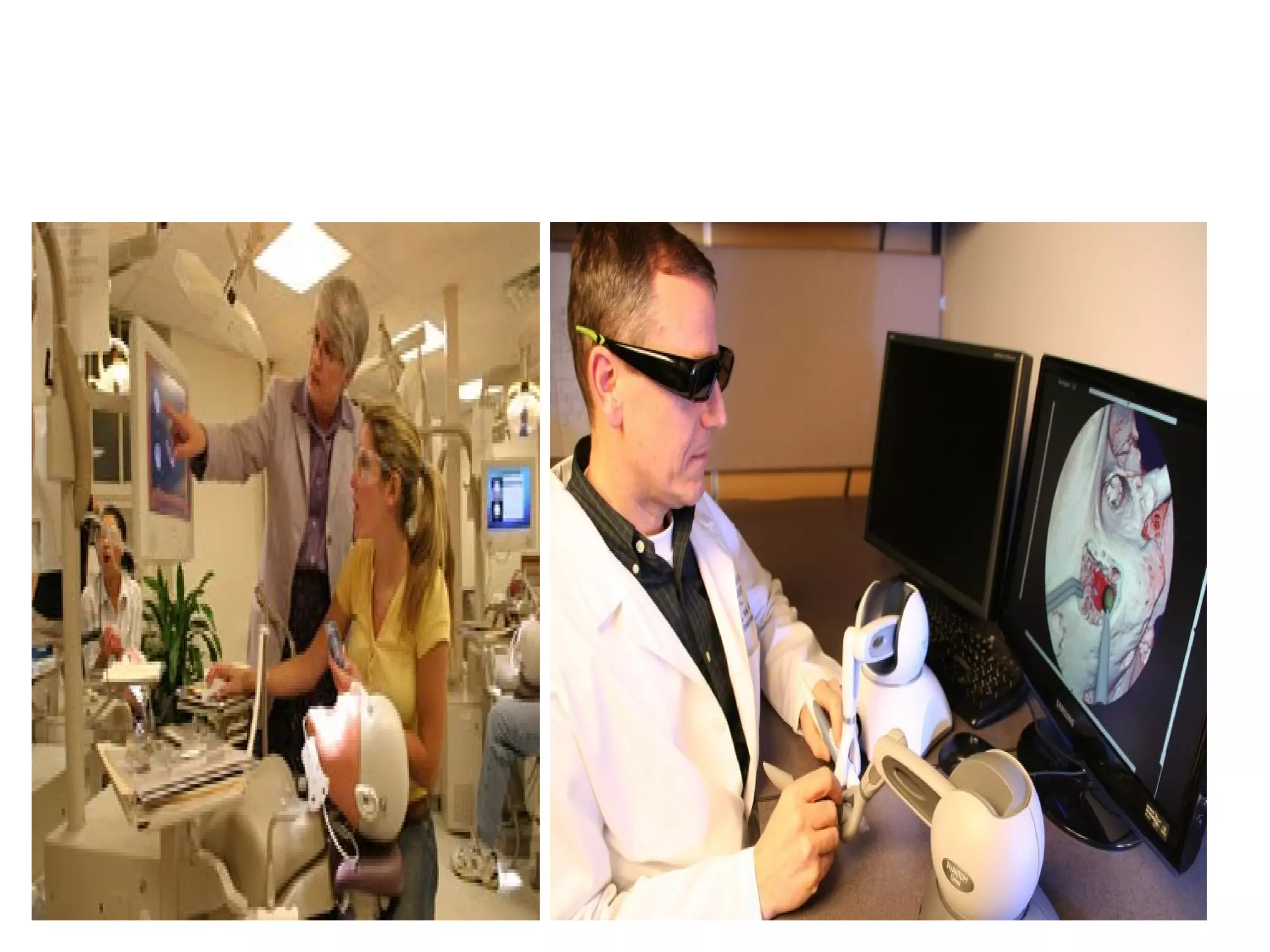
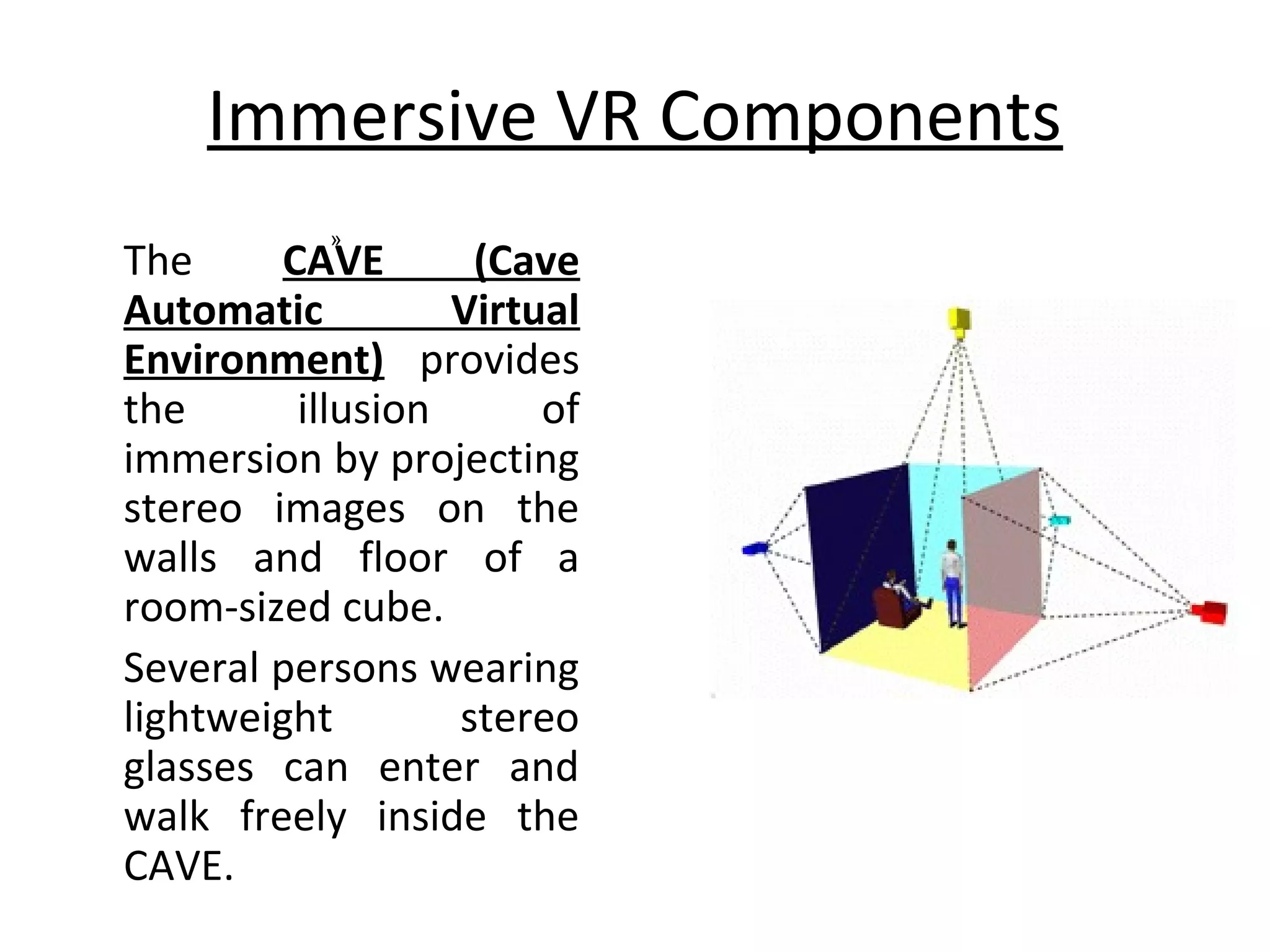
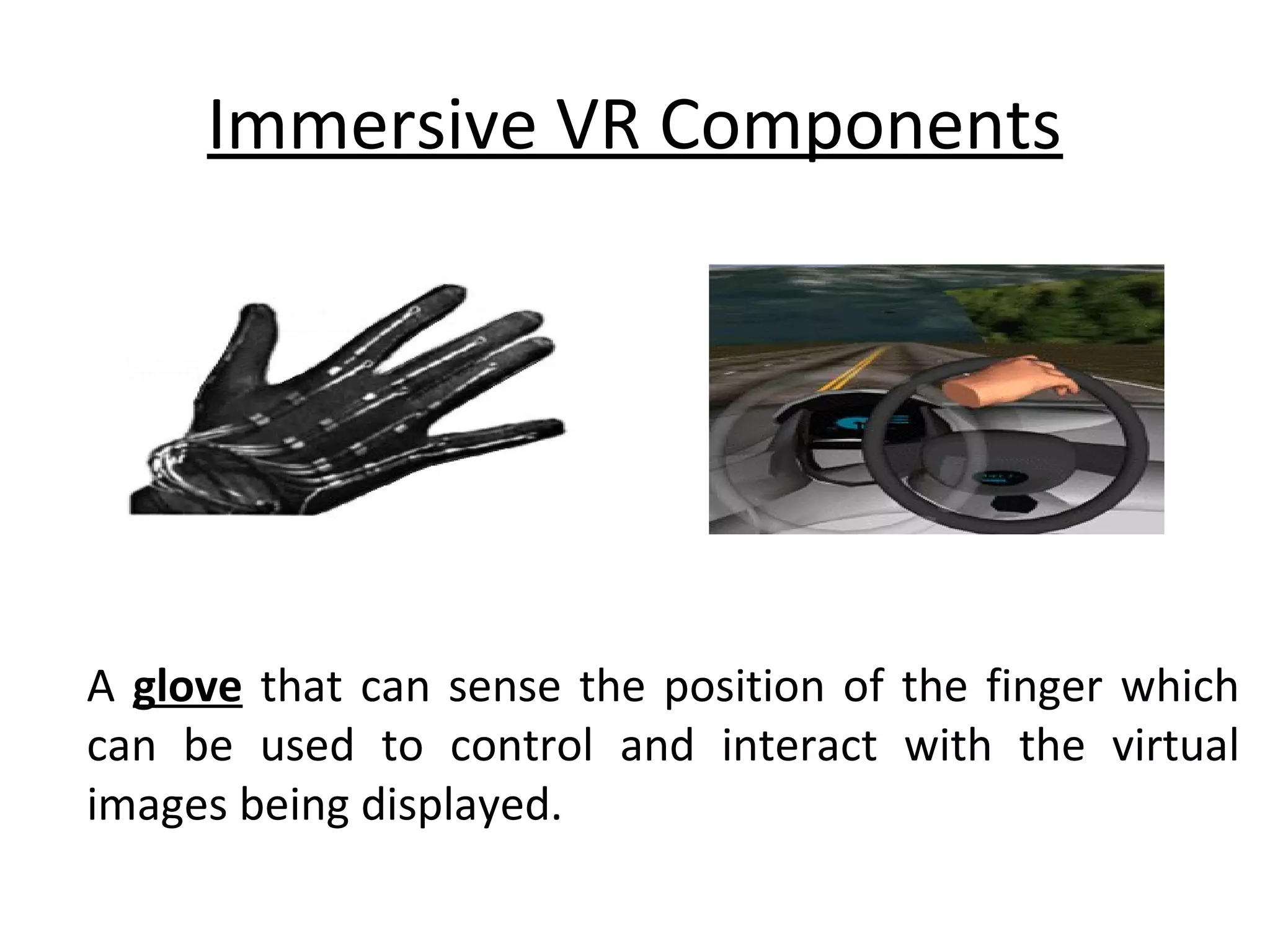
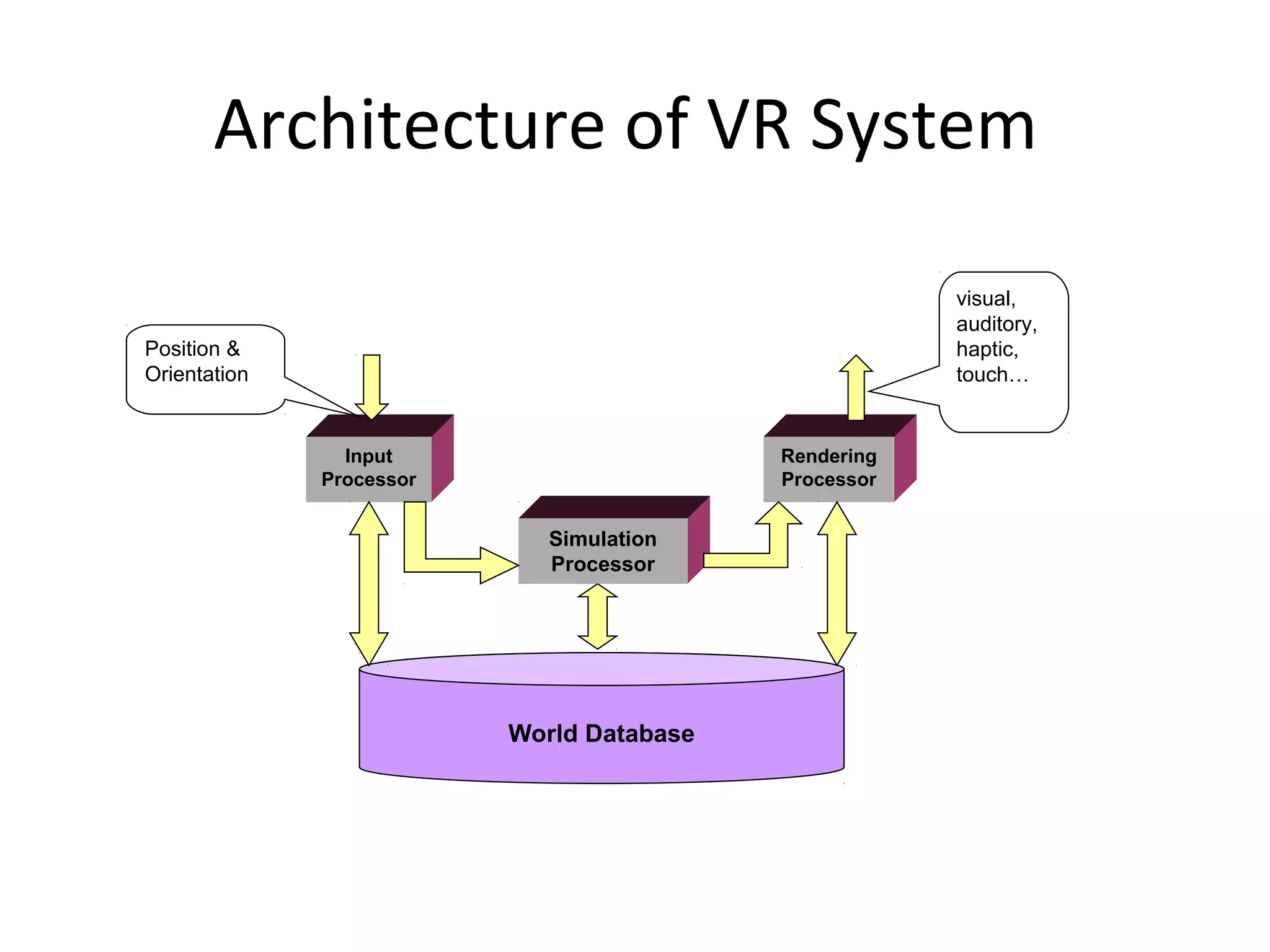
