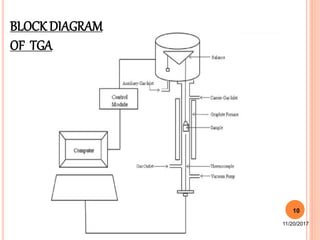
This document discusses thermo-analytical techniques, specifically thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). It begins with an introduction to thermo-analytical methods and defines the difference between these methods and traditional analytical techniques. TGA is then explained in more detail, including the principles behind how it works, instrumentation involved consisting of a thermo-balance, furnace, and recording device, and factors that can affect TGA results such as sample characteristics and instrumental factors. Applications of TGA include stability studies, oxidation reactions, and pharmacokinetics studies.









![APPLICATION
1)Stability studies
2)Oxidation and Combustion reaction
3) Combined Operation [ TGA with mass
spectroscopy]
4)Pharmacokinetics Studies
11/20/2017
15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thermo-analytic12300-171120102119/85/Thermoanalytical-Techniques-15-320.jpg)



