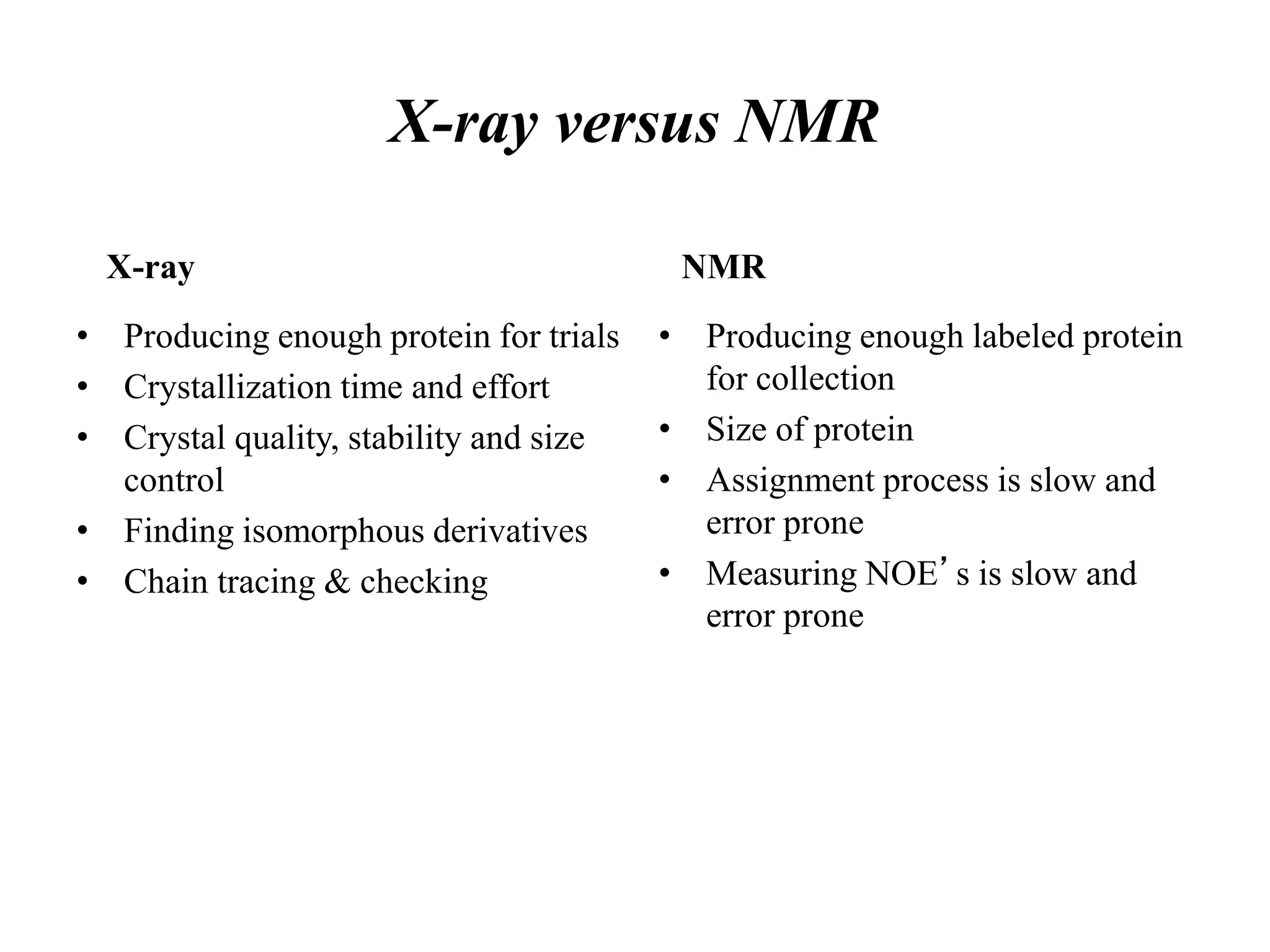
This document provides an overview of structural biology, including its focus on determining the molecular structures of biological macromolecules like proteins and nucleic acids. It discusses key developments in the field, such as Watson and Crick's discovery of DNA's structure, and the two main experimental approaches used today: X-ray crystallography and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. X-ray crystallography involves crystallizing a protein and analyzing its diffraction pattern to determine structure, while NMR studies protein structures in solution using magnetic fields. Both techniques have benefits and limitations related to the size of molecule that can be studied and experimental requirements.





![Tertiary protein structure: protein folding
Three main approaches:
[1] experimental determination
(X-ray crystallography, NMR)
[2] Comparative modeling (based on homology)
[3] Ab initio (de novo) prediction
(Dr. Ingo Ruczinski at JHSPH)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/topic1-overviewstructuralbiology-160523074001/75/Topic-1-overview-structural-biology-8-2048.jpg)
![Experimental approaches to protein structure
[1] X-ray crystallography
• Used to determine 80% of structures
• Requires high protein concentration
• Requires crystals
• Able to trace amino acid side chains
• Earliest structure solved was myoglobin
• Solubilization of the over-expressed protein
• Obtaining crystals that diffract
• Structure determination by diffraction of protein crystals
• Size of a molecule: no theoretical limit](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/topic1-overviewstructuralbiology-160523074001/75/Topic-1-overview-structural-biology-9-2048.jpg)
![[2] NMR
• Magnetic field applied to proteins in solution
• Largest structures: 350 amino acids (40 kD)
• Does not require crystallization
• Solubilization of the over-expressed protein
• Structure determination of a molecule as it exists in
solution
• Size-limit is a major factor](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/topic1-overviewstructuralbiology-160523074001/75/Topic-1-overview-structural-biology-10-2048.jpg)