This document provides an overview of quality management concepts and techniques for software engineering. It discusses quality assurance, software reviews, formal technical reviews, statistical quality assurance, software reliability, and the ISO 9000 quality standards. The document includes slides on these topics with definitions, descriptions, and examples.


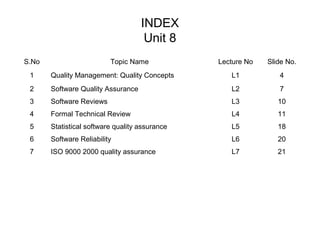
















![Software Reliability
• Defined as the probability of failure free operation of a
• computer program in a specified environment for a specified
• time period
• Can be measured directly and estimated using historical and
• developmental data
• Software reliability problems can usually be traced back to
• errors in design or implementation.
• Measures of Reliability
• Mean time between failure (MTBF) = MTTF + MTTR
• MTTF = mean time to failure
• MTTR = mean time to repair
• Availability = [MTTF / (MTTF + MTTR)] x 100%
20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit8-130409095158-phpapp02/85/Unit-8-20-320.jpg)
