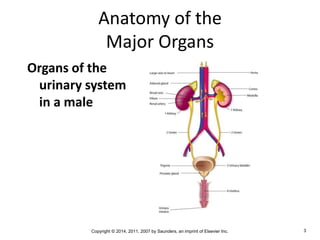
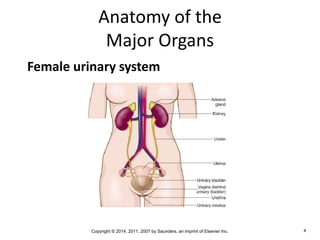
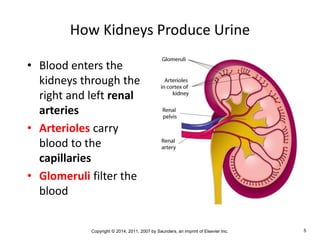
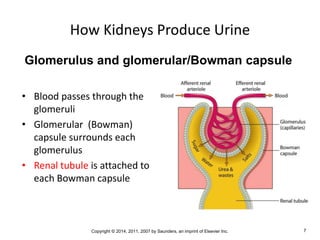
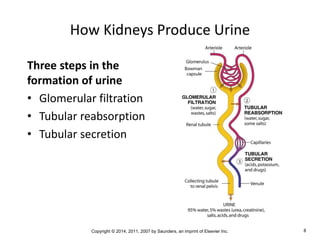
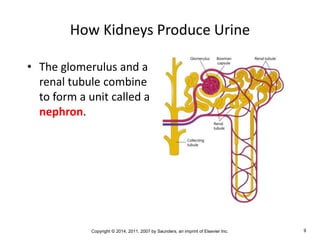
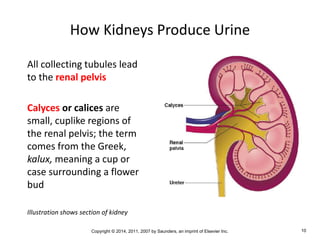
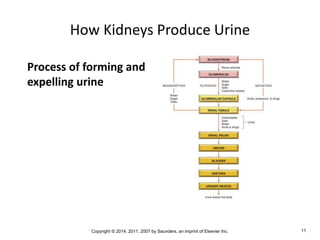
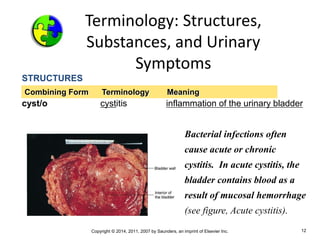
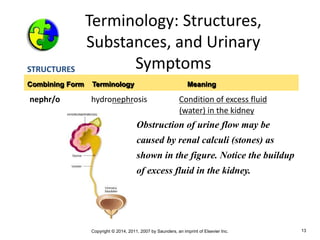
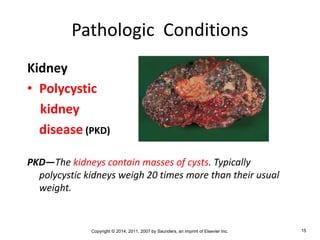
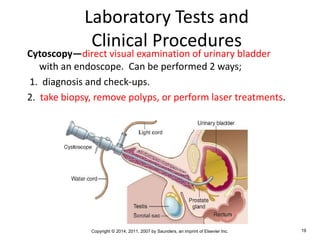
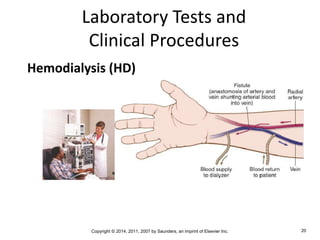
The document is a chapter about the urinary system from a medical textbook. It discusses the goals of understanding the anatomy and functions of the urinary system, identifying pathological conditions, and interpreting urinalysis tests. It describes the locations and roles of the kidneys and other urinary organs. It also explains how the kidneys filter blood to produce urine and outlines some clinical procedures related to the urinary system like dialysis and kidney biopsies.