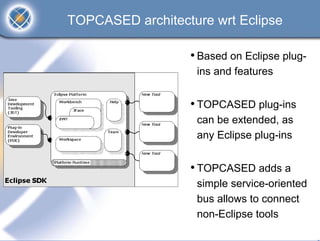
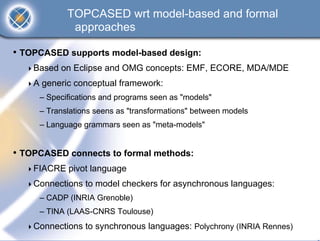
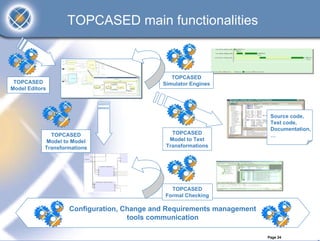
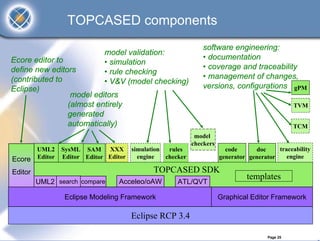
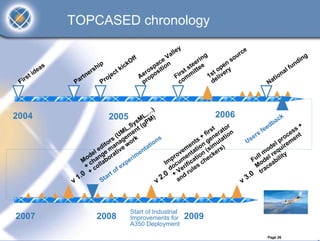
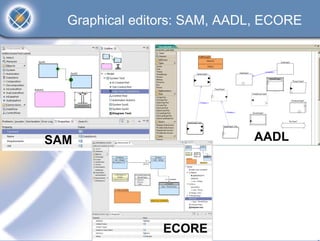
The TOPCASED project, led by Airbus and Inria, focuses on developing open-source tools for safety-critical embedded systems in various industries such as aerospace and automotive. It aims to create a long-term software platform that fosters a collaborative community, ensuring the availability and support of development tools, while addressing common issues faced by software editors. The initiative promotes an innovative approach to software development, integrating academic research and practical industrial needs, and has already reached significant milestones since its launch in 2004.