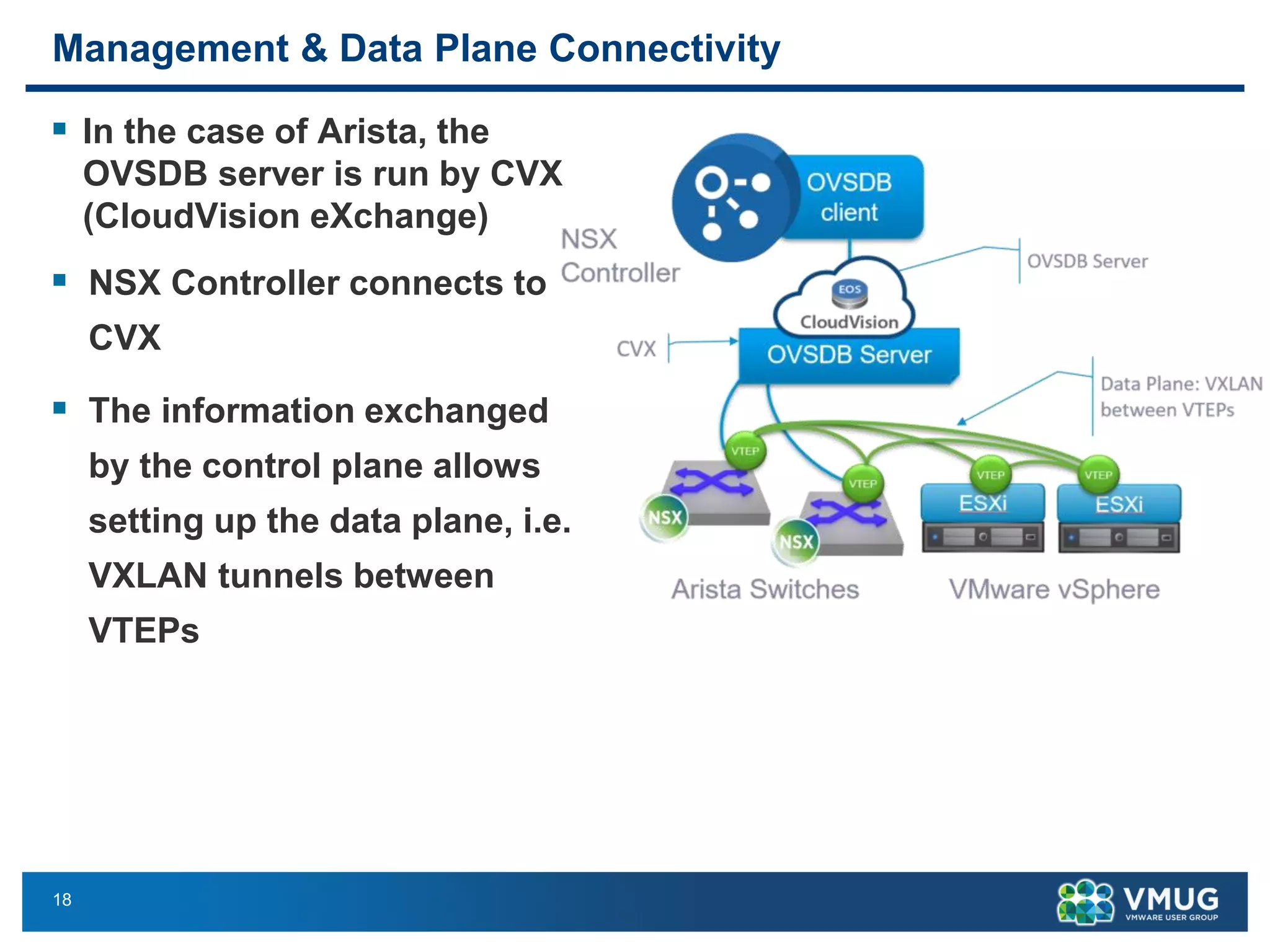
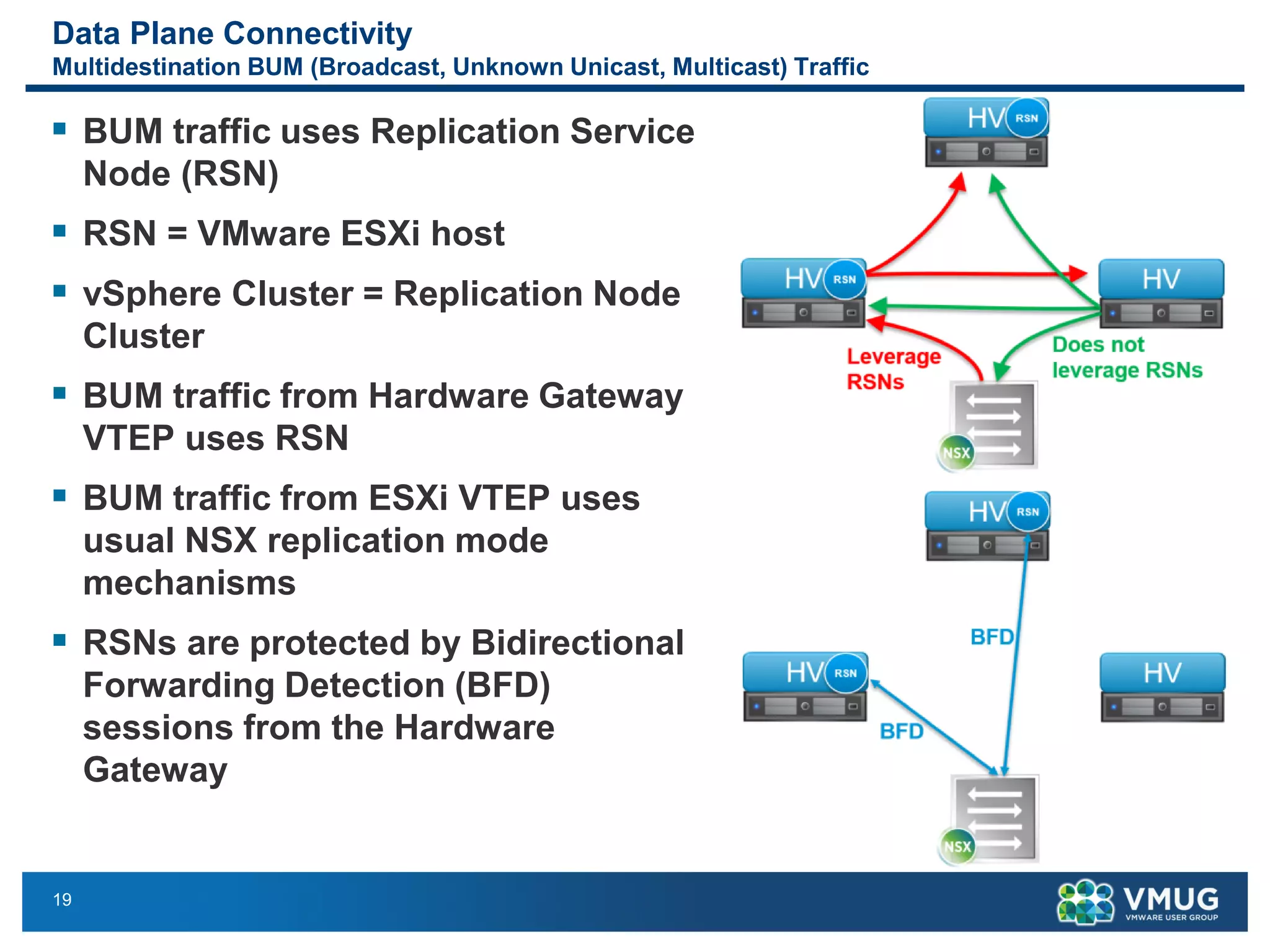
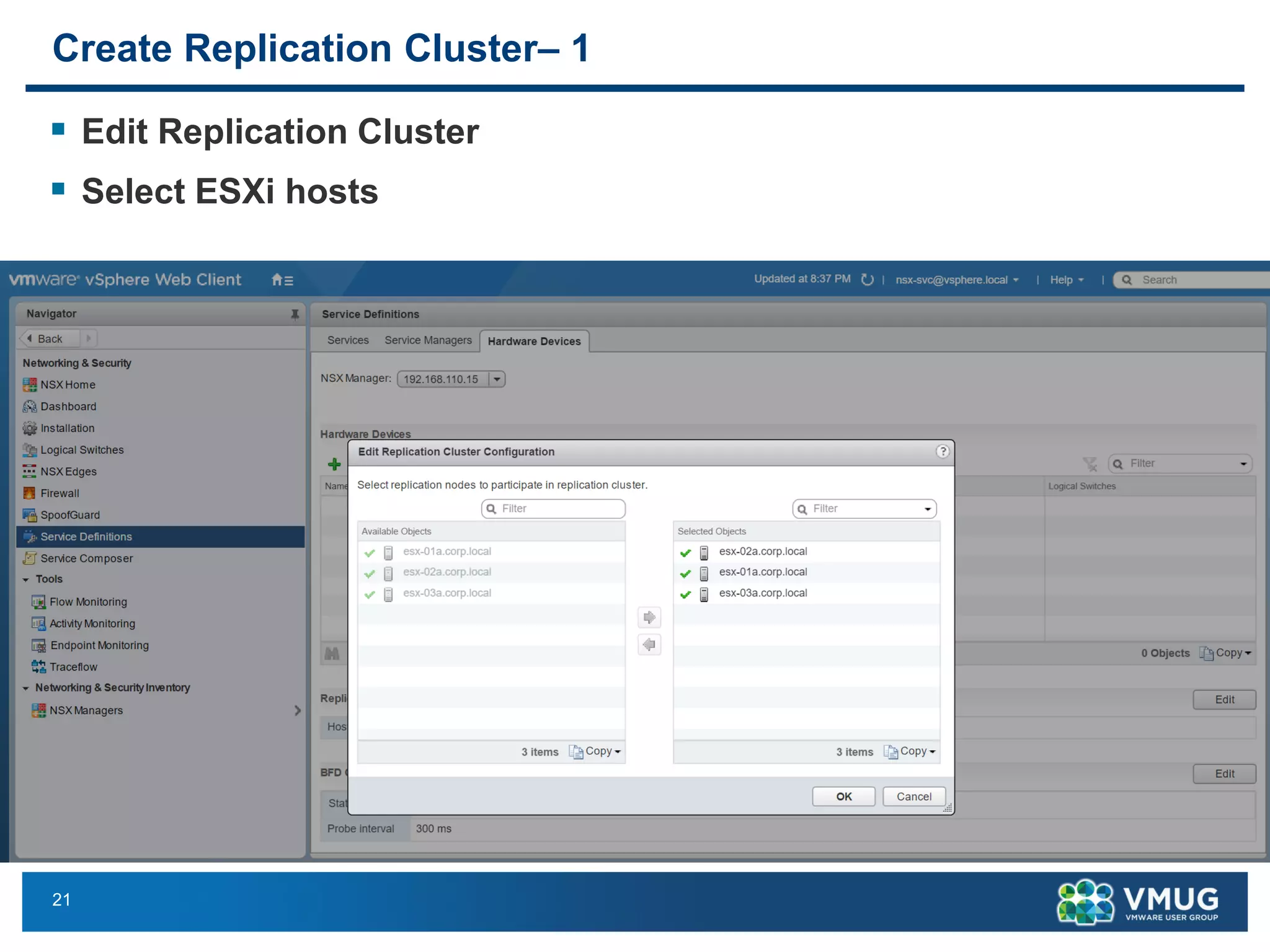
