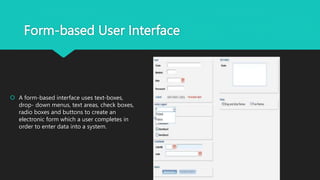
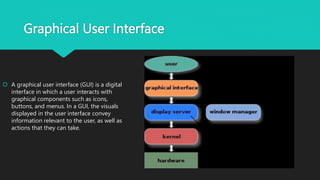
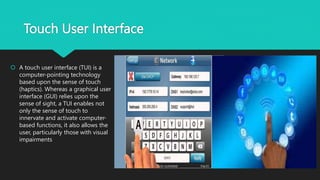
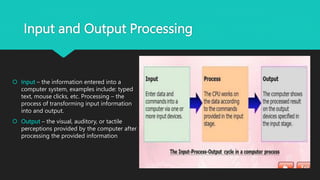
The user interface is the point of interaction between users and technology like computers, websites, and applications. The goal is to make the experience intuitive with minimal effort. User interfaces use various input methods like keyboards, mice, and touchscreens along with output displays like monitors and speakers. Common interface types include form-based, graphical, menu-driven, touch-based, and voice-controlled interfaces. Form-based interfaces use fields to enter data while graphical interfaces rely on visual elements. Menu interfaces provide navigational options and touch interfaces are controlled by touch. Voice interfaces accept spoken commands. Effective user interfaces balance input and output processing to transform user inputs into clear outputs.