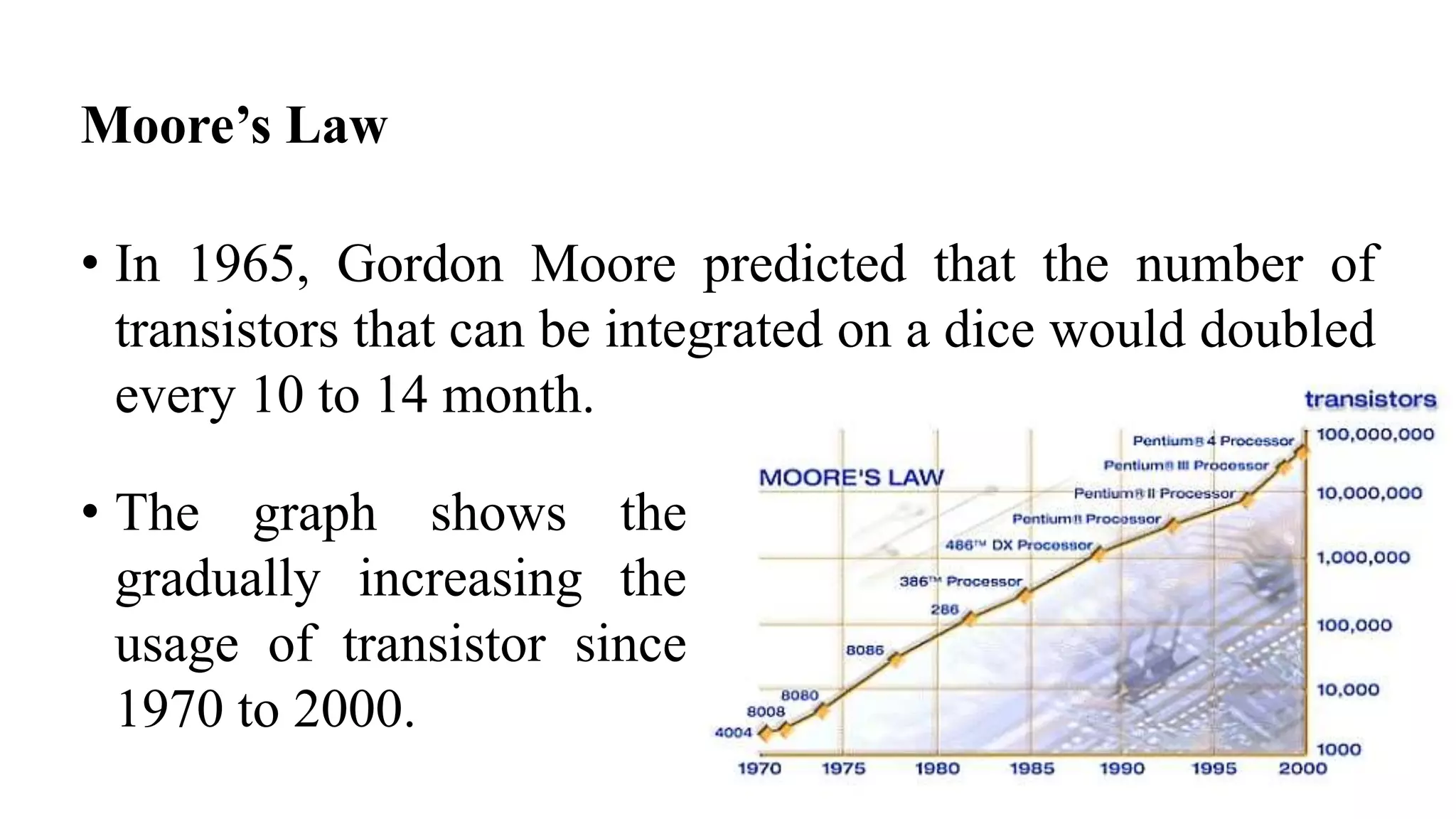
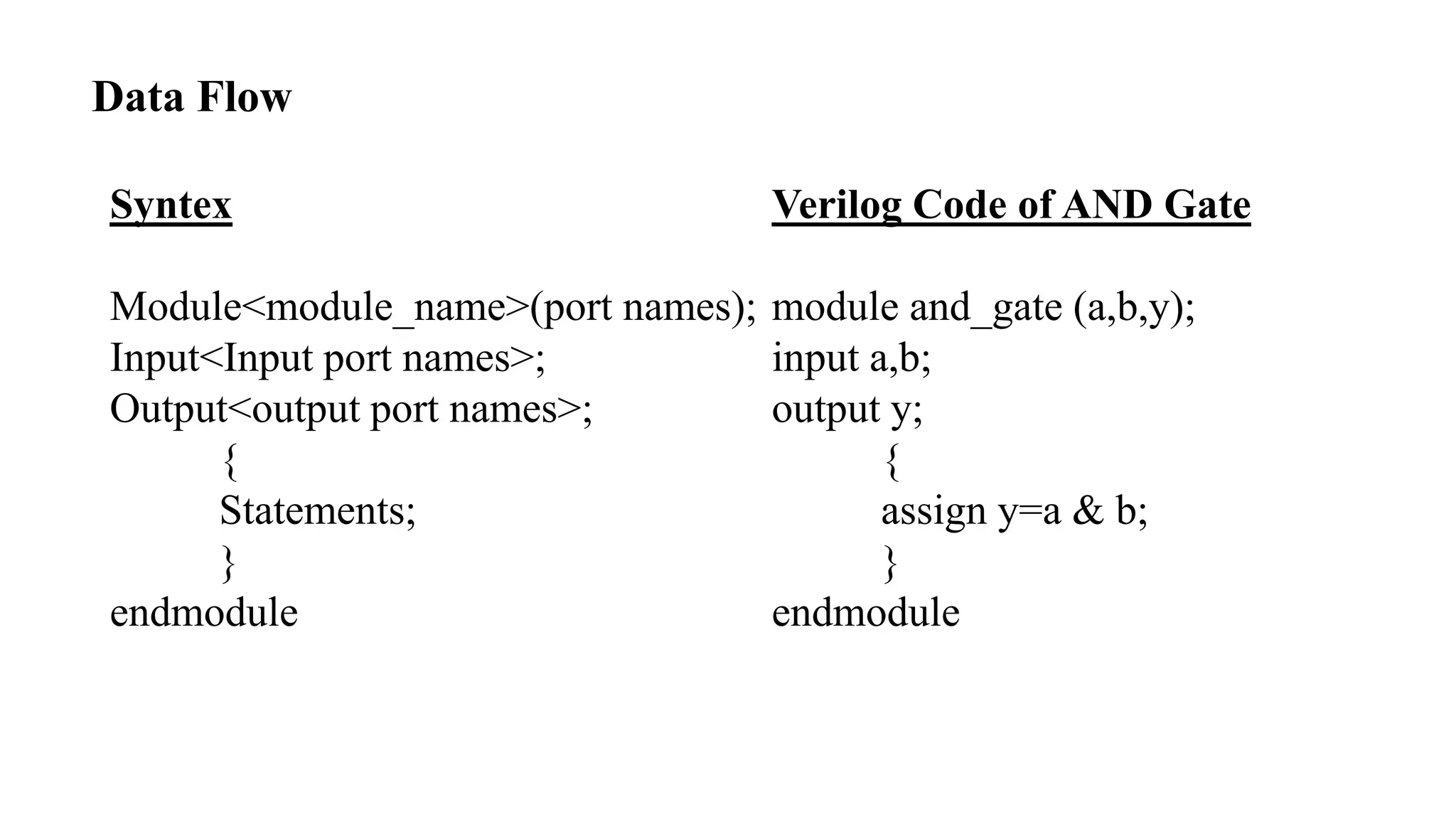
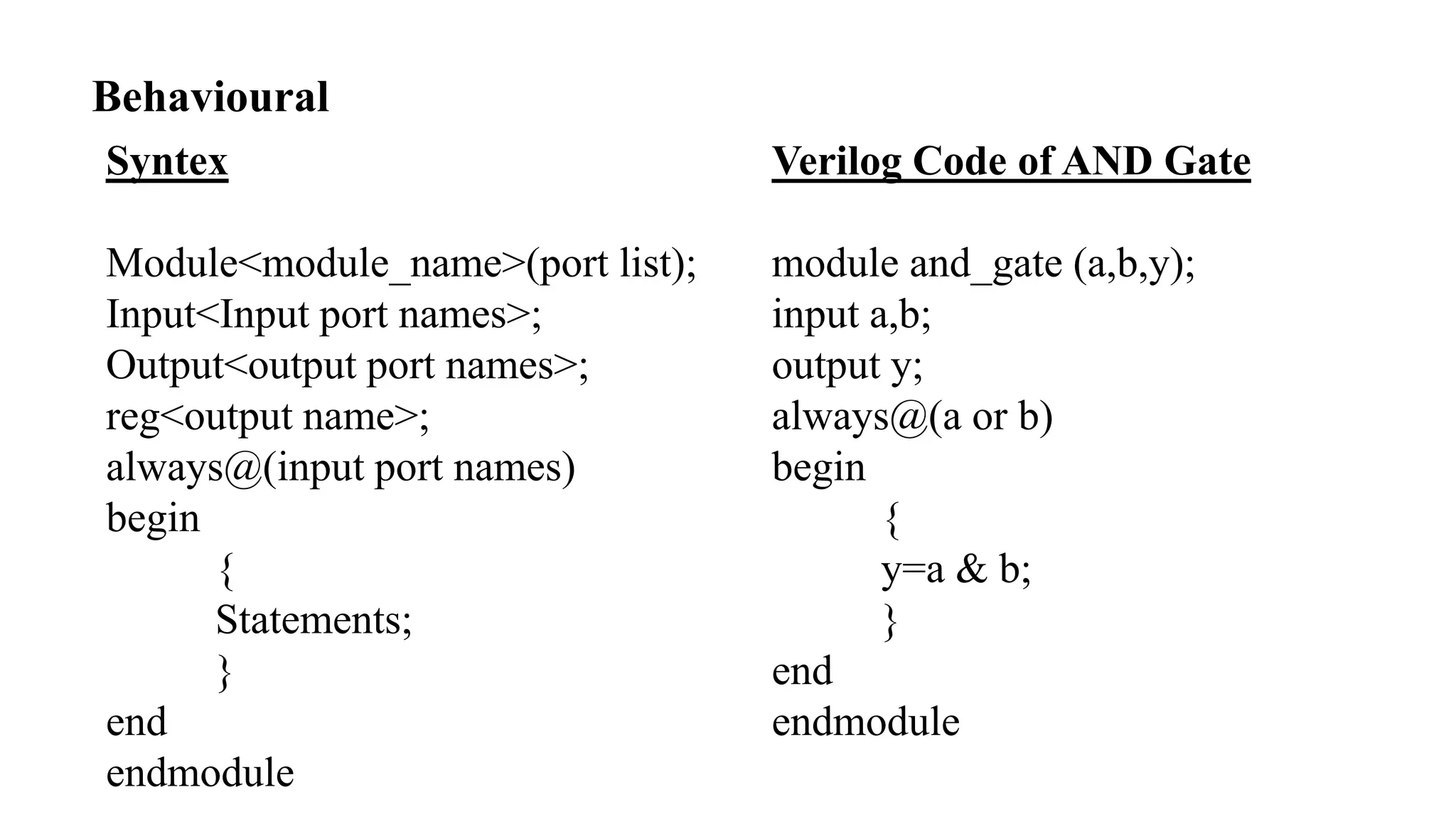