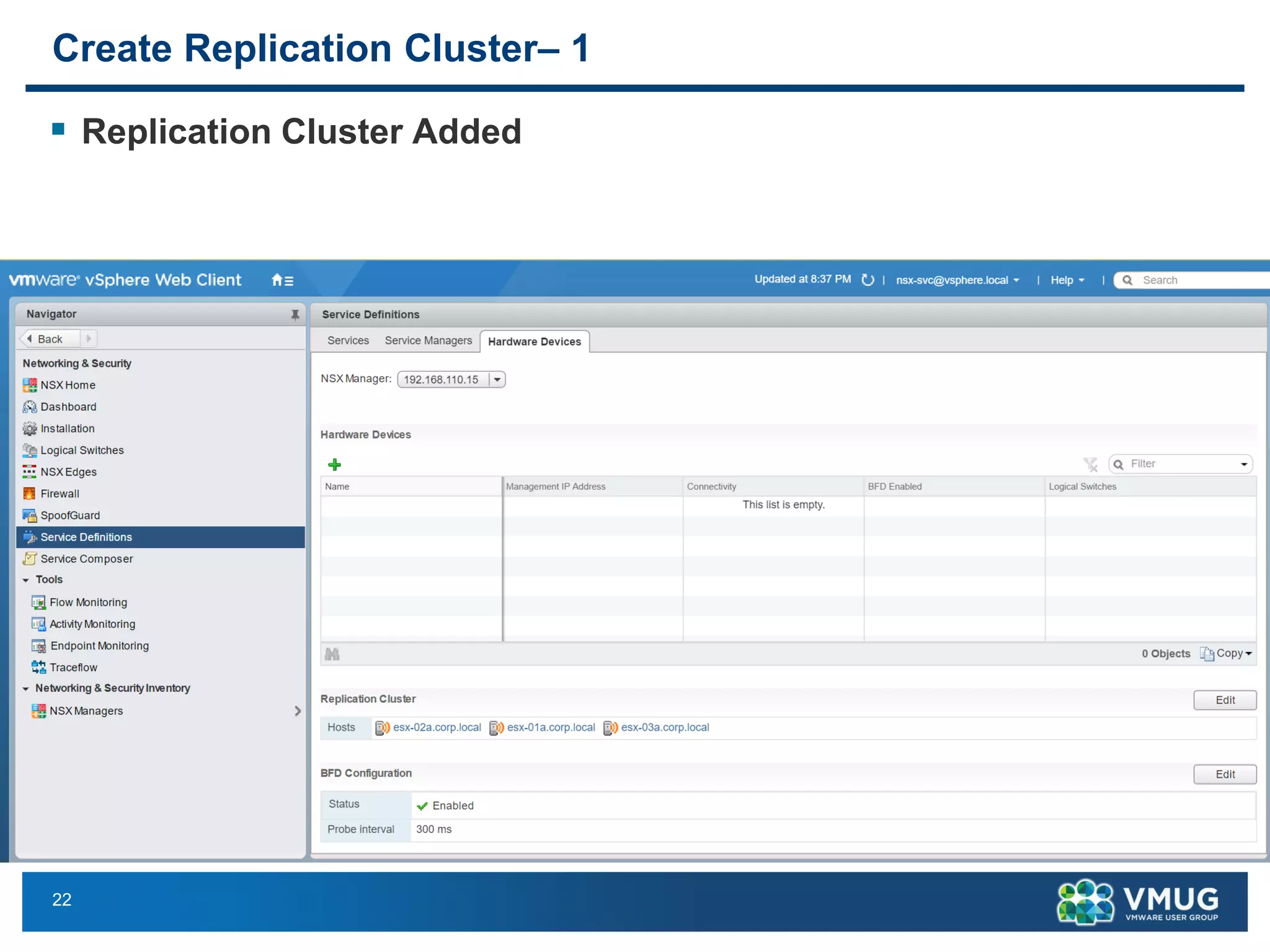
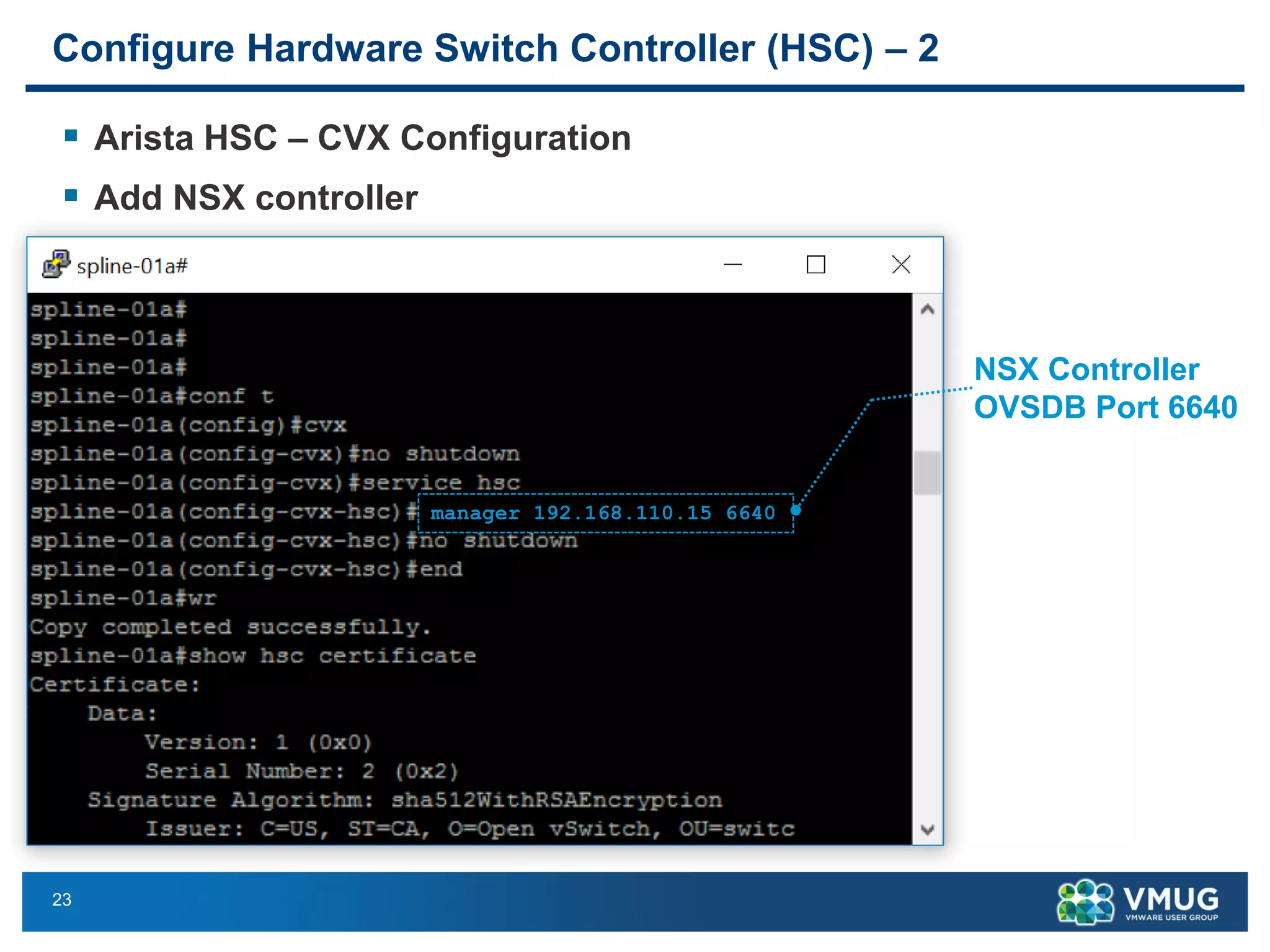
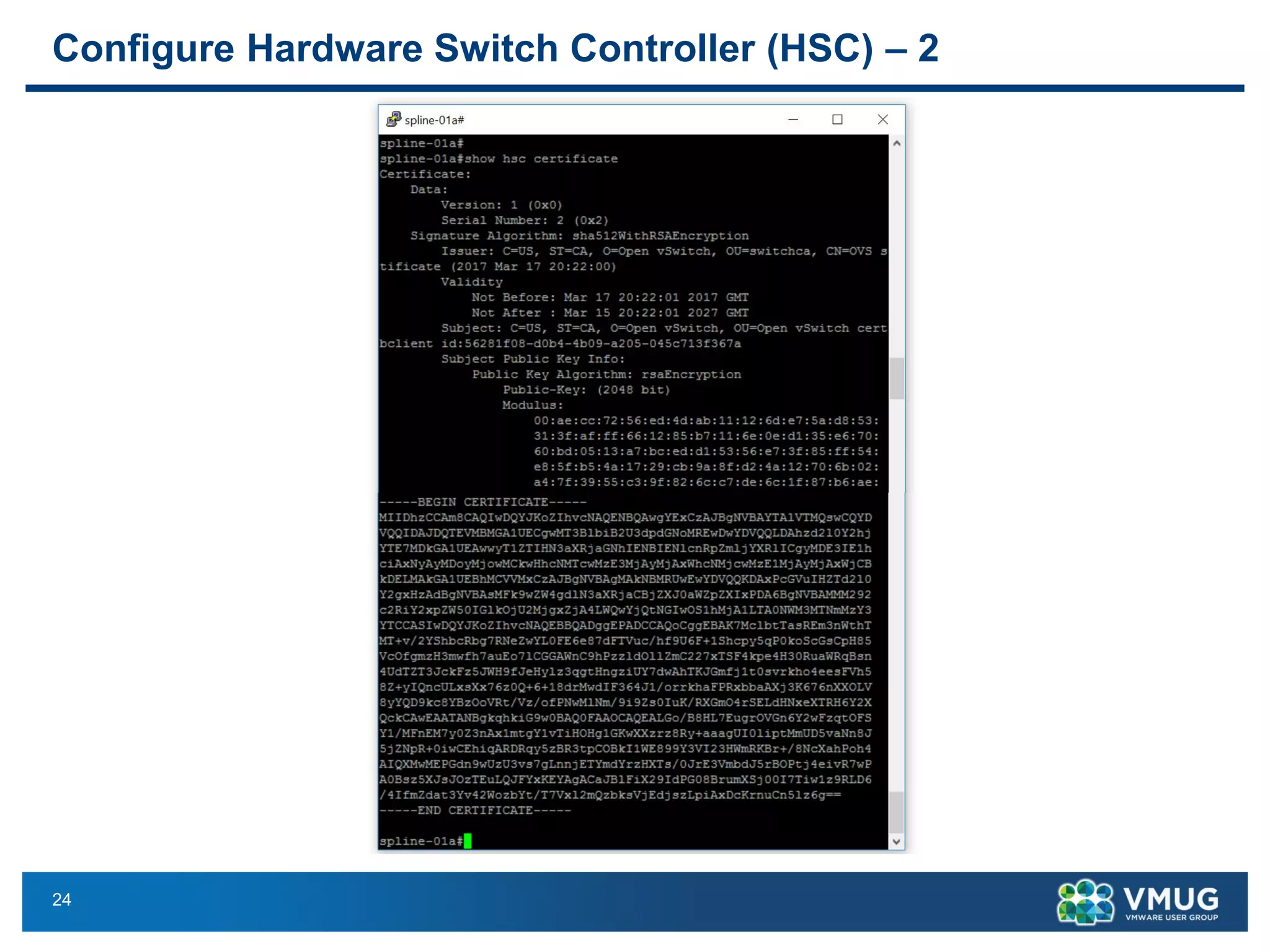
