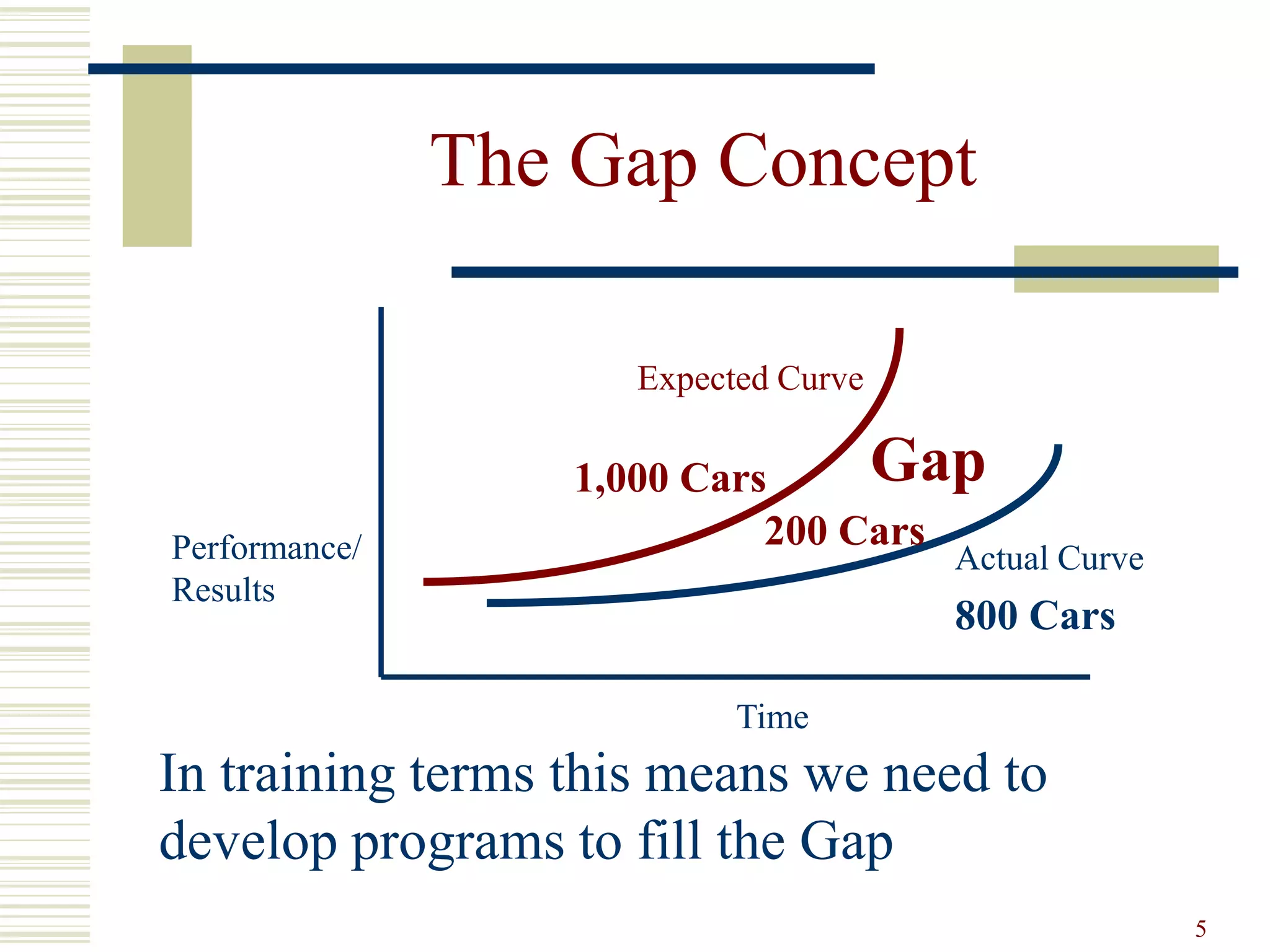
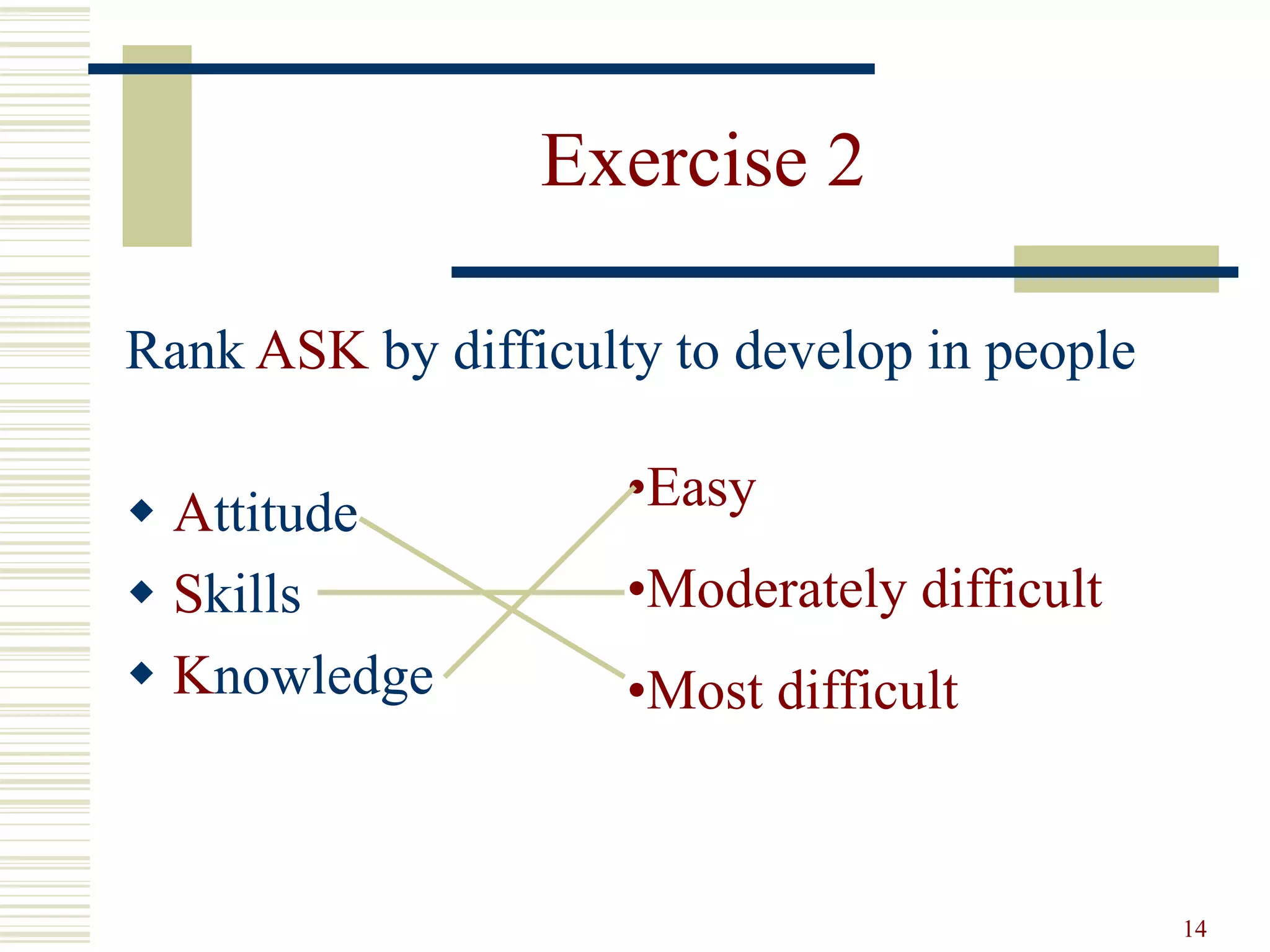
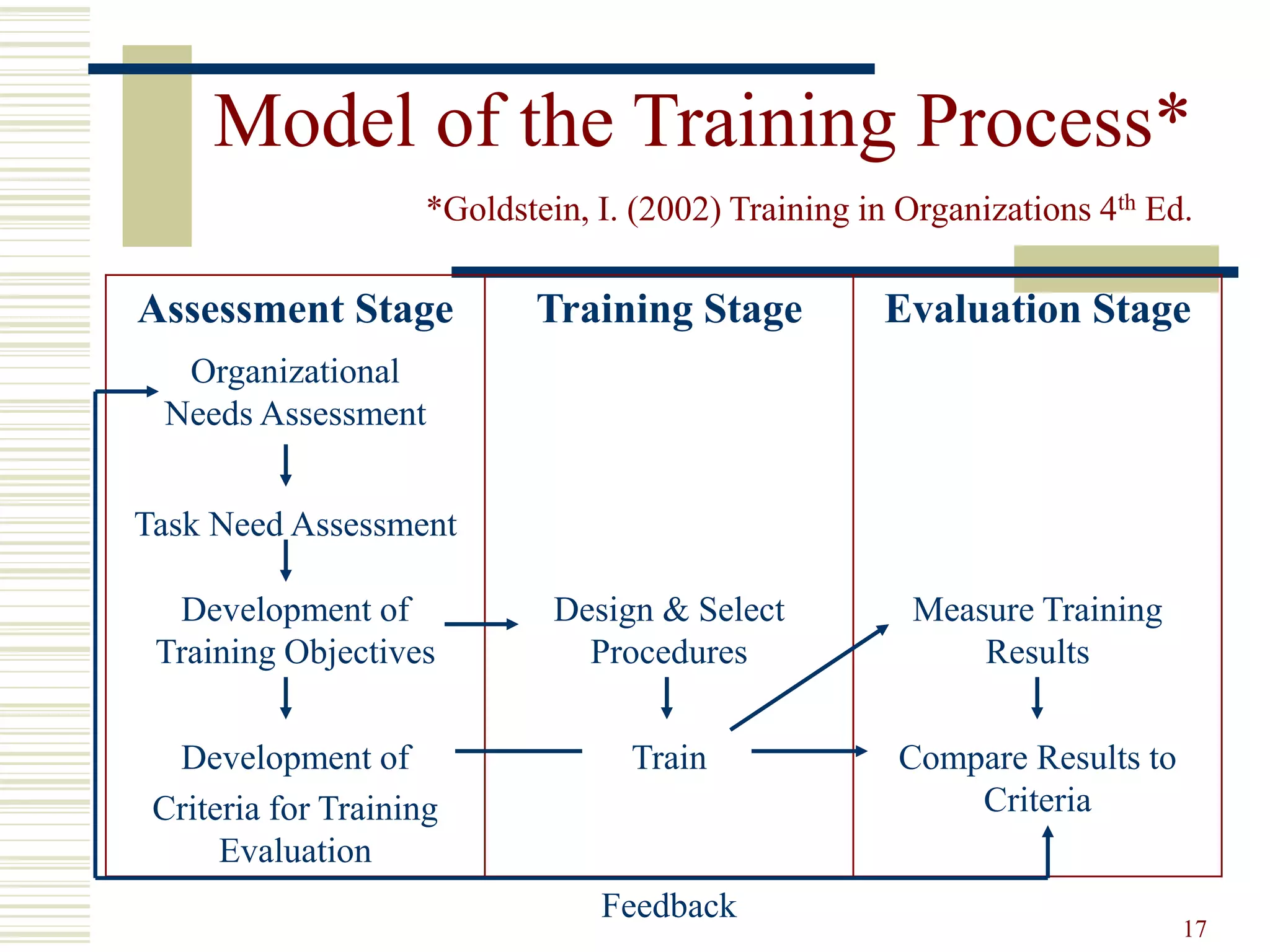
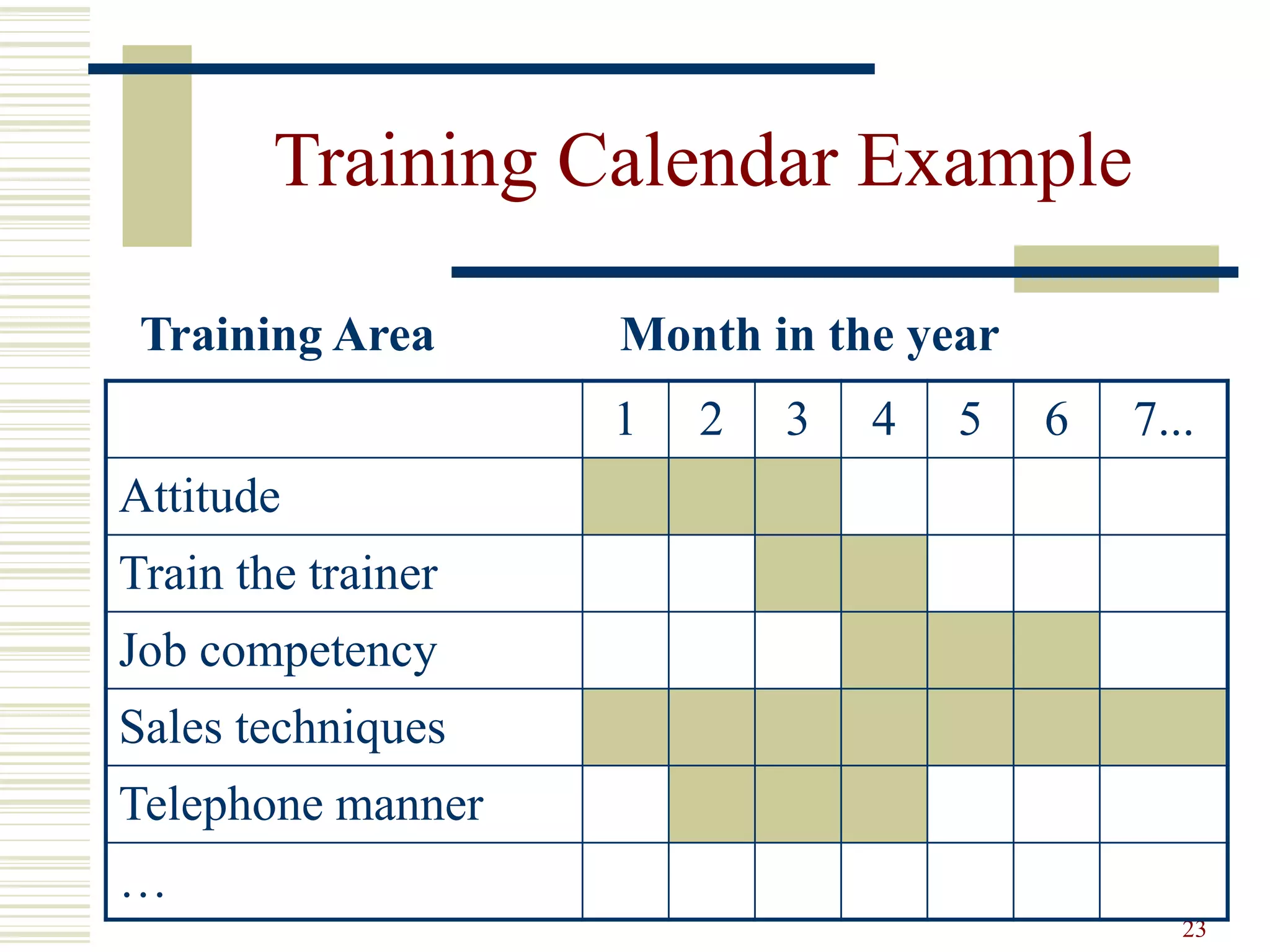
