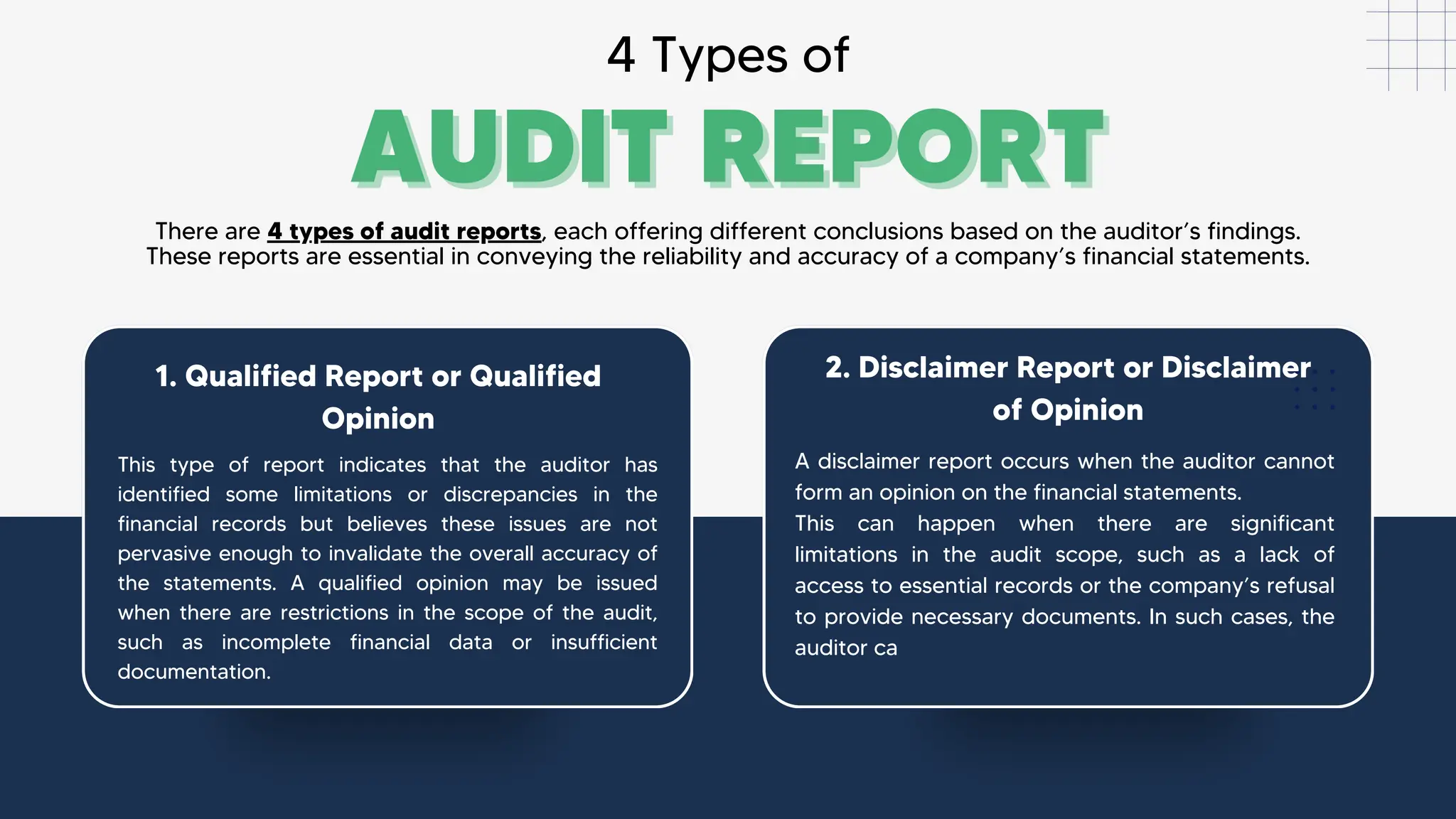
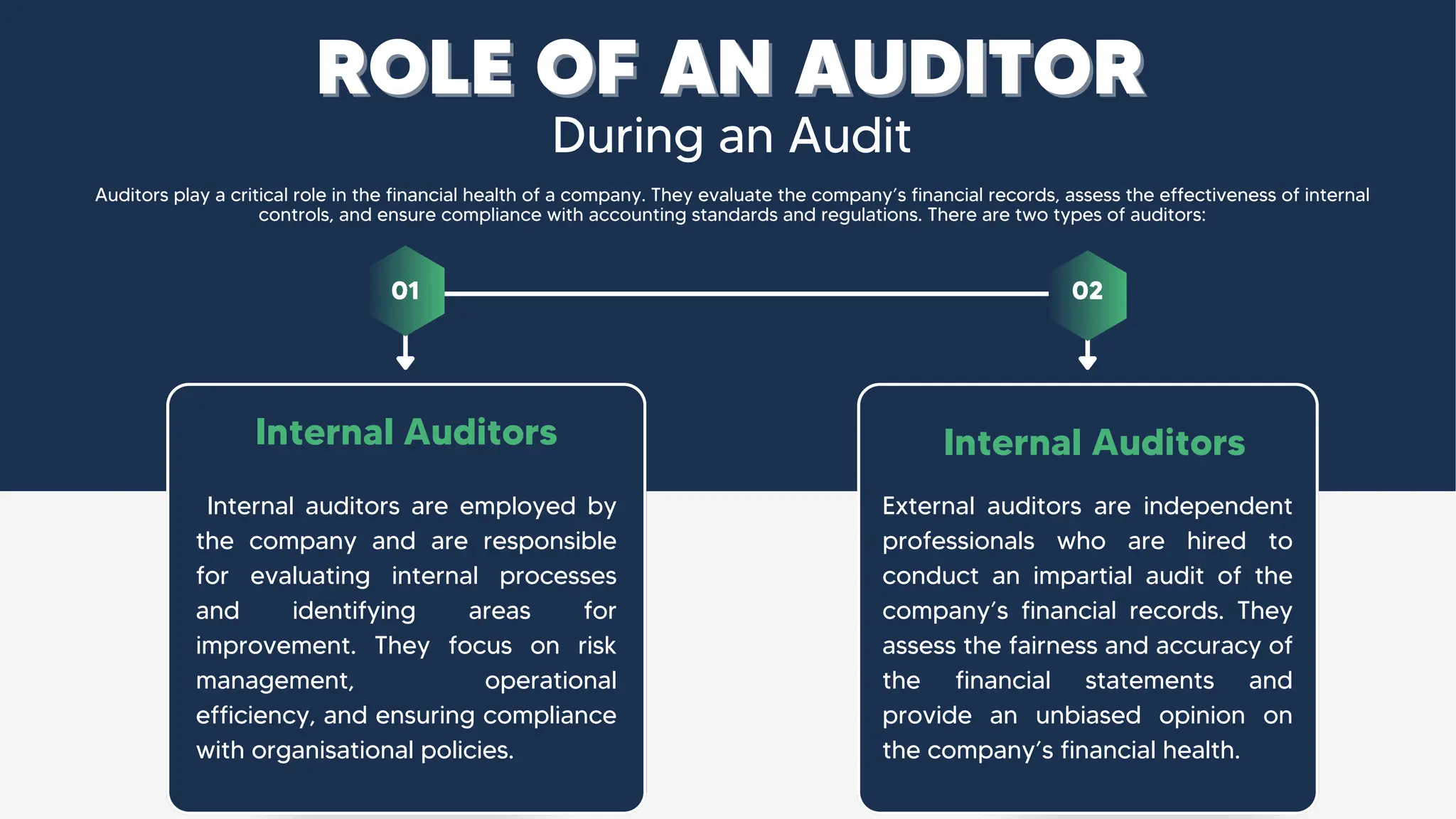
The document provides an overview of audit reports, discussing their importance in financial transparency, accuracy, and accountability. It outlines the four types of audit reports—qualified, disclaimer, adverse, and unqualified—along with their implications and best practices for reporting. Understanding these types is crucial for stakeholders to assess a company's financial health and make informed decisions.