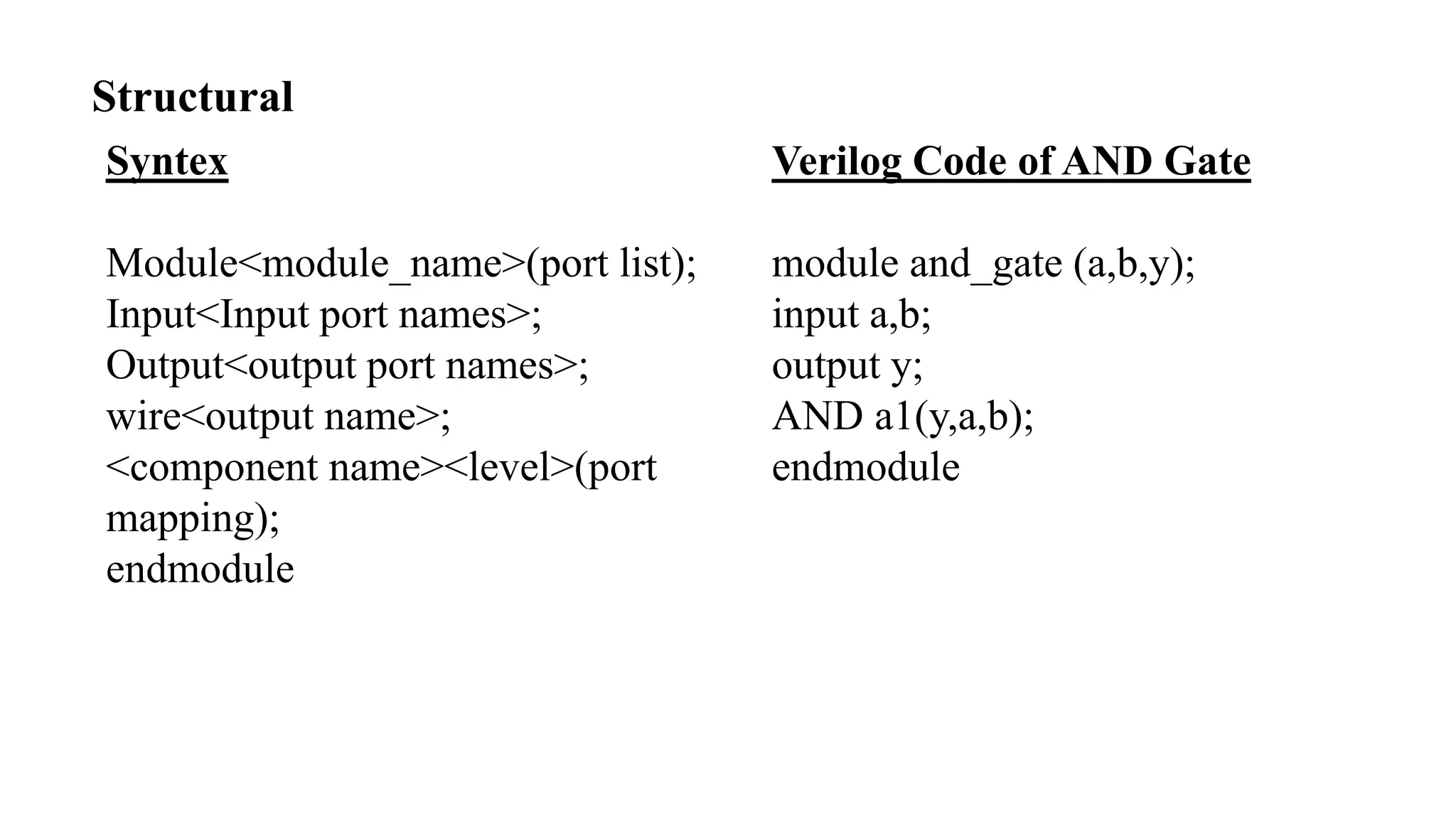
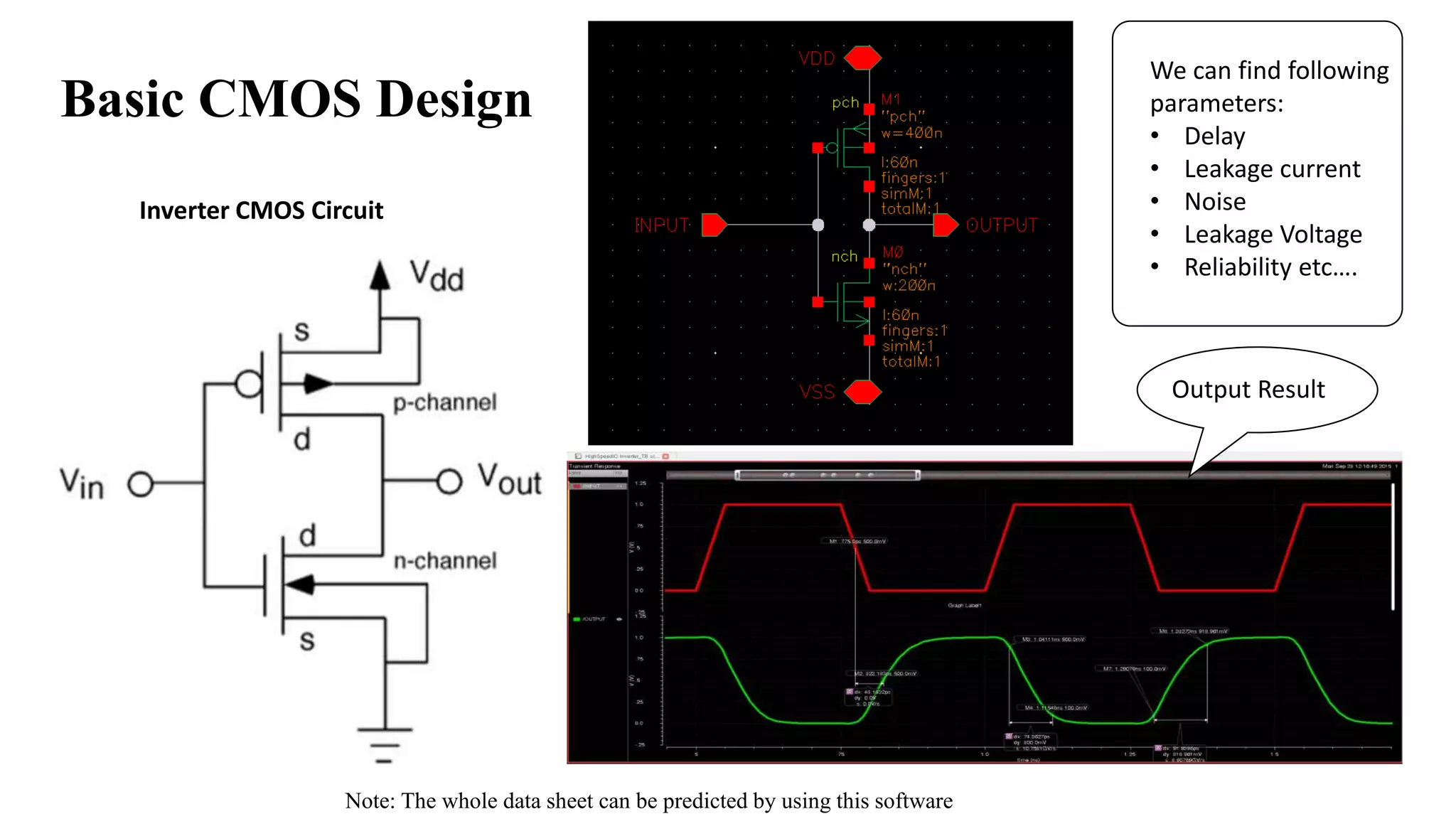
