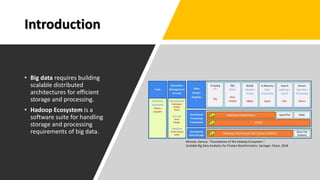
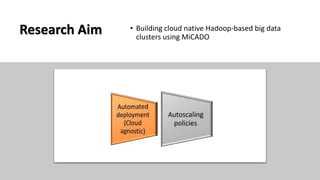
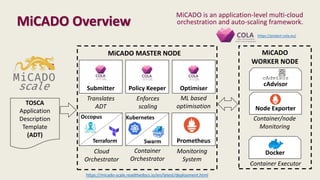
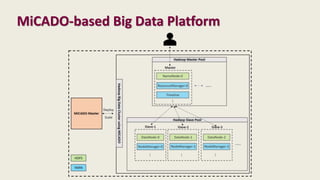
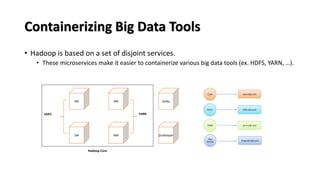
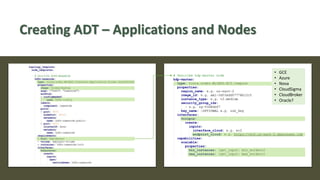
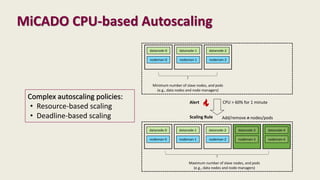
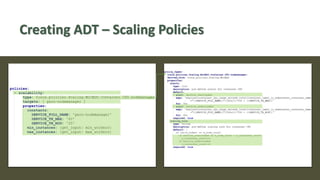
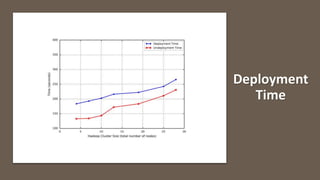
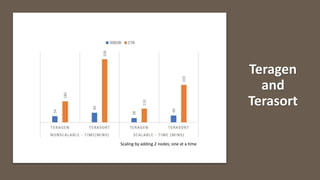
The document discusses the development of a cloud-native big data platform using Micado, aiming to address the challenges of deploying Hadoop clusters by automating and containerizing big data tools. It highlights the importance of separating compute and storage for better resource utilization and provides a detailed overview of the Micado framework, including its deployment and autoscaling capabilities. The conclusion emphasizes Micado's role in creating a scalable and portable deployment solution for big data applications, responding to organizational demands for improved cost, security, and control.