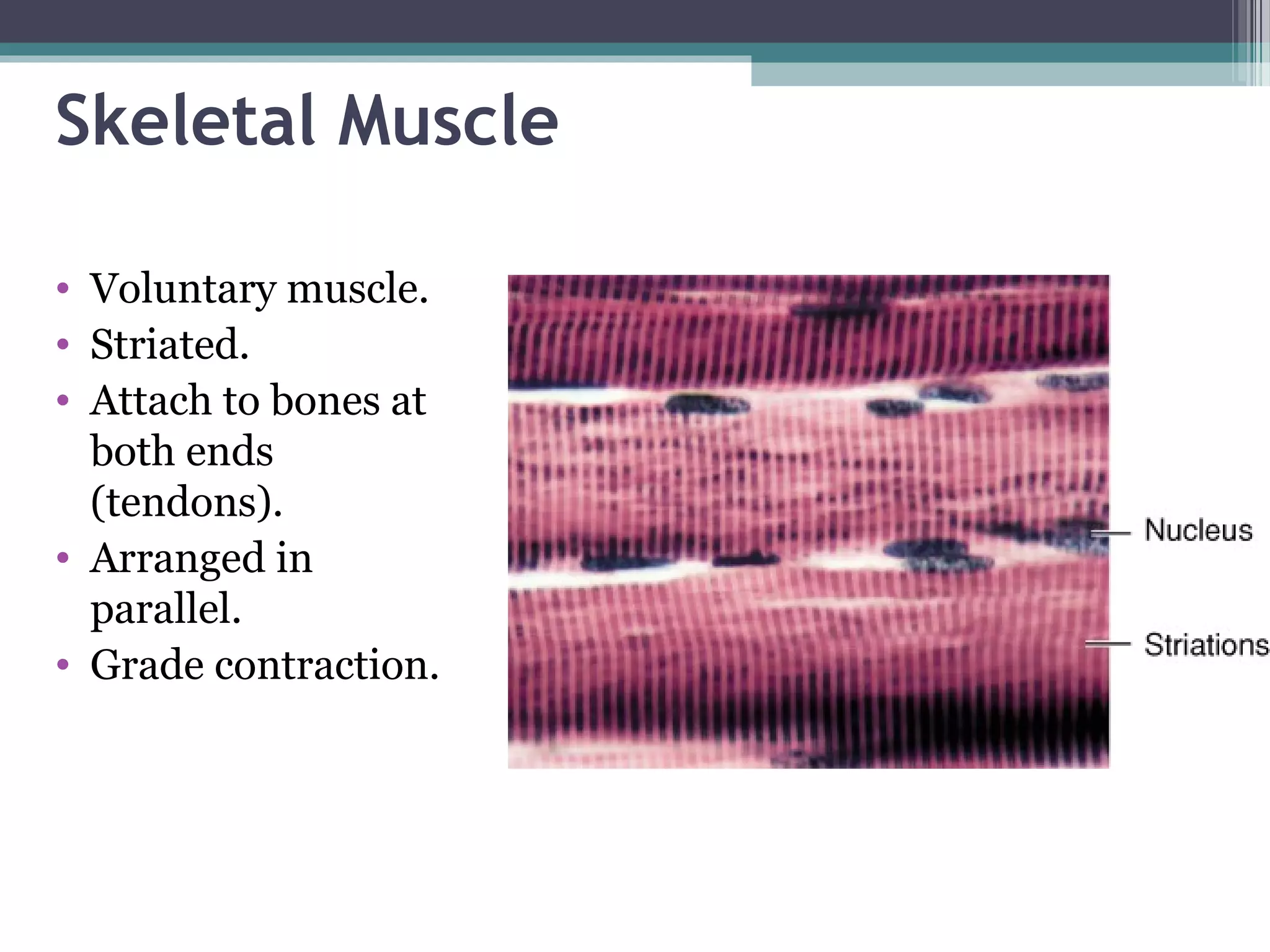
