This document describes six geometric transformations: reflection, rotation, translation, enlargement, stretch, and shear. For each transformation it provides:
1) A definition of the transformation and how to describe it mathematically.
2) How to draw the image resulting from the transformation given the original figure.
3) How to determine key aspects of the transformation such as the line of reflection, center of rotation, scale factor, or invariant line.
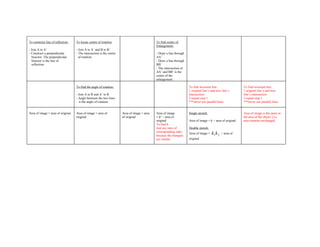
![Reflection Rotation Translation Enlargement Stretch Shear
To describe, state: To describe, state: To describe, state: To describe, state: To describe, state: To describe, state:
Equation of line of reflection Angle Column vector Centre Invariant line Invariant line
Direction Scale factor Scale factor Scale factor
Centre
- - -
Scale factor Scale factor Scale factor
= distance of A’E = distance of A’ from invariant line = distance of AA’
distance of AE distance of A from the invariant line distance of A from invariant
= Length of A’B’ *Stretch image is perpendicular to * Sheared image moves
invariant line parallel to the invariant line
Length of AB
To draw image: To draw image: To draw image: To draw image: To draw image: To draw image:
- Drop a perpendicular from A - Join A to centre of rotation - move each points x - Join A to E and * Given stretch factor and invariant 1. Extend 2 pairs of
to [R]. units along the x axis extend the line. line corresponding sides.
the line of reflection. [Draw a - Measure angle of rotation in and y units along the y - Mark A’ such that -Join A to invariant line 2. Mark the intersection
produce] specified direction of RA axis according to the EA’ = k EA (perpendicular) points.
- Mark A’ on the produce where - Use a compass to mark A’ - Repeat for the other Therefore, stretch image will be 3. The line passes through the
x
column vector,
y .
distance of A to the produce = where RA = RA’ points perpendicular to the invariant two points is the invariant
distance of A’ to the produce. - Repeat for other points. - join all points to i.e. LA’=kLA line.
- Join the points to complete form image. Note: If k<0 (neg), then image lies on **Note: Pick the sides that are
the image. Note: opposite sides of invariant line not parallel. A shear is a non-
Note: isometric transformation that
x > 0 – move points to preserves the area of the
the right k>1 figure
x < 0 – move points to - increase in size
the left - image and original
y > 0 – move points lie on the same side
up
y < 0 – move points 0<k<1
down – decrease in size
- image and original
lie on opposite sides](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/transformationnotes-edited1-120326022944-phpapp02/75/Transformationnotes-edited-1-1-2048.jpg)