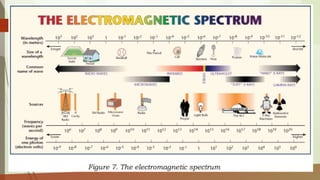
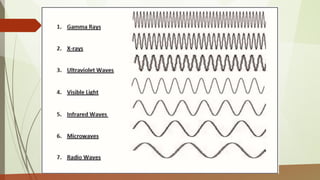
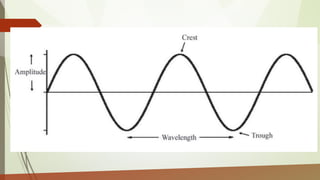
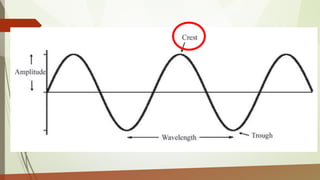
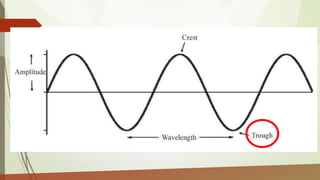
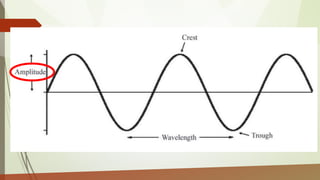
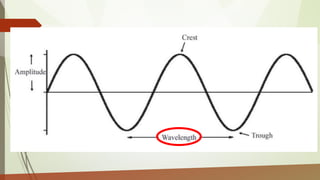
This document discusses different types of waves including transverse, longitudinal, and surface waves. It defines key wave properties like amplitude, wavelength, frequency, period, and speed. It explains the relationships between these properties and how they apply to mechanical and electromagnetic waves. Examples are provided for calculating wave speed from wavelength and frequency. The document also previews the next module on sound waves.























![A spring vibrates 24, 000 times
in 1.00 minutes. What are the
frequency and period. [Hint:
frequency is cycles per second.]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/module2-wavesaroundyou-151201130335-lva1-app6892/85/Third-Grading-Module-2-Waves-Around-You-31-320.jpg)