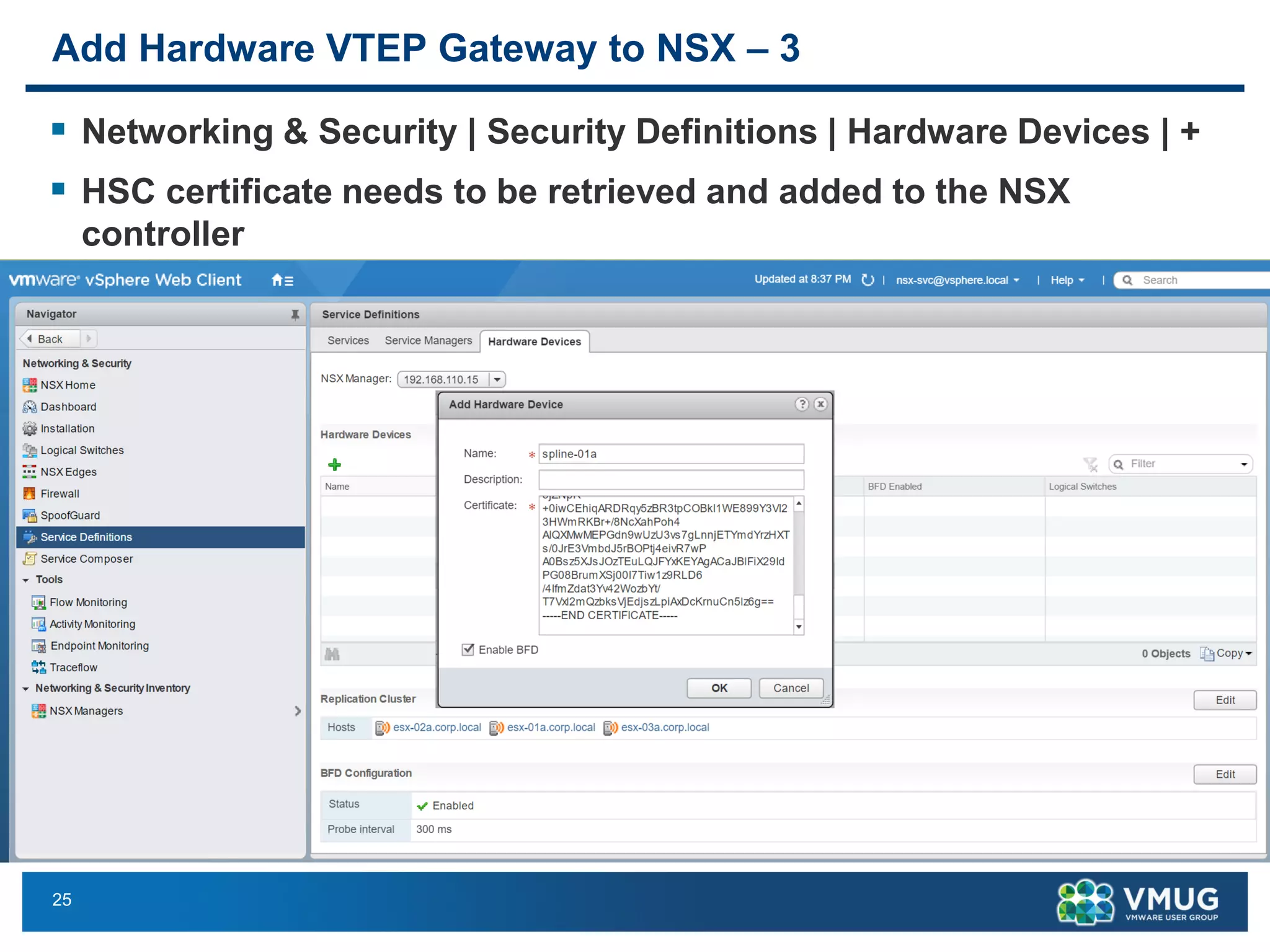
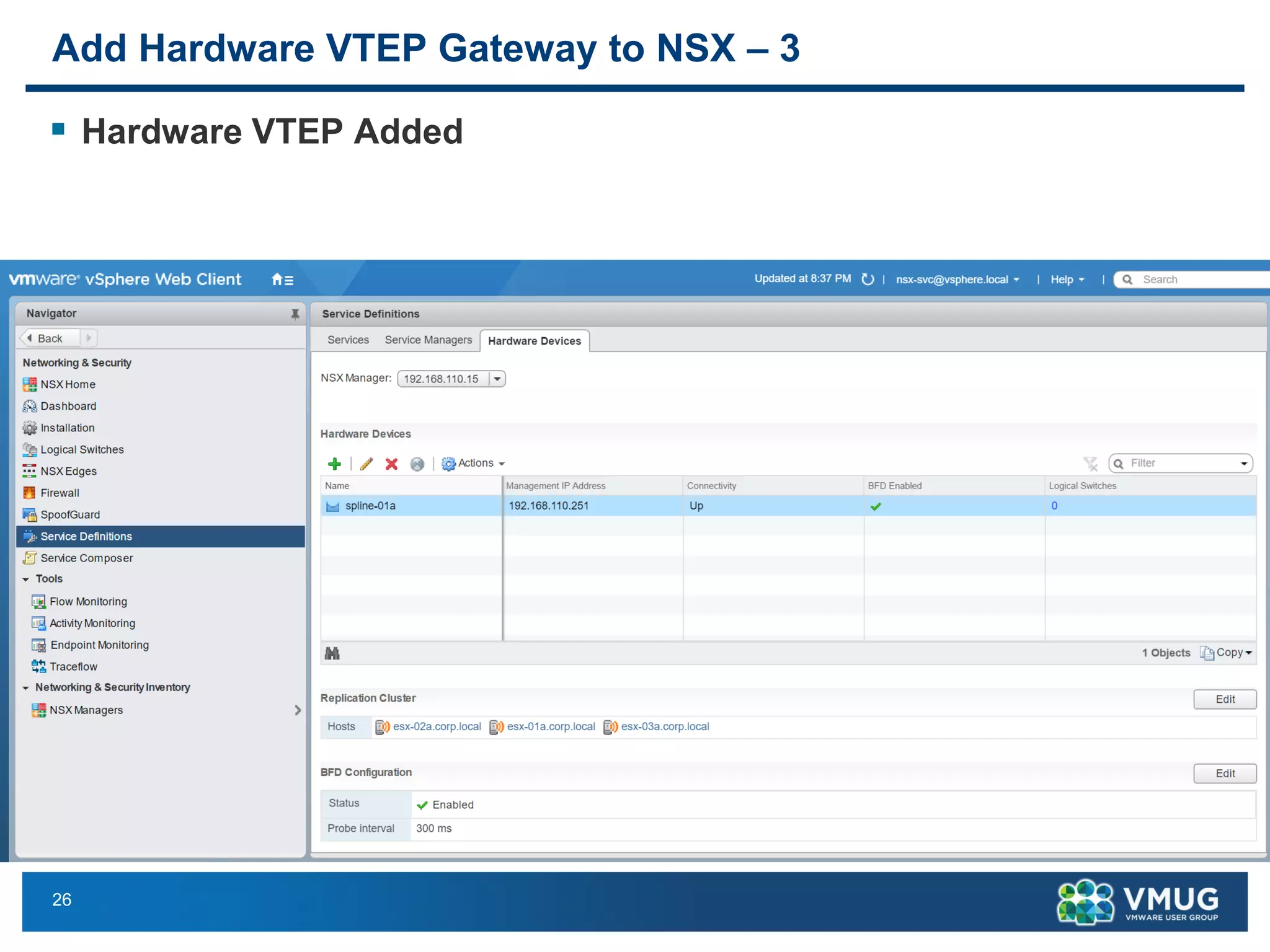
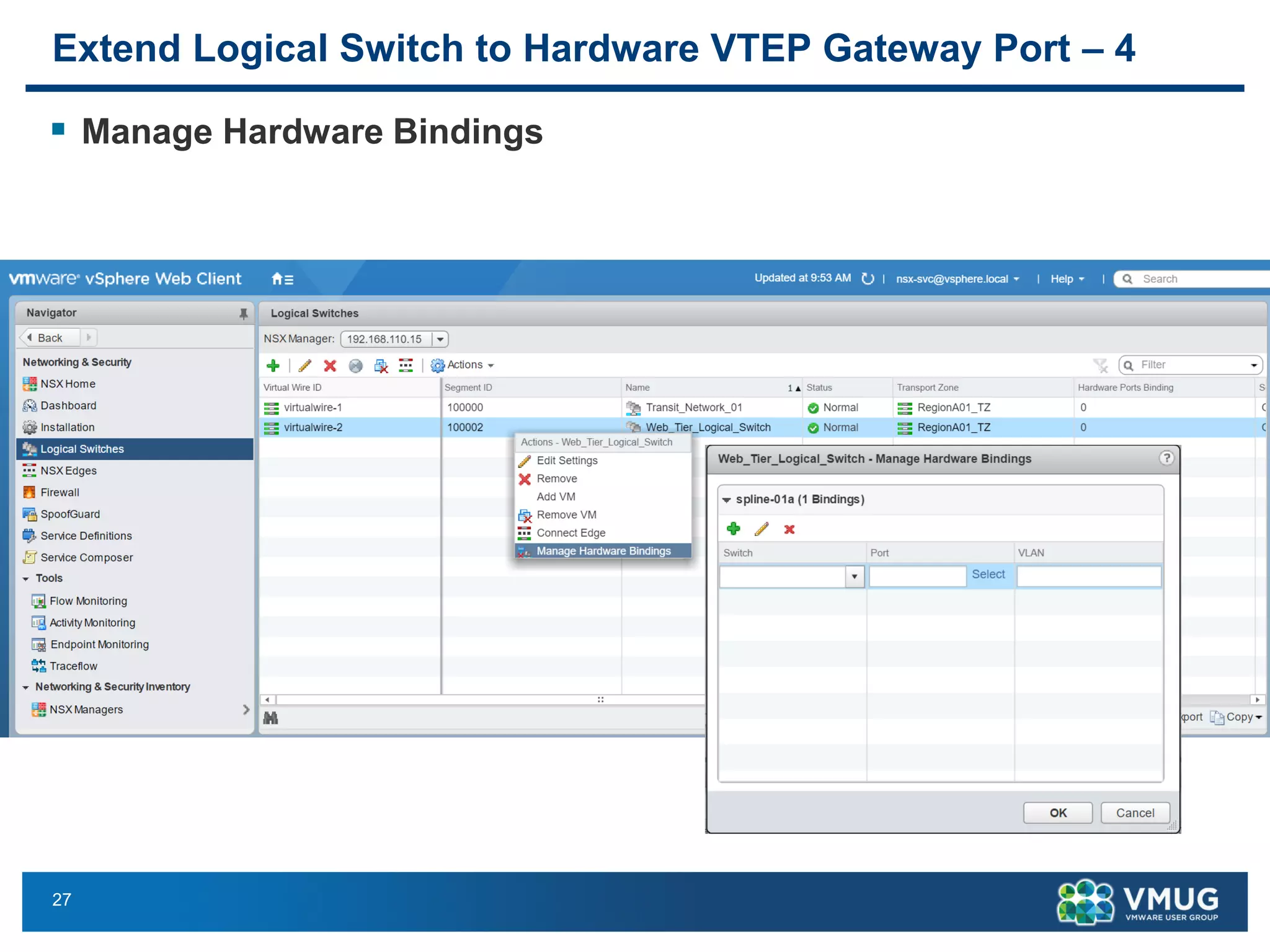