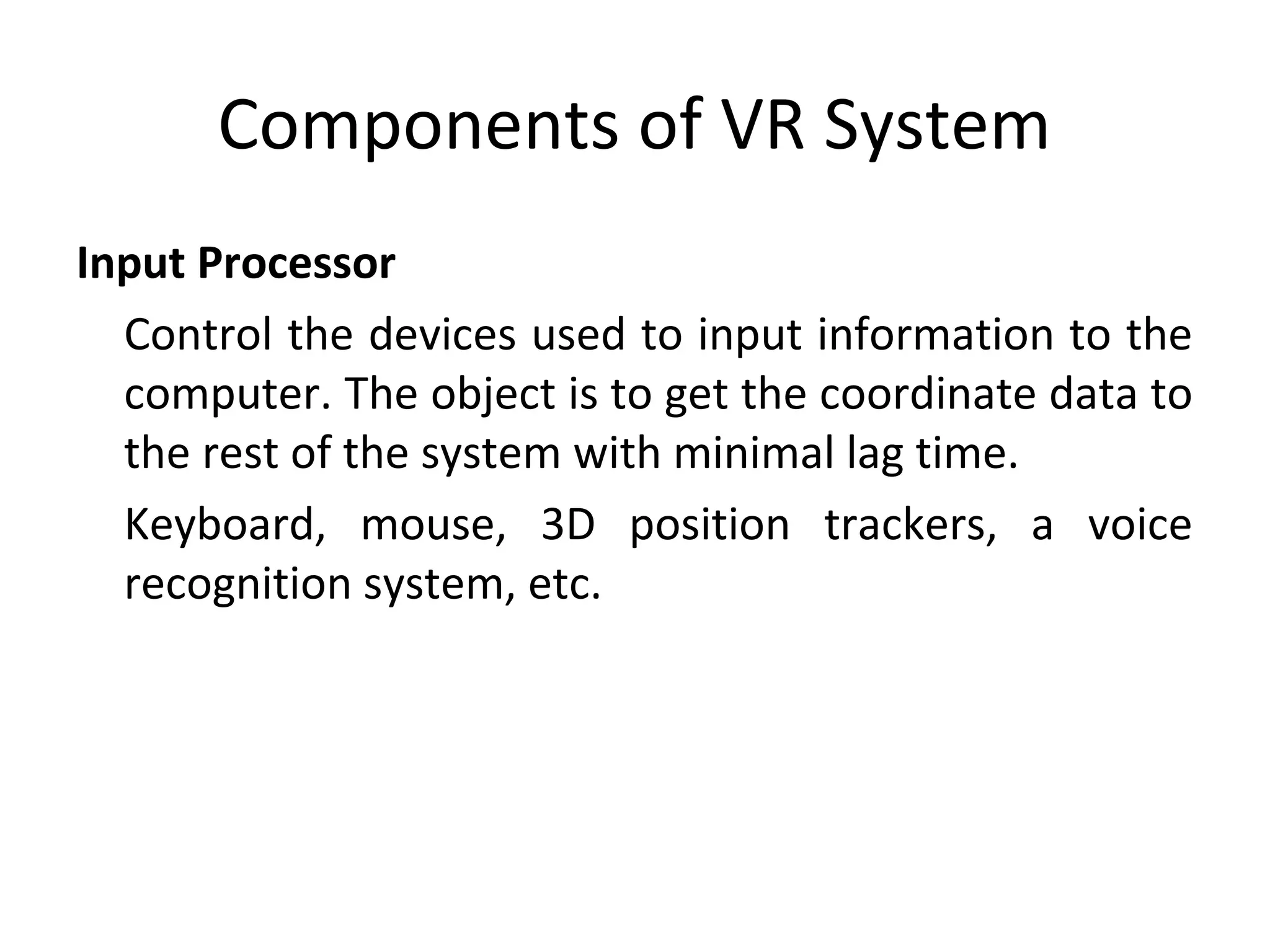
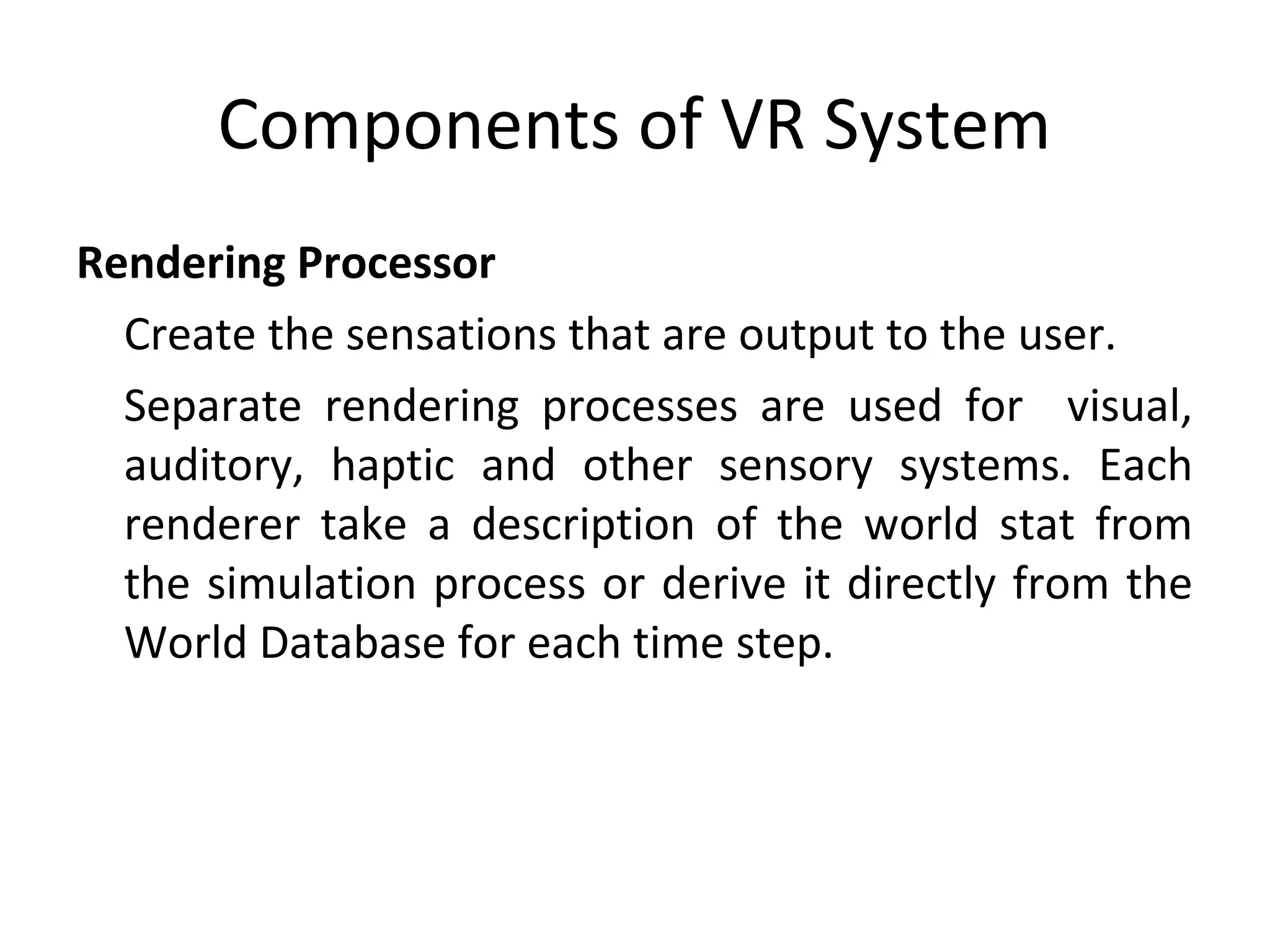
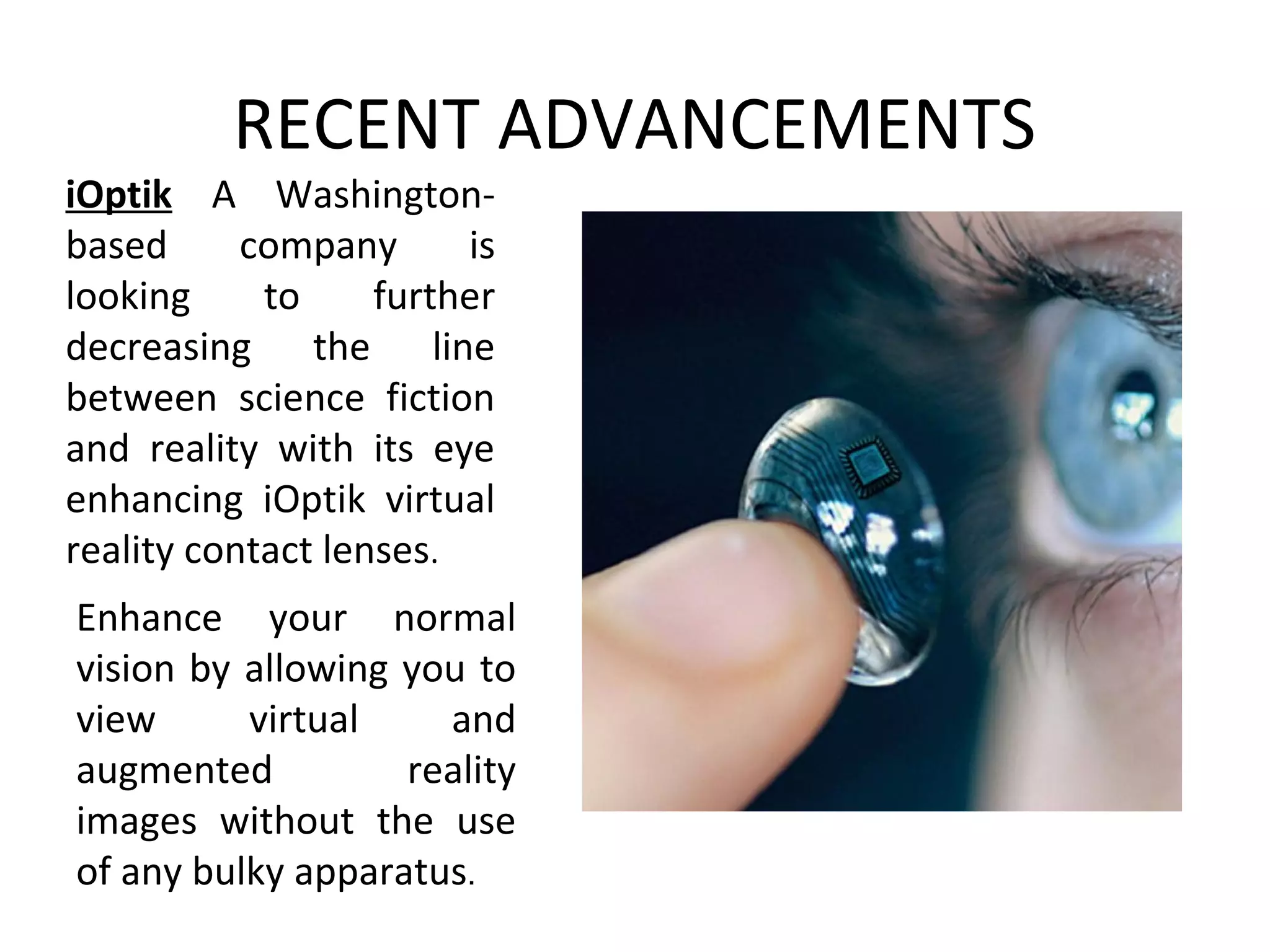
Virtual reality allows users to interact with simulated environments, whether based on real or imaginary places. Most VR is visual, displayed on screens or through stereoscopic displays, though some systems include sound, and experimental systems have limited tactile feedback. VR is useful for operations in dangerous environments through telepresence, scientific visualization, medicine for research and training, and education in areas like driving, flight, and vehicle simulators. VR systems have input, processing, rendering, and world database components. Recent advancements include VR contact lenses and tools to more easily develop content across VR platforms. While offering interaction and interfaces, VR also faces challenges regarding side effects, usability, and standardization.