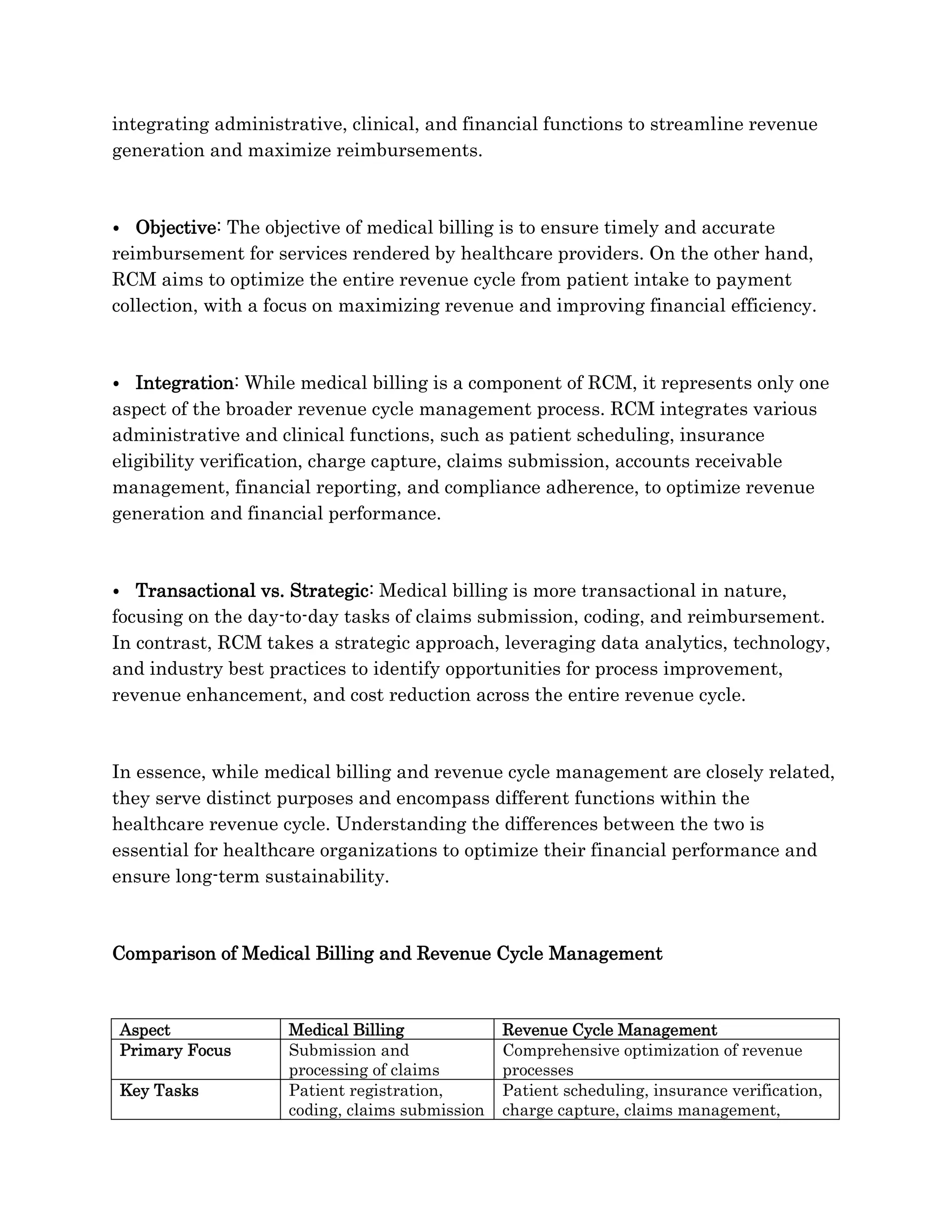
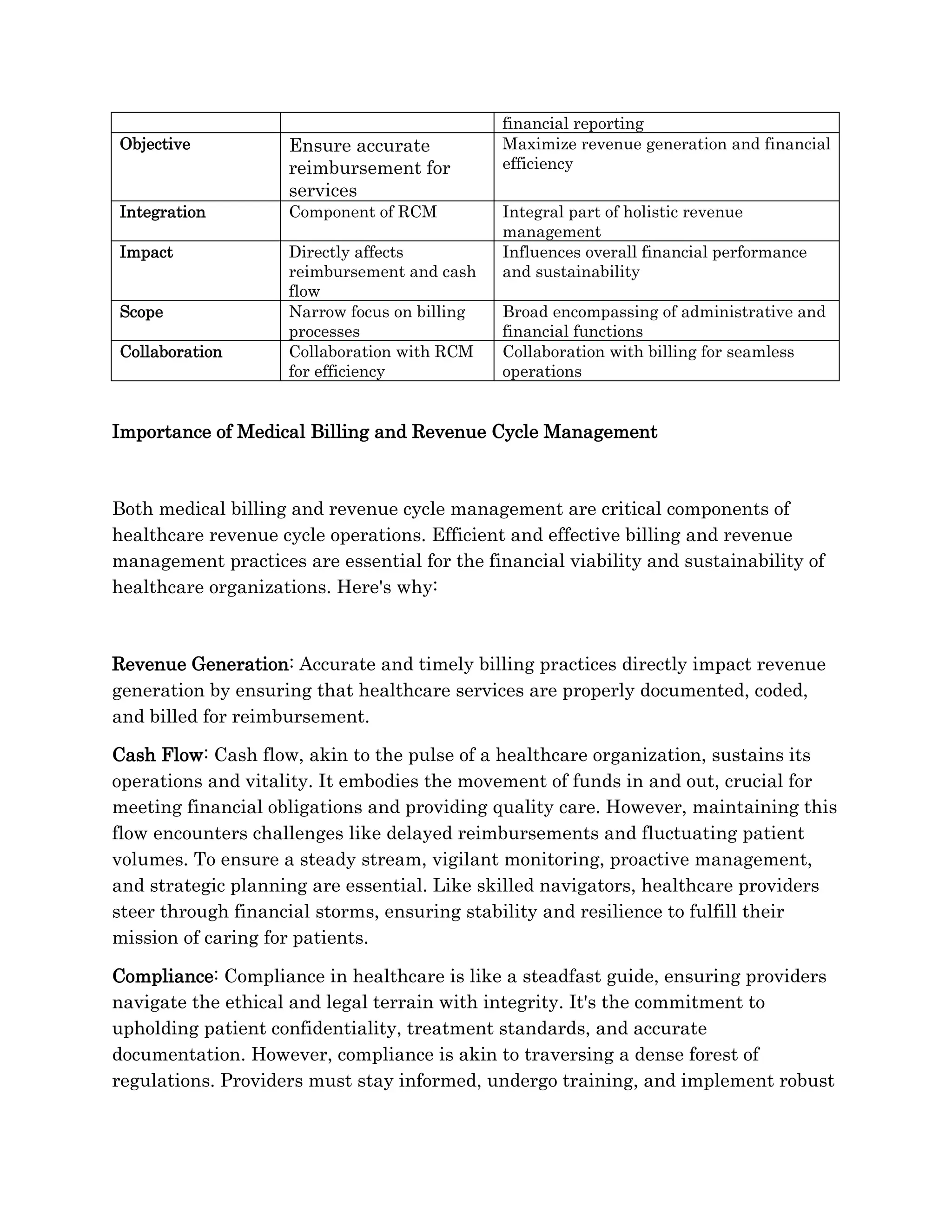
Medical billing and revenue cycle management (RCM) are vital yet distinct elements within healthcare finance, with medical billing focused on claims processing while RCM encompasses broader financial optimization functions. Each process plays a critical role in ensuring accurate reimbursements and enhancing revenue generation, highlighting their interdependent relationships. Understanding their differences is essential for healthcare organizations to improve financial performance and sustainability.