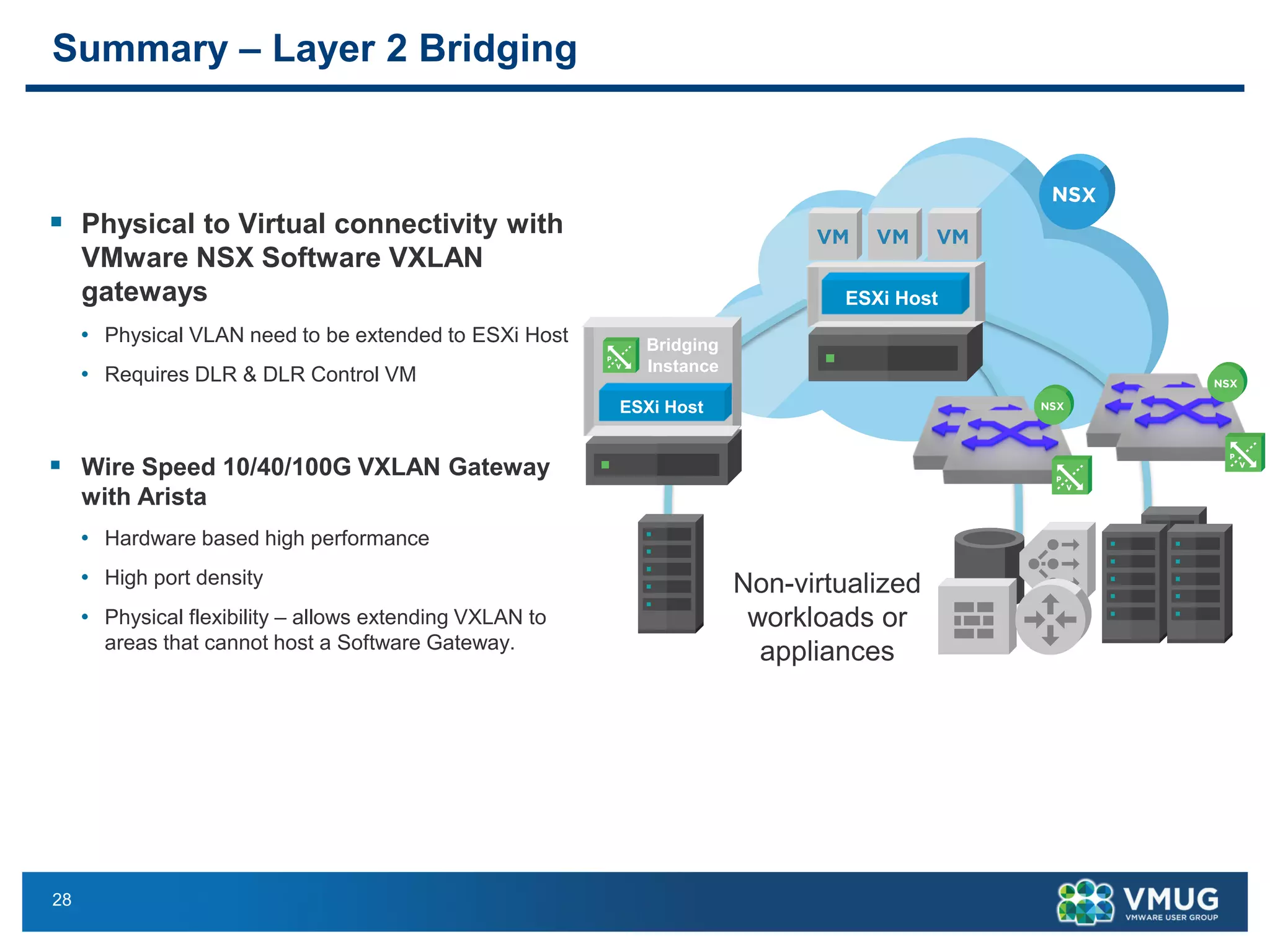
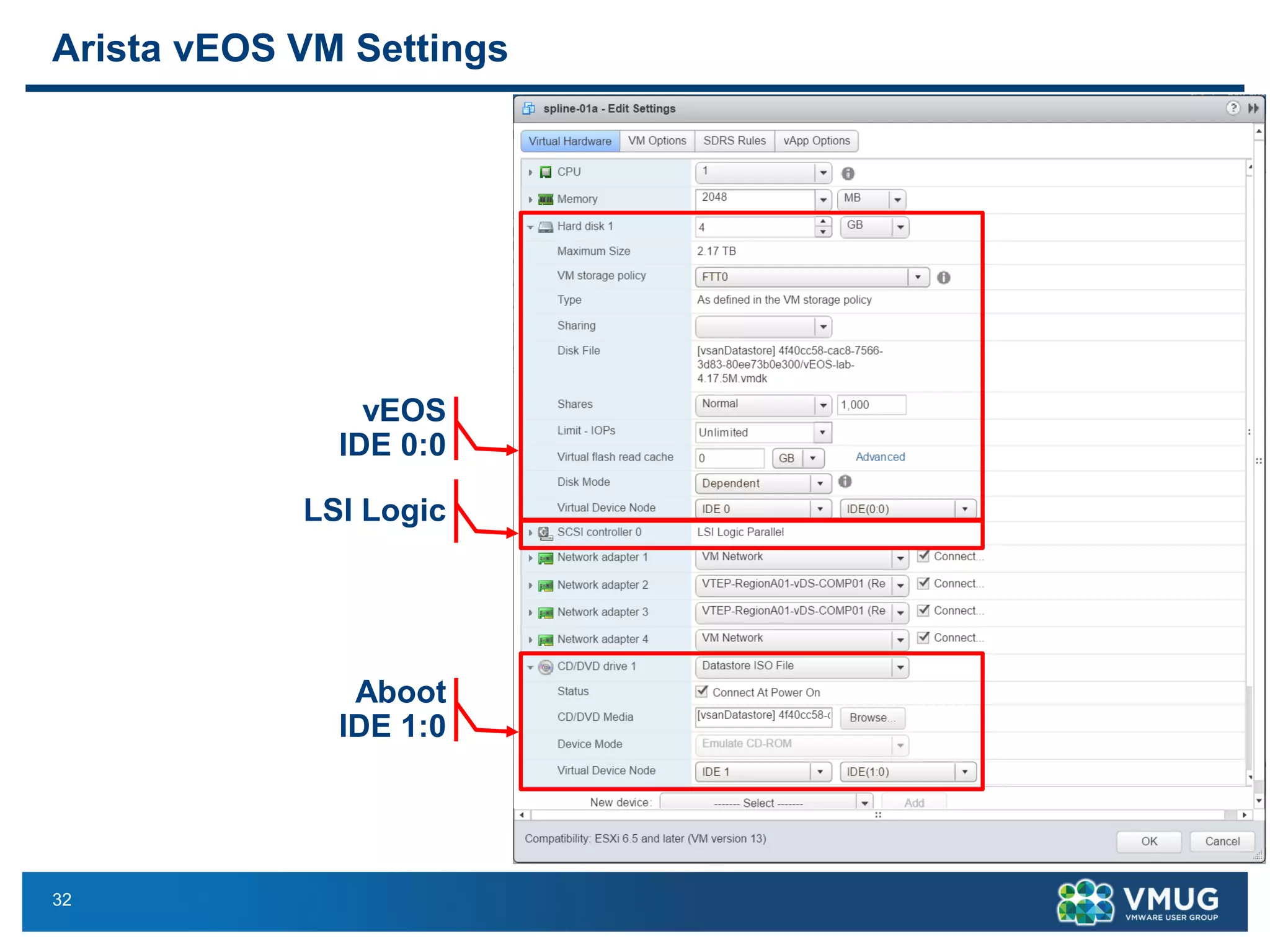
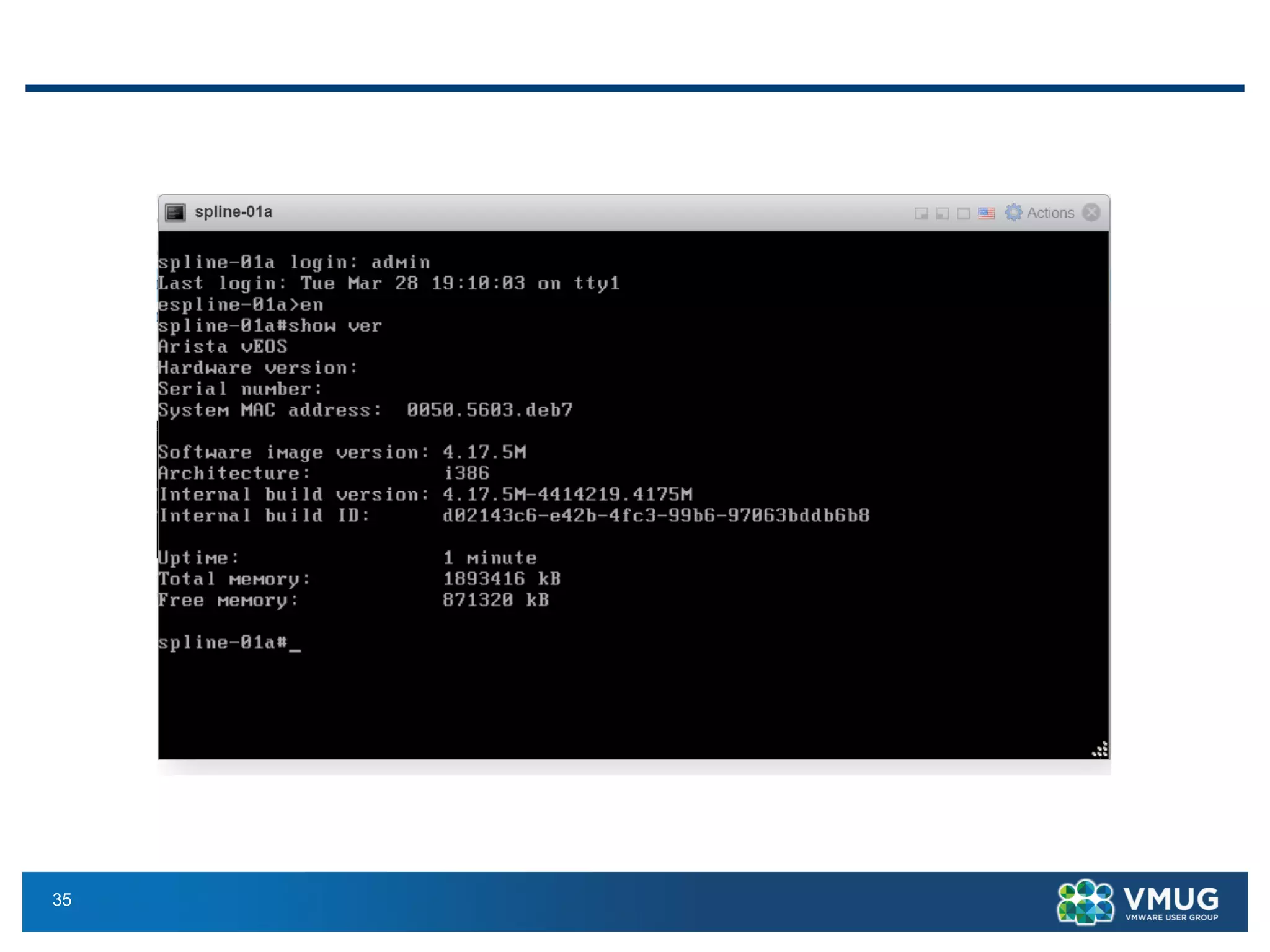
