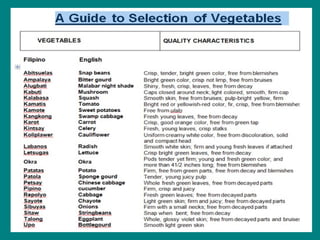
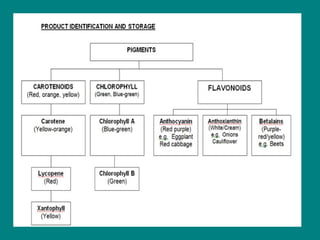
The document provides an extensive classification of vegetables, including families such as squash, roots, legumes, and various leafy greens. It describes quality characteristics, storage methods, and preparation techniques for different vegetable types, along with guidelines for cooking to preserve flavor, nutrients, and texture. Additionally, it covers aspects of purchasing, preserving, and the nutritional benefits of vegetables, along with information on processing methods like irradiation and canning.