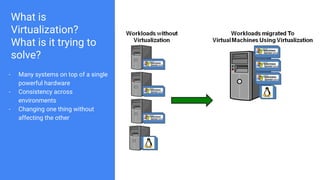
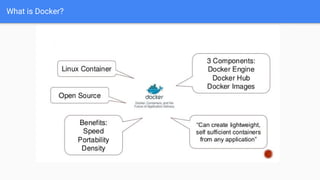
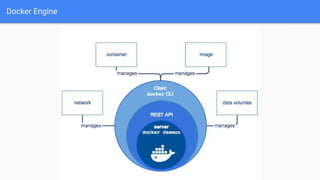
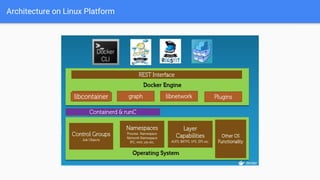
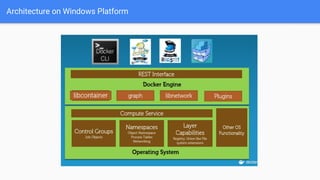
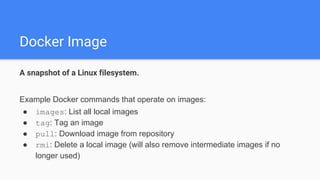
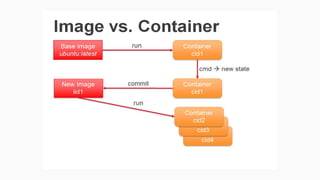
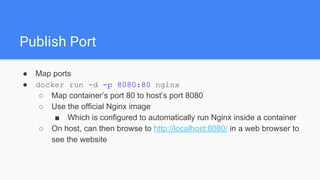
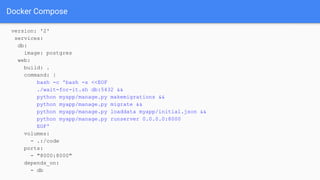
The document provides an overview of virtualization and its solutions, comparing traditional virtualization with Docker technology, highlighting the pros and cons of each. It explains Docker's architecture, commands related to images and containers, and how to manage them using Docker Compose and Docker Swarm for microservices. Additionally, it covers use cases for Docker, emphasizing its speed, lightweight nature, and portability.