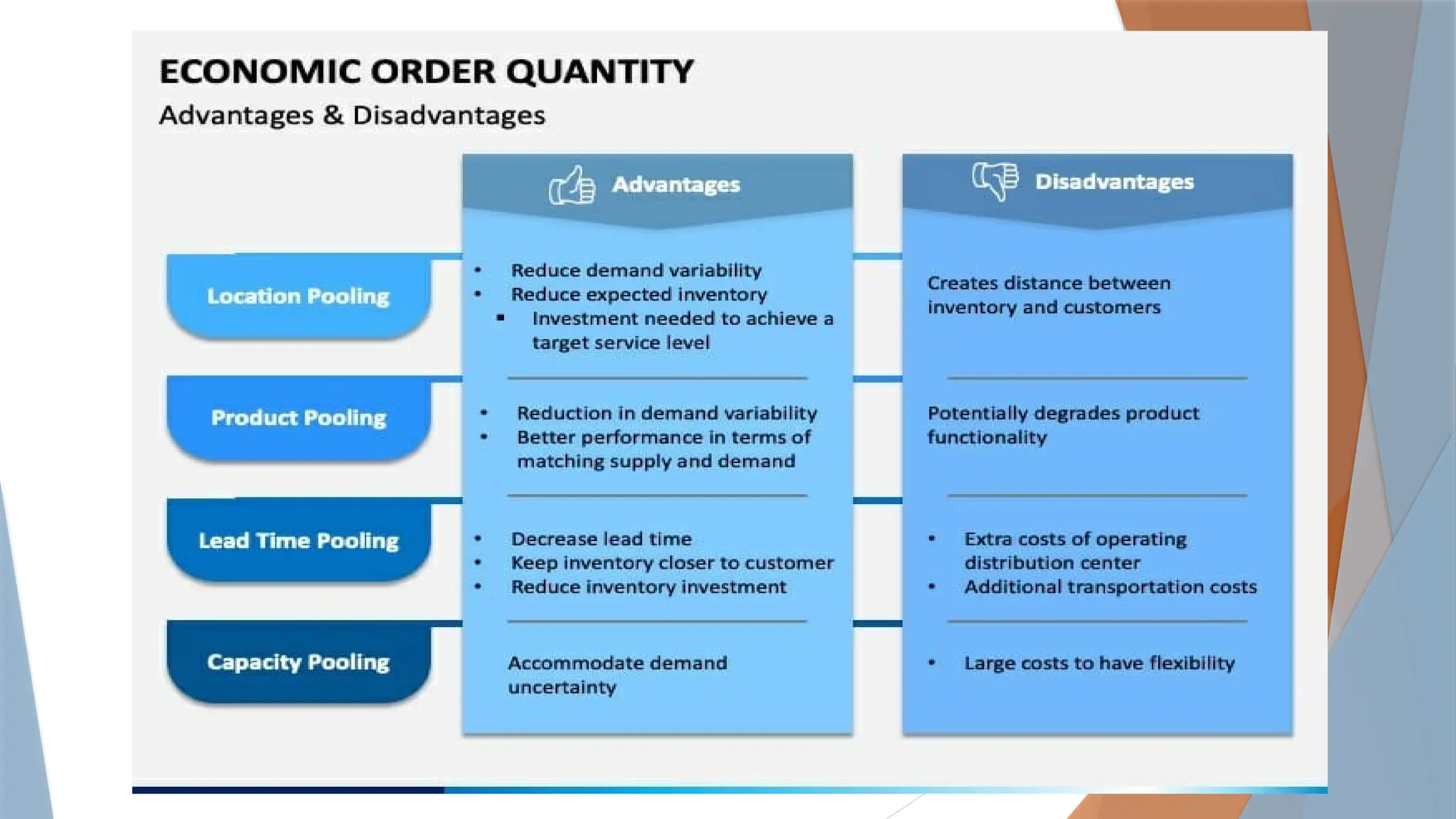
Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) is a crucial inventory management tool designed to determine the optimal order size that minimizes total inventory costs, including ordering, holding, and shortage costs. It aids businesses in making informed decisions about inventory levels and order timings, thus preventing overstocking and understocking while ensuring sufficient stock availability. The EOQ formula balances ordering and holding costs, providing insights into order frequency and cash flow management.