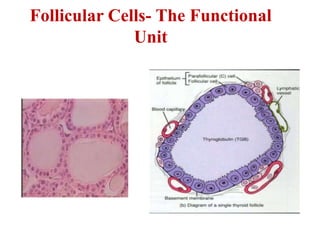
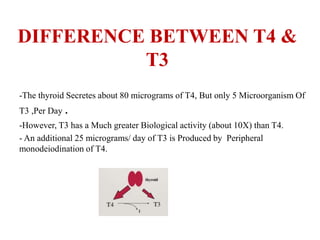
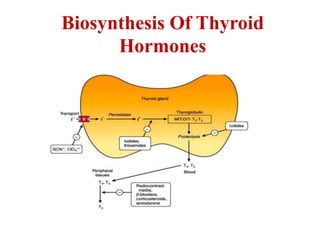
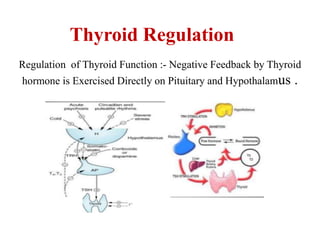
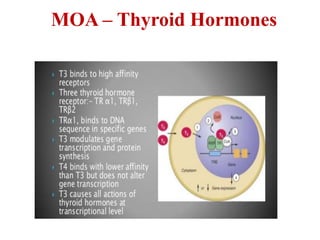
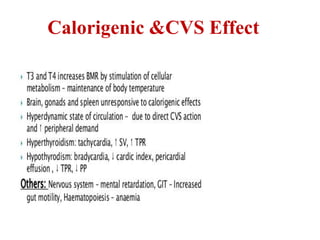
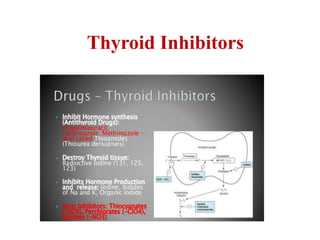
The thyroid gland secretes three main hormones: thyroxine (T4), triiodothyronine (T3), and calcitonin. T4 is secreted in the largest amount but T3 has higher biological activity. The thyroid regulates metabolism, growth, and development through a negative feedback loop with the pituitary gland and hypothalamus. Hypothyroidism can cause myxedema coma, a life-threatening condition treated with thyroid hormone replacement. Hyperthyroidism treatments include anti-thyroid drugs that block hormone synthesis or radioactive iodine that destroys the thyroid gland.





































![Radioiodine (I[3]1)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation2-201119091332/85/Thyroid-Hormone-45-320.jpg)