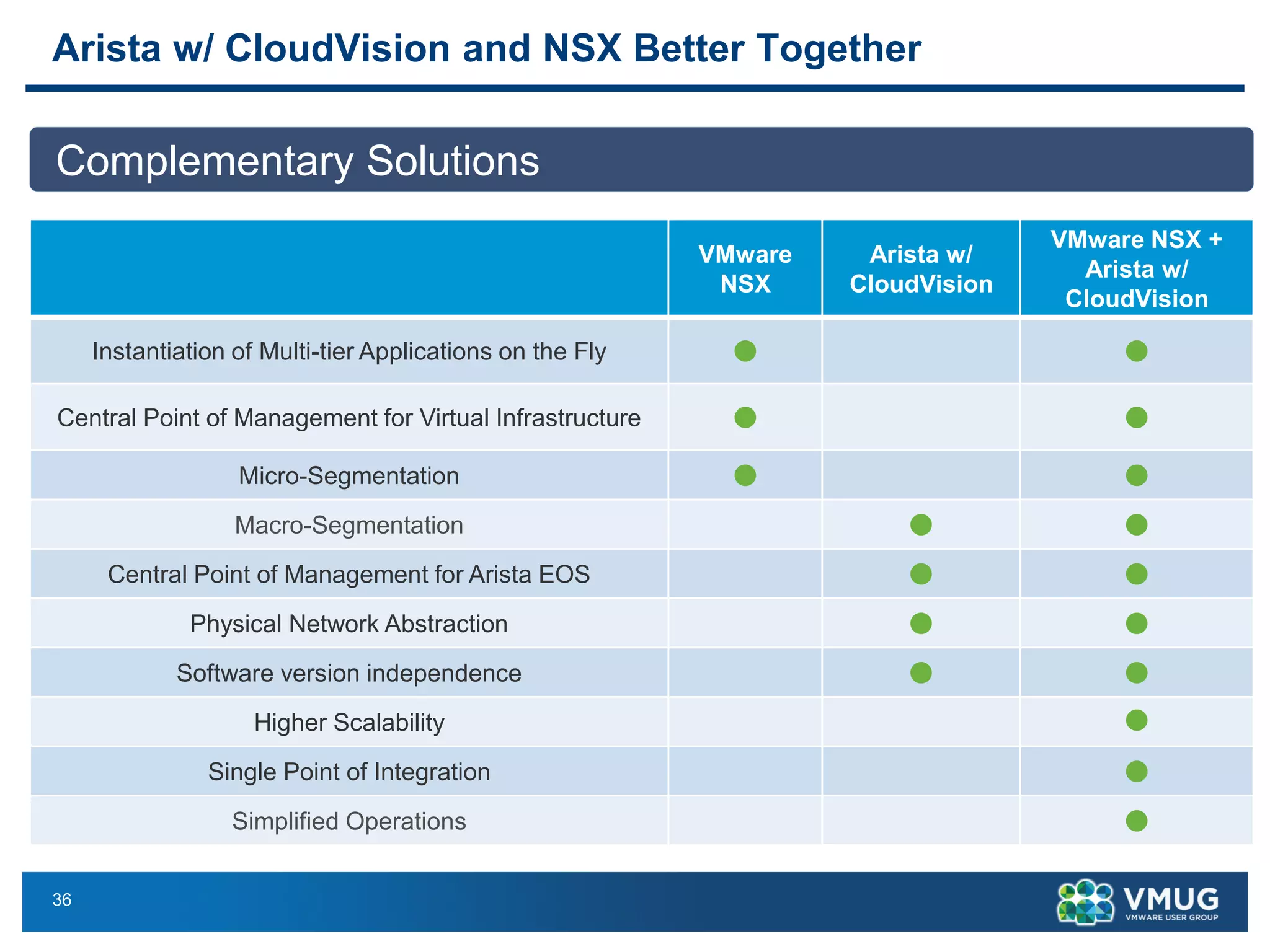
The document provides an overview of VMware NSX and Arista VTEP Layer 2 gateway integration, detailing hardware and software configurations for efficient network communication. It covers key topics such as VXLAN to VLAN bridging, NSX layer 2 enhancements, and configuration steps for hardware VTEPs. Additional references and community engagement opportunities related to the integration of these technologies are also mentioned.