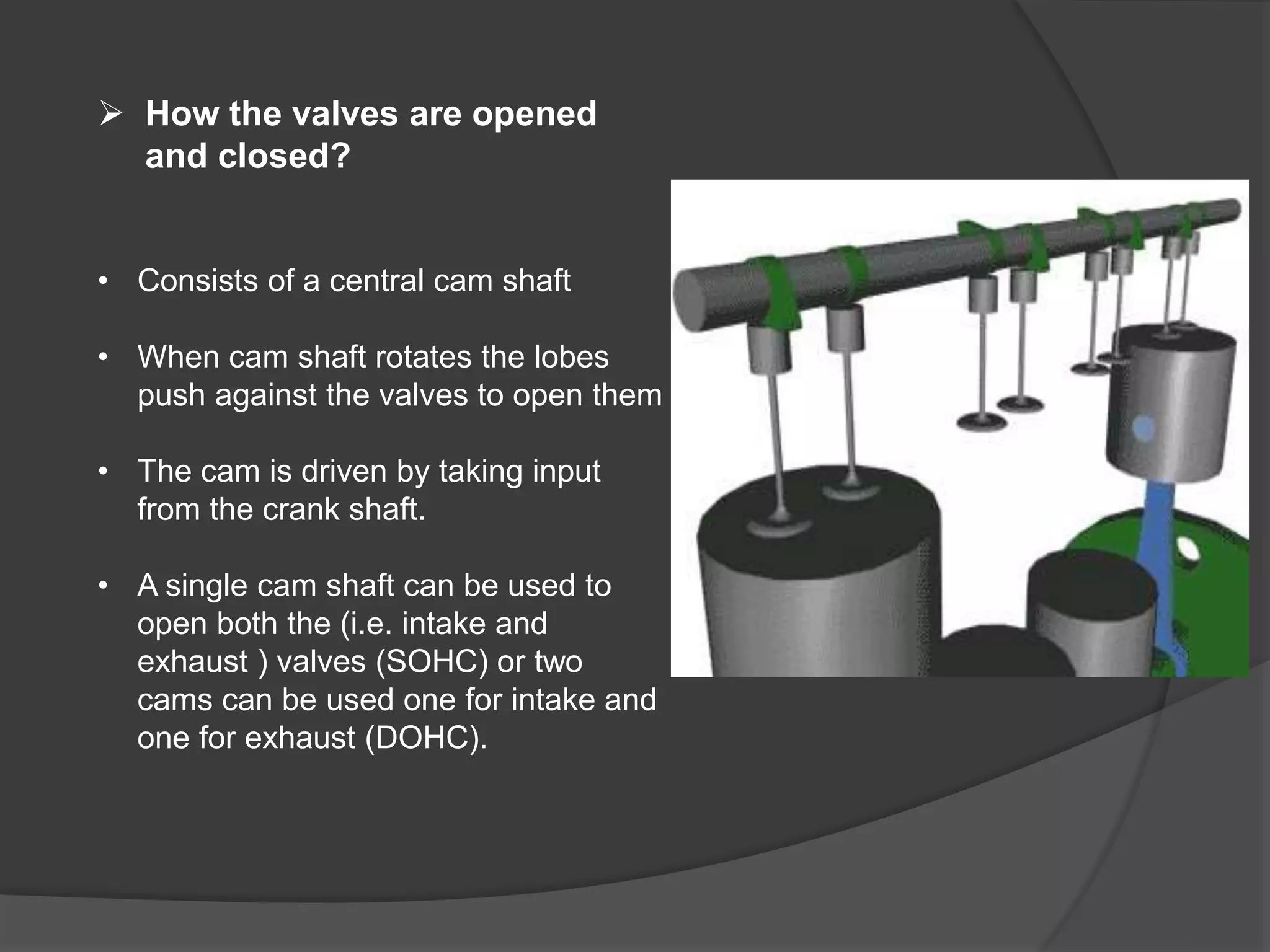
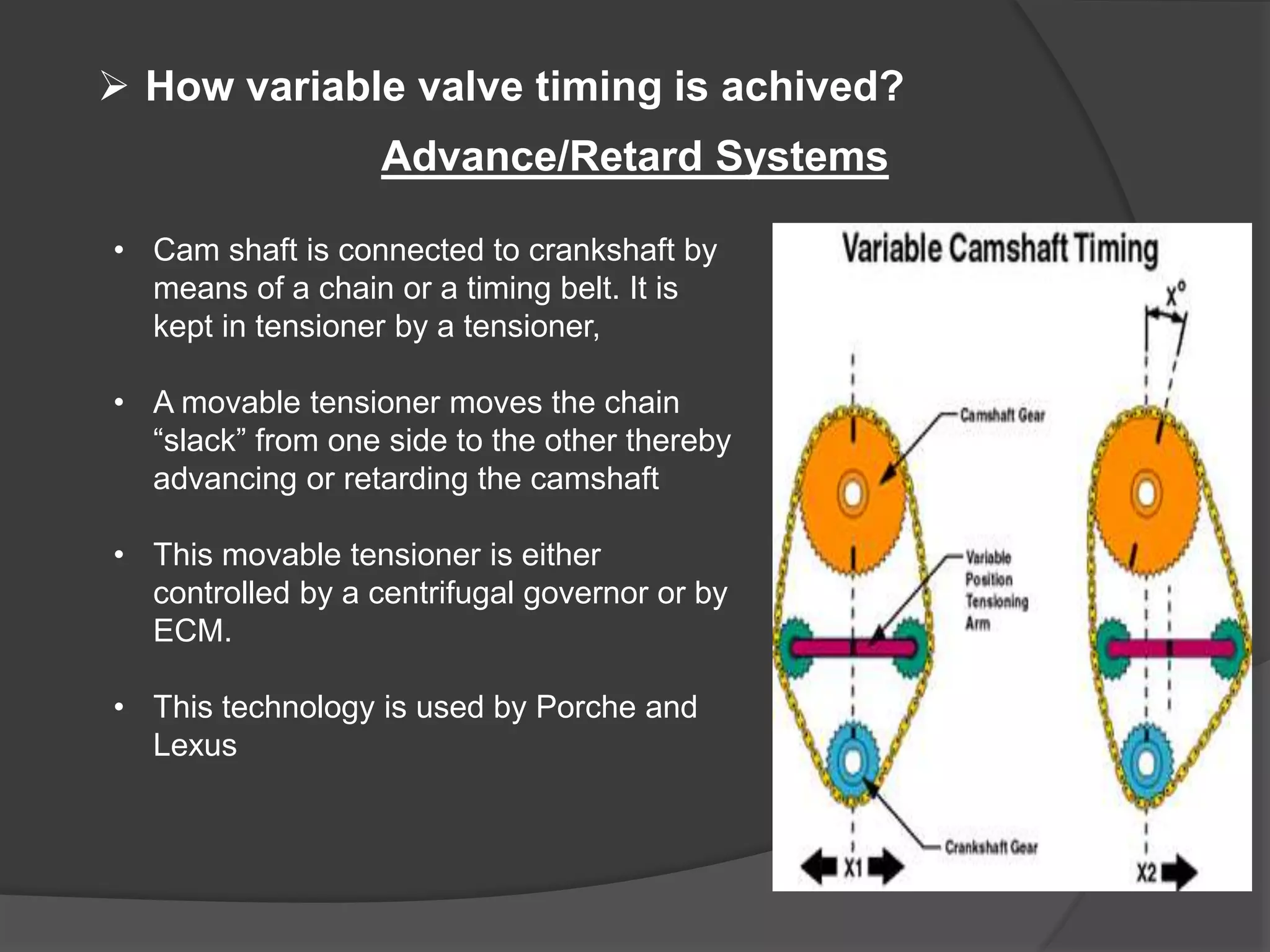
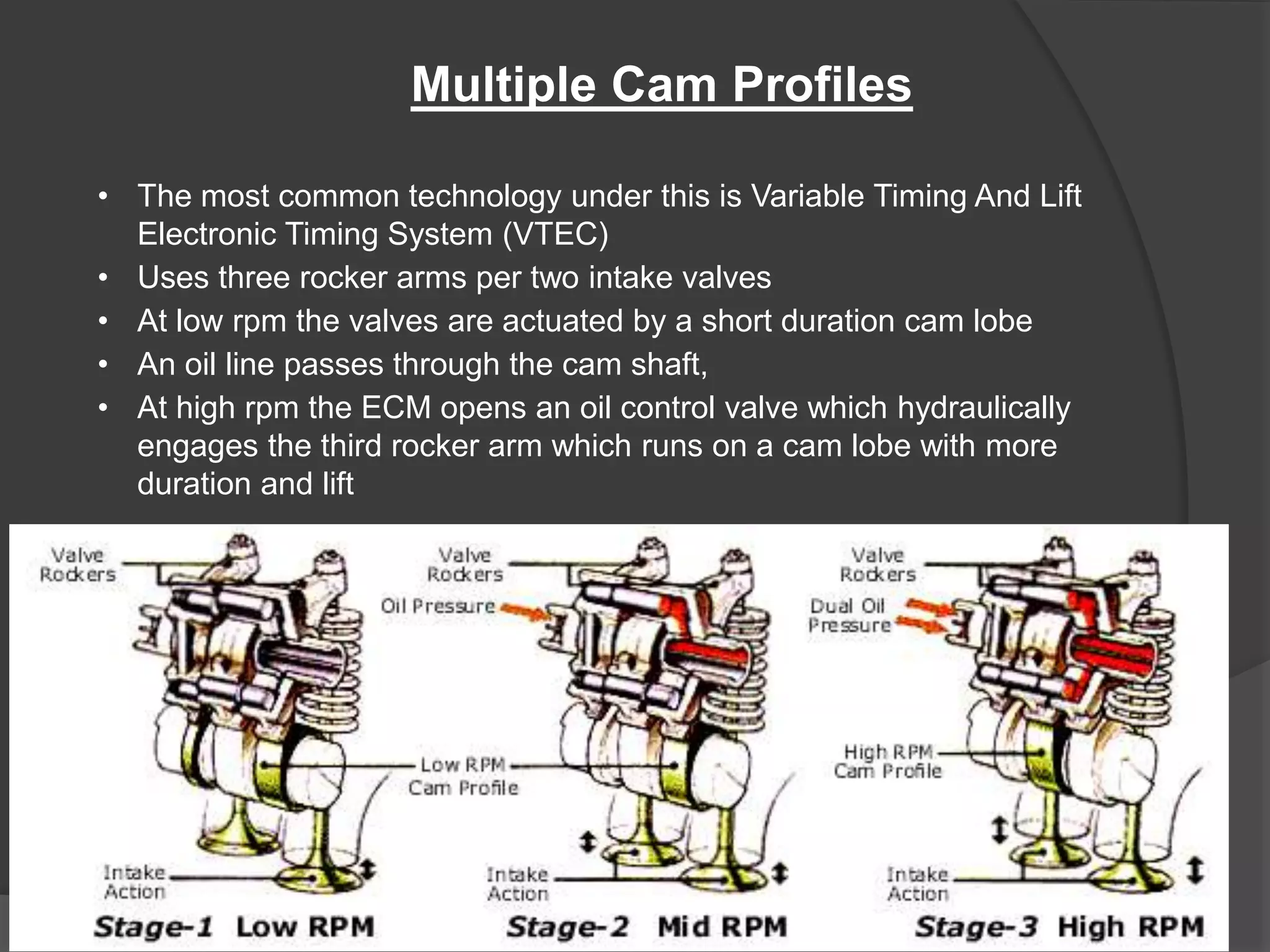
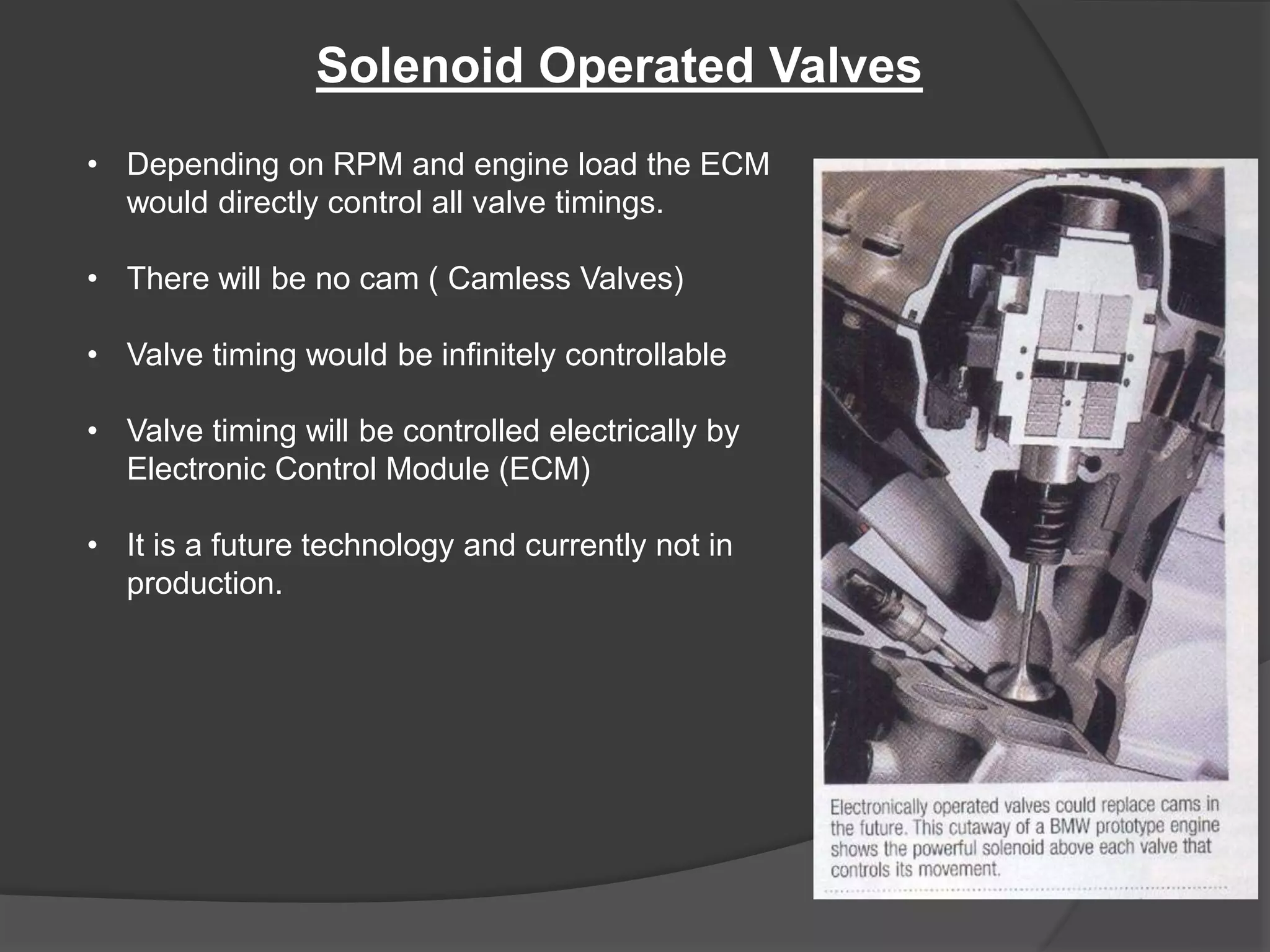
Variable valve timing allows the valve opening and closing points to be adjusted based on engine speed and load conditions. This improves engine performance and fuel economy over a fixed valve timing system. Variable valve timing is achieved through advance/retard systems that adjust the cam shaft timing using a movable tensioner controlled by the engine control module. Another method uses multiple cam profiles activated by oil pressure to vary the valve lift and duration. Variable valve timing provides benefits like better fuel efficiency, torque, and emissions but at a higher cost and complexity over a standard cam shaft setup.