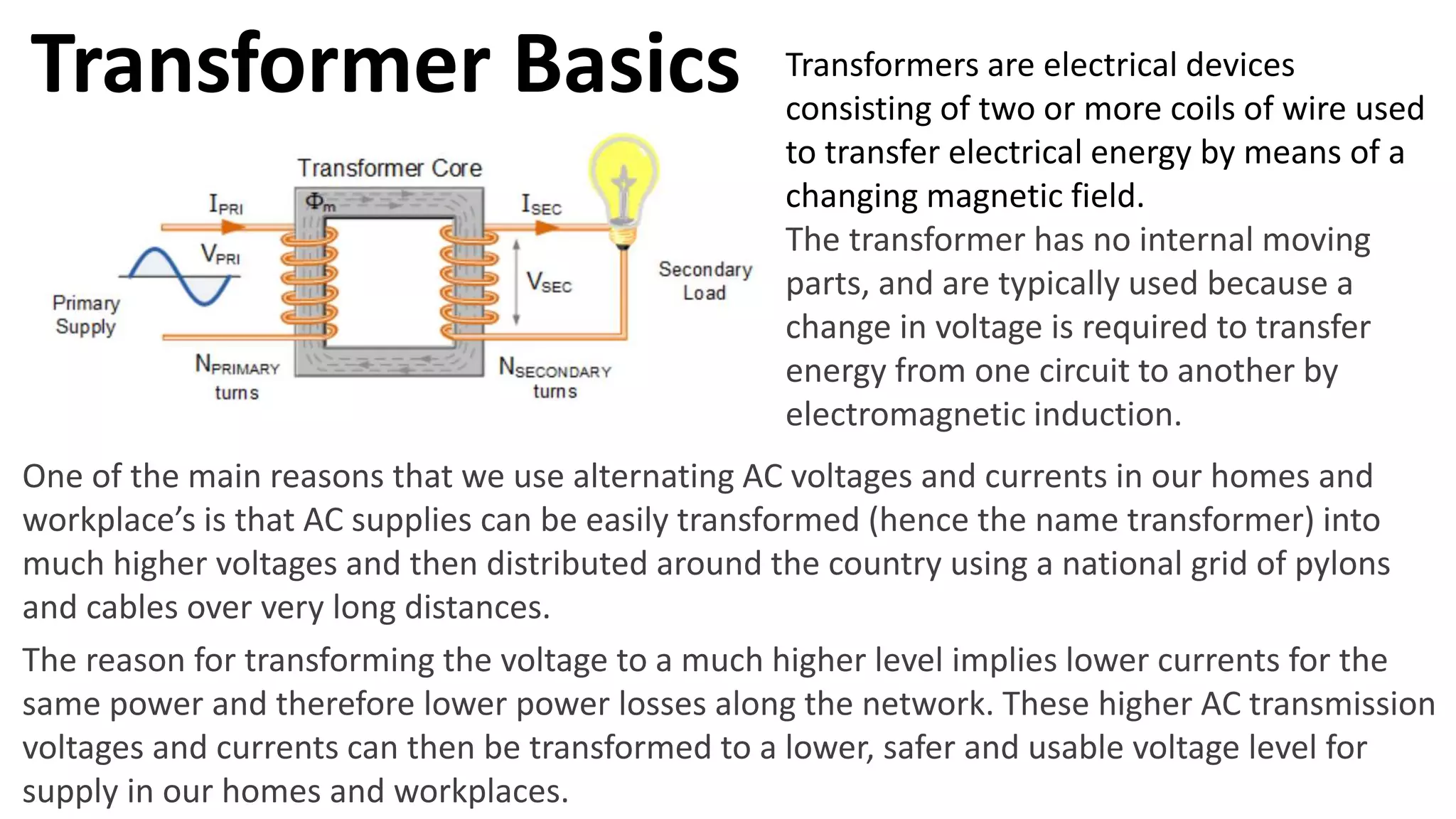
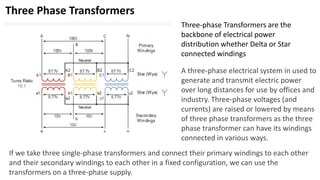
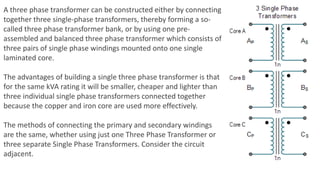
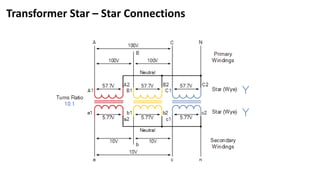
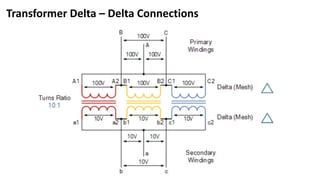
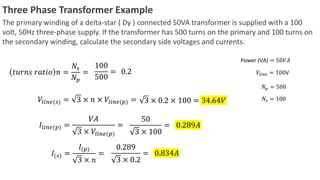
Transformers are electrical devices that transfer energy between circuits via changing magnetic fields without moving parts. They work by mutual induction between two coils: the primary winding receives energy which is then induced into the secondary winding. Transformers can increase or decrease voltage and current levels while maintaining frequency and power. Three-phase transformers have primary and secondary windings that can be connected in star or delta configurations to meet different voltage and current requirements.