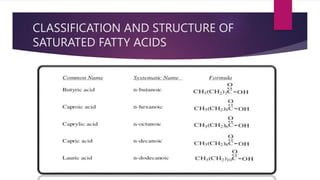
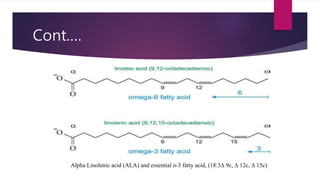
1) The document discusses fatty acid nomenclature, noting that names reflect double bond location and common names are used.
2) It provides examples to illustrate nomenclature conventions like "linoleic" meaning an 18 carbon chain with 2 double bonds on the 6th carbon.
3) The lecture covers classification and structures of saturated and unsaturated fatty acids, including examples like arachidonic and alpha-linolenic acids.