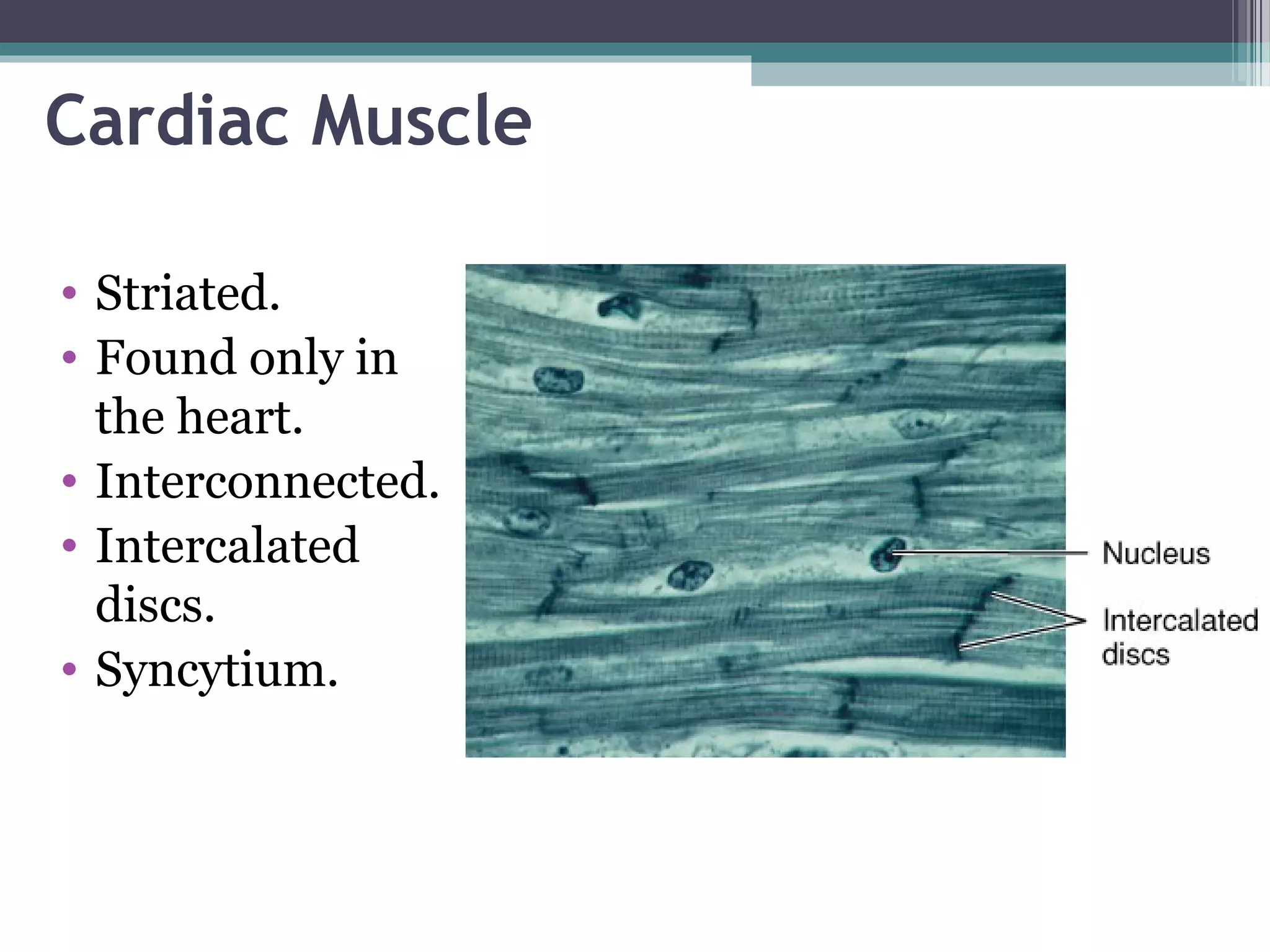
