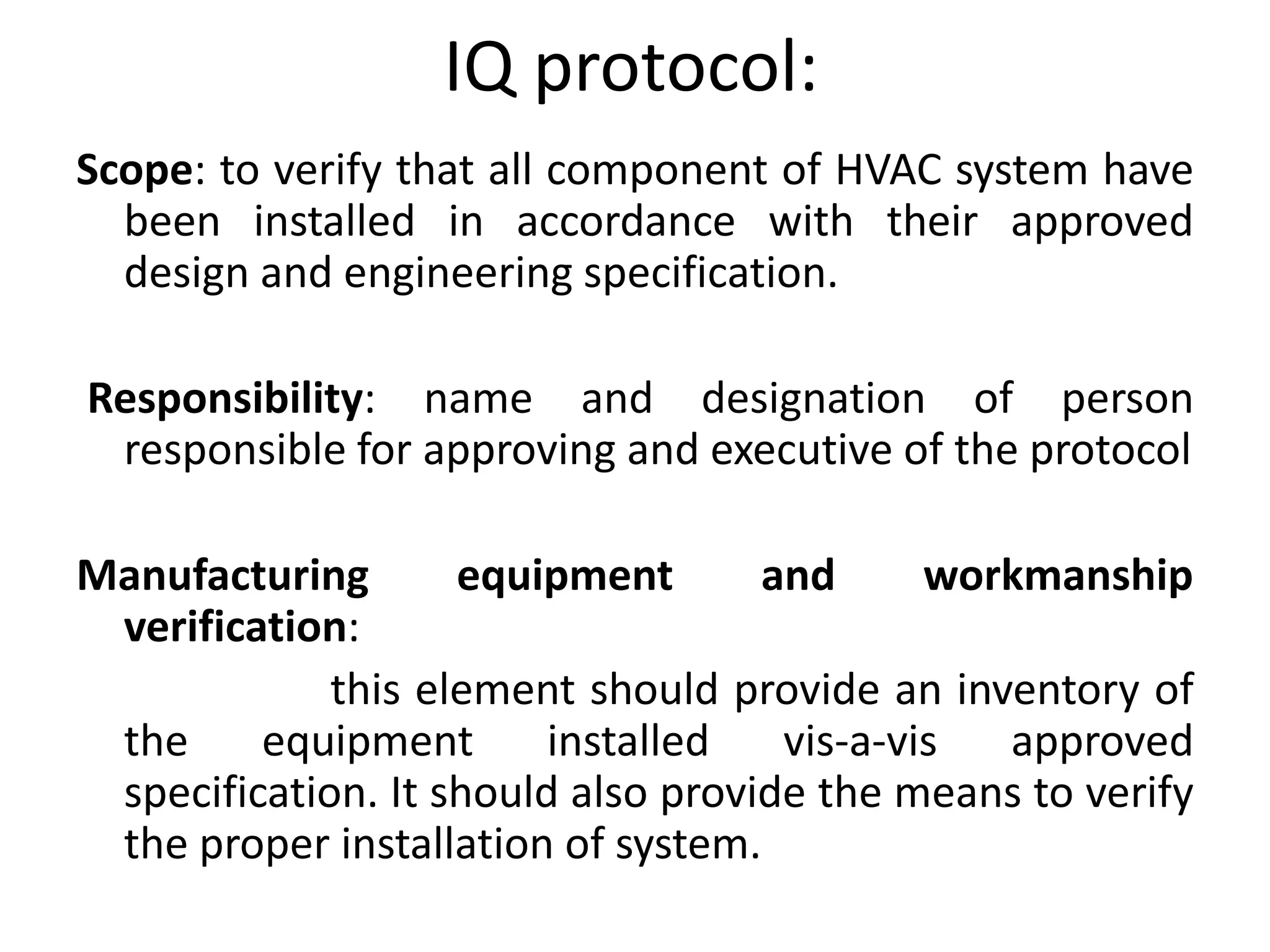
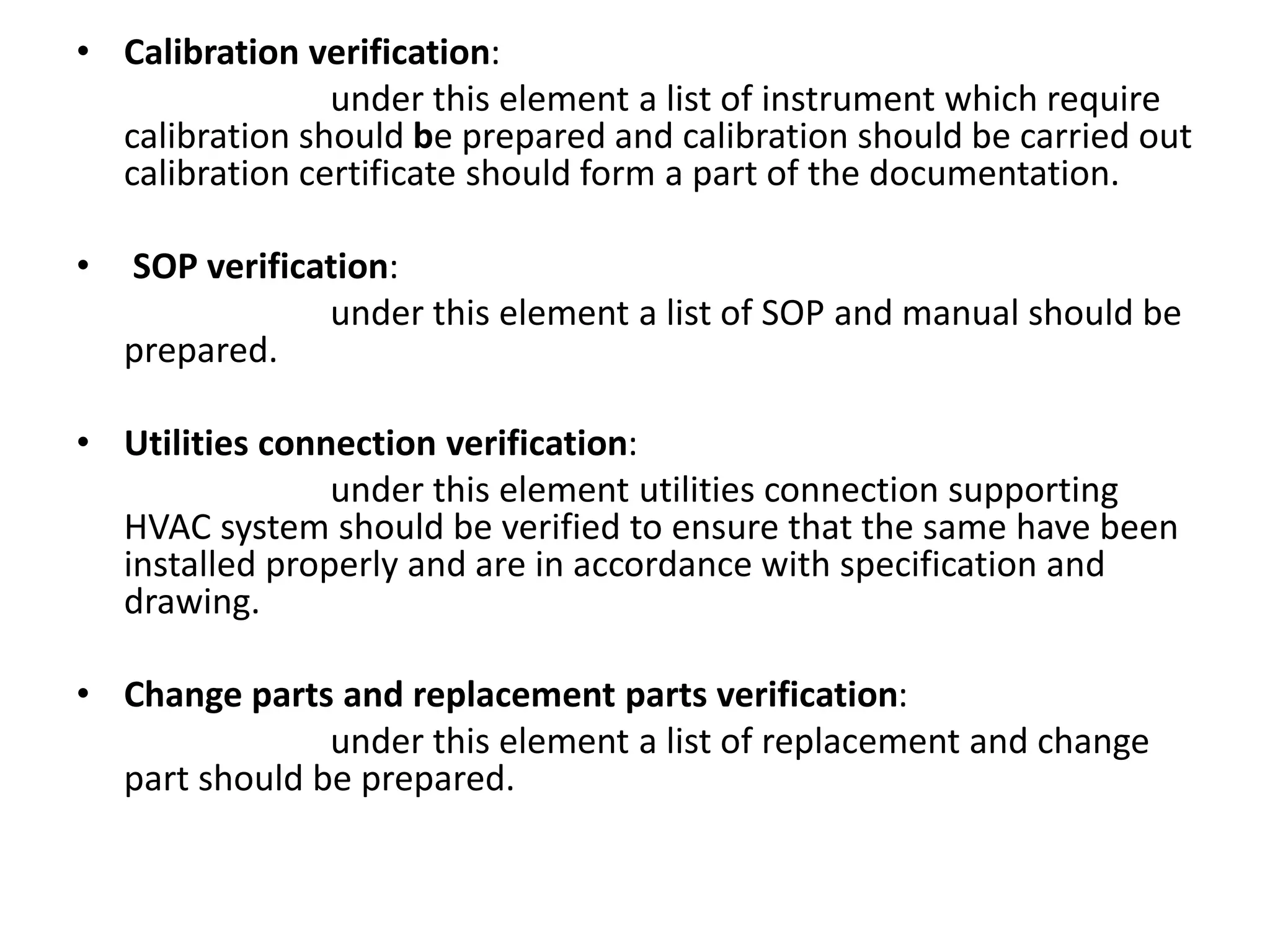
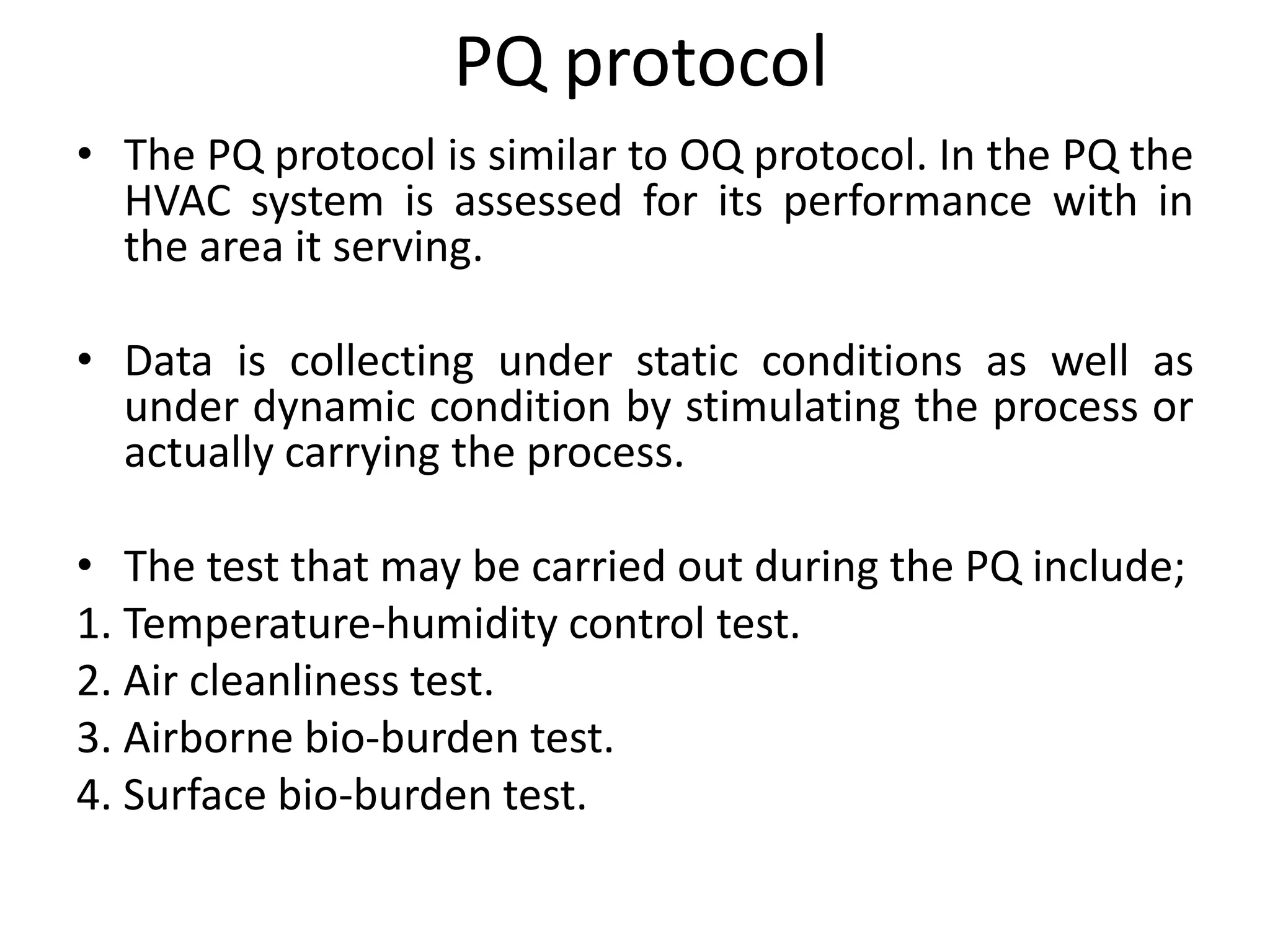
The document discusses validation of critical utility systems used in pharmaceutical manufacturing facilities. It focuses on validation of HVAC, water, and steam systems. For HVAC validation, it provides details on DQ, IQ, OQ, and PQ protocols including objectives, responsibilities, tests performed. It discusses user requirements, specifications for HVAC control and monitoring. For water system validation, it discusses purification methods, grade of water, and protocols for IQ, OQ and PQ. It also discusses two types of steam systems - house steam and clean steam - and validation considerations for each.