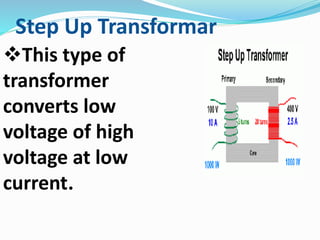
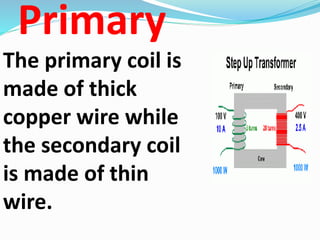
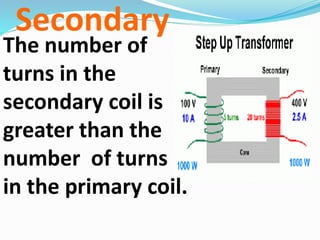
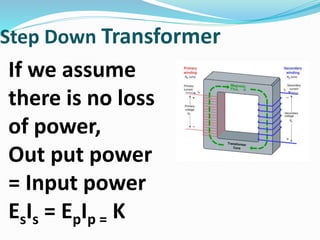
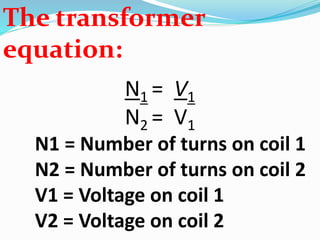
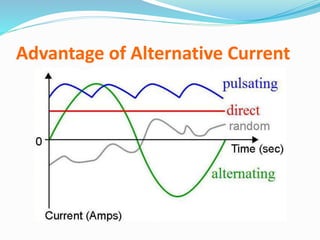
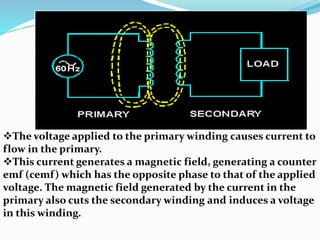
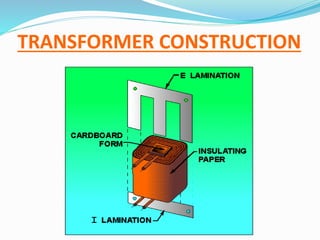
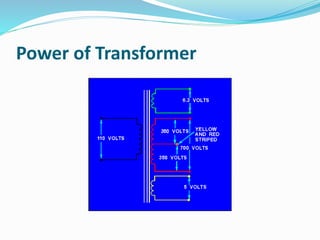
A transformer transfers electrical energy between two circuits through electromagnetic induction. It works by using a primary coil to produce a varying magnetic field that induces a voltage in a secondary coil. This allows transformers to increase or decrease voltage levels in an electrical circuit. The number of turns in each coil and the ratio of their turns determines the relationship between the voltages in the primary and secondary circuits. Transformers are commonly used to increase voltage for power transmission over long distances and decrease voltage for safe use in electronic devices.