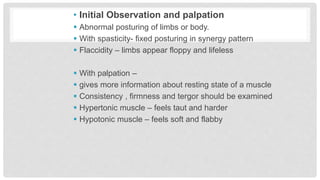
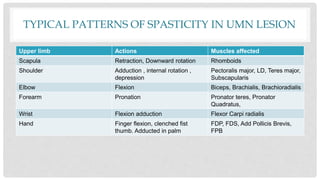
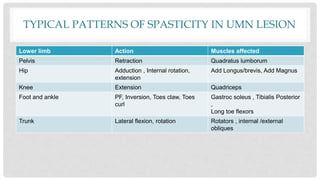
Spasticity, rigidity, hypotonia, dystonia, decerebrate rigidity, and decorticate rigidity are abnormal tones that can occur. Examination of tone includes initial observation, passive and active motion testing using scales like the Modified Ashworth Scale. Typical patterns of spasticity in upper and lower limbs are described for upper motor neuron lesions.