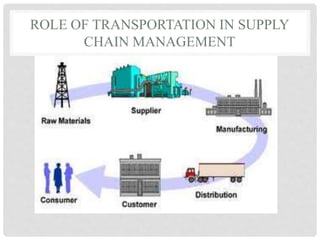
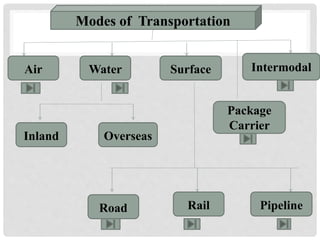
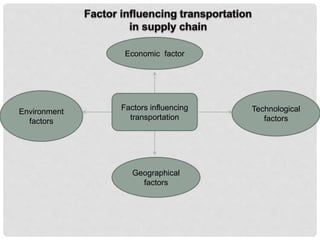
Transportation involves moving products from their point of origin to customers. It plays an important role in supply chain management since products are rarely produced and consumed in the same location. There are various modes of transportation including air, water, surface, and intermodal. The most common modes are truck, rail, air, water, and package carriers which use a combination of these modes. The optimal transportation method depends on factors like cost, delivery time requirements, product characteristics, and distance.