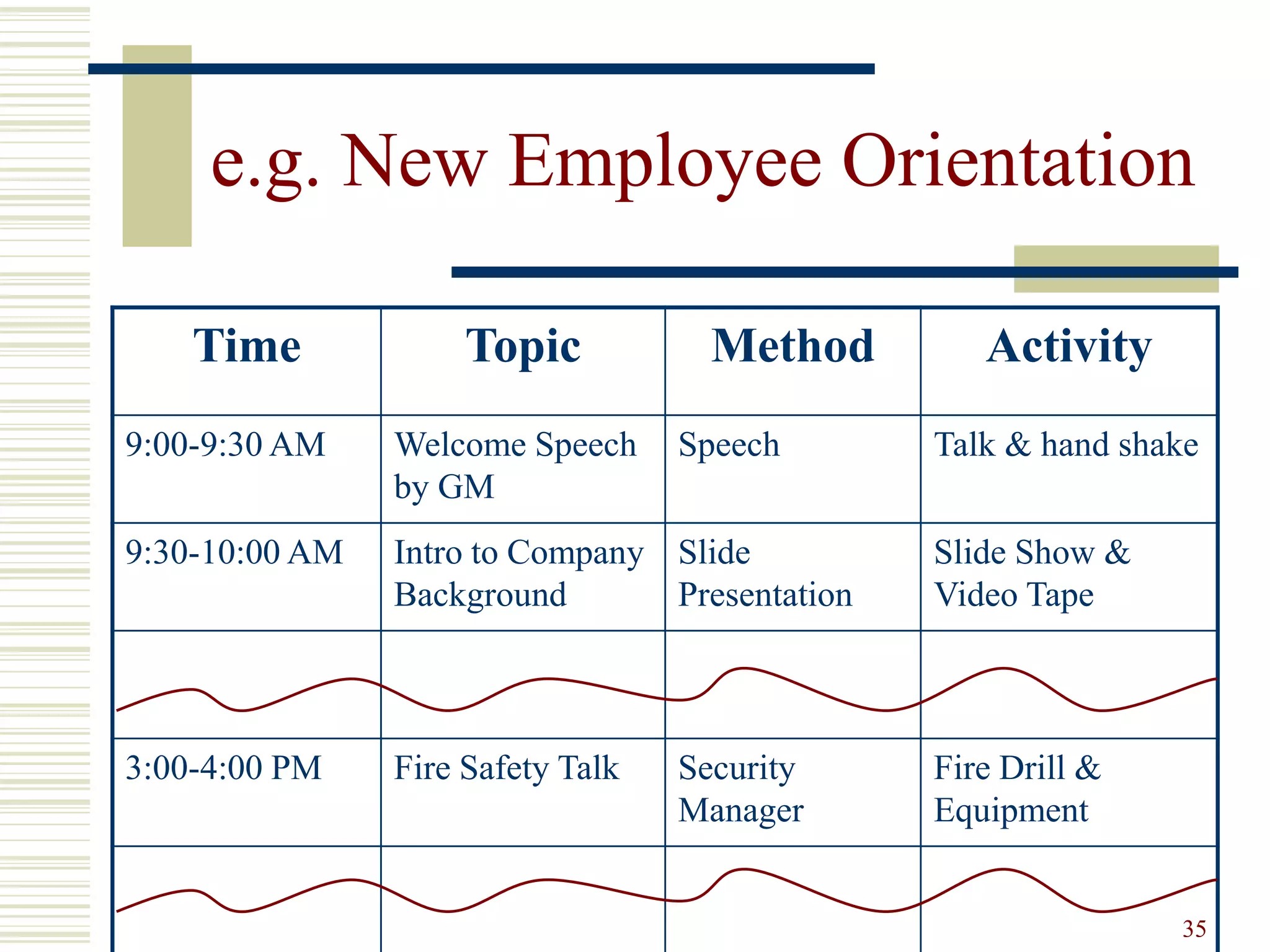
This document provides an overview of training and development principles for staff. It discusses why training is important, defines key concepts like the ASK model of addressing attitudes, skills and knowledge, and outlines a nine step process for developing and implementing training programs. Examples are provided for each step, including assessing needs, creating objectives and lesson plans, and evaluating impact. A variety of training methods are also described. The overall document serves as a guide for human resources professionals to systematically plan and deliver effective training that improves organizational performance.