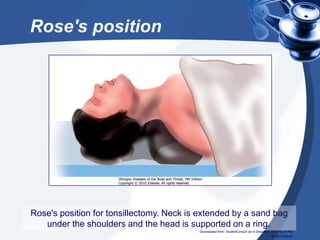
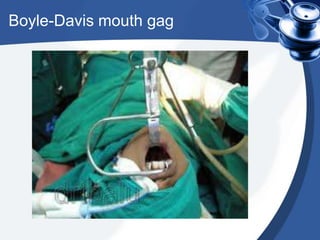
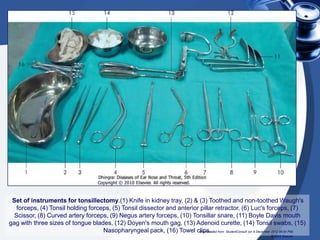
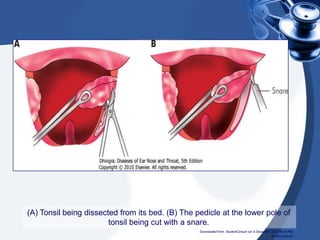
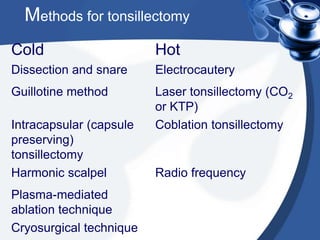
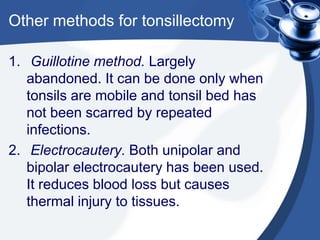
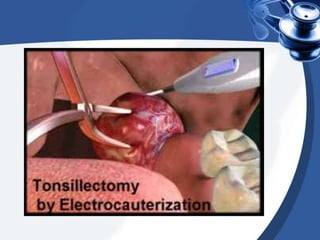
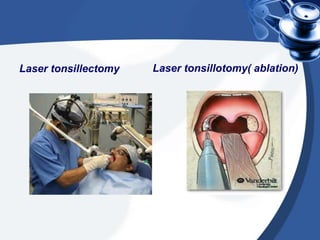
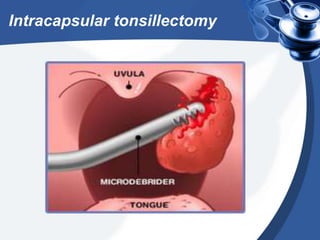
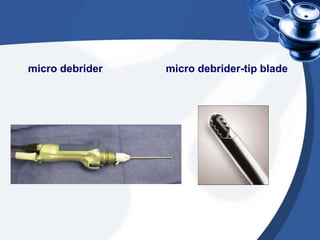
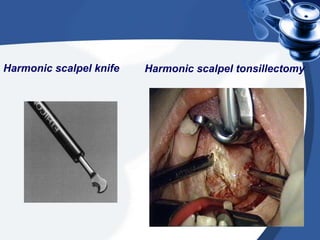
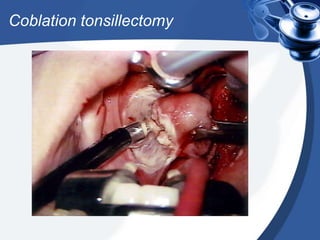
Tonsillectomy is commonly performed to treat recurrent throat infections. Absolute indications for tonsillectomy include recurrent infections, peritonsillar abscesses, tonsillitis causing seizures, tonsil hypertrophy causing obstruction, and suspicion of malignancy. Relative indications include being a carrier of diphtheria or streptococcus. The operation is usually done under general anesthesia with the patient in Rose's position. The tonsils are grasped, dissected from surrounding tissue, and removed using a wire snare. Post-operative care involves pain management, oral hygiene, diet progression, and antibiotics to prevent infection. Potential complications include bleeding, infection, and scarring.