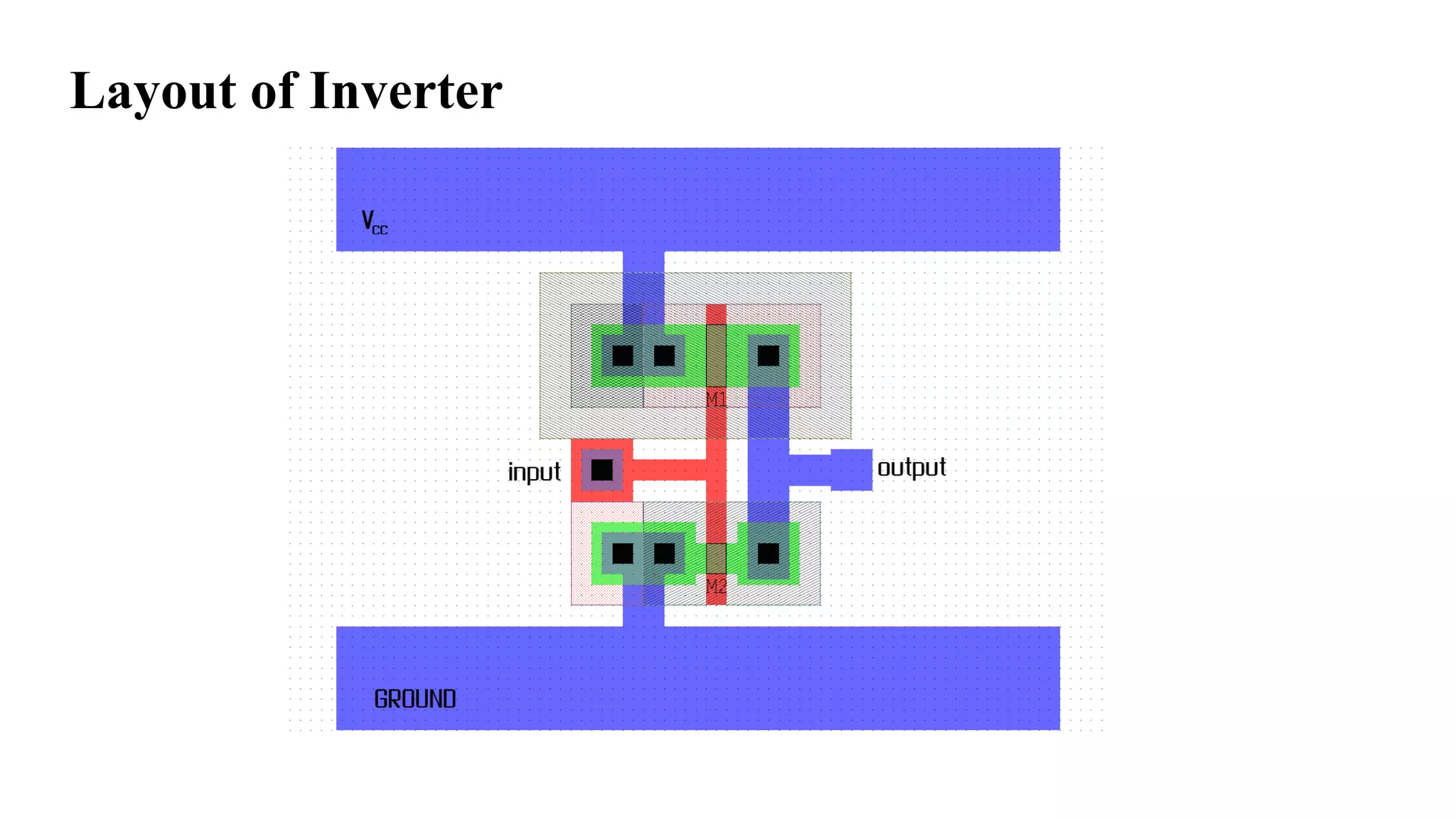
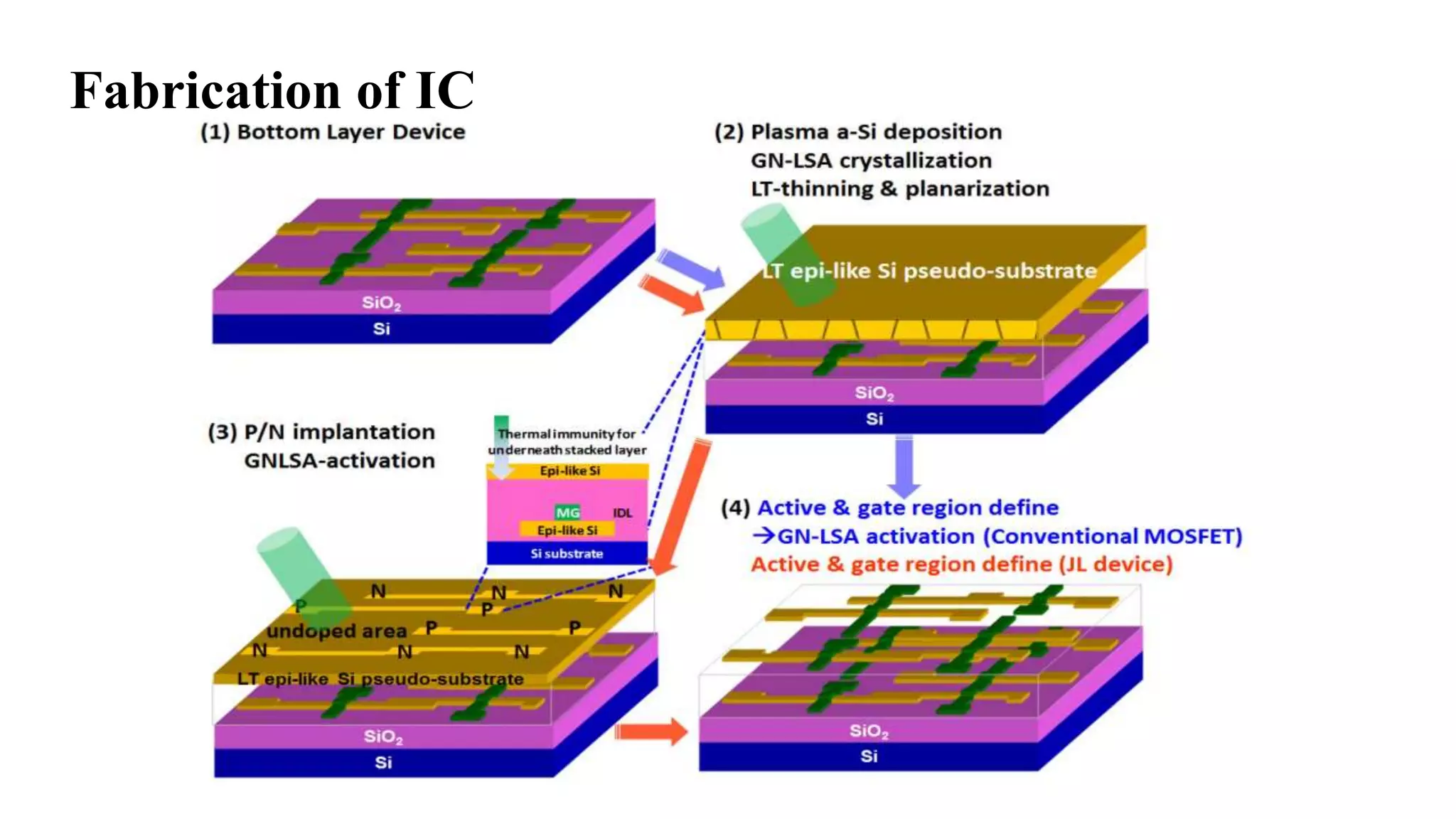
The document is a presentation on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) technology, covering its definition, design processes, tools used, and the differences between various programming languages like Verilog and VHDL. It also discusses CMOS technology, advantages and disadvantages of VLSI, and various companies in India related to this field. The conclusion emphasizes the scope and applications of VLSI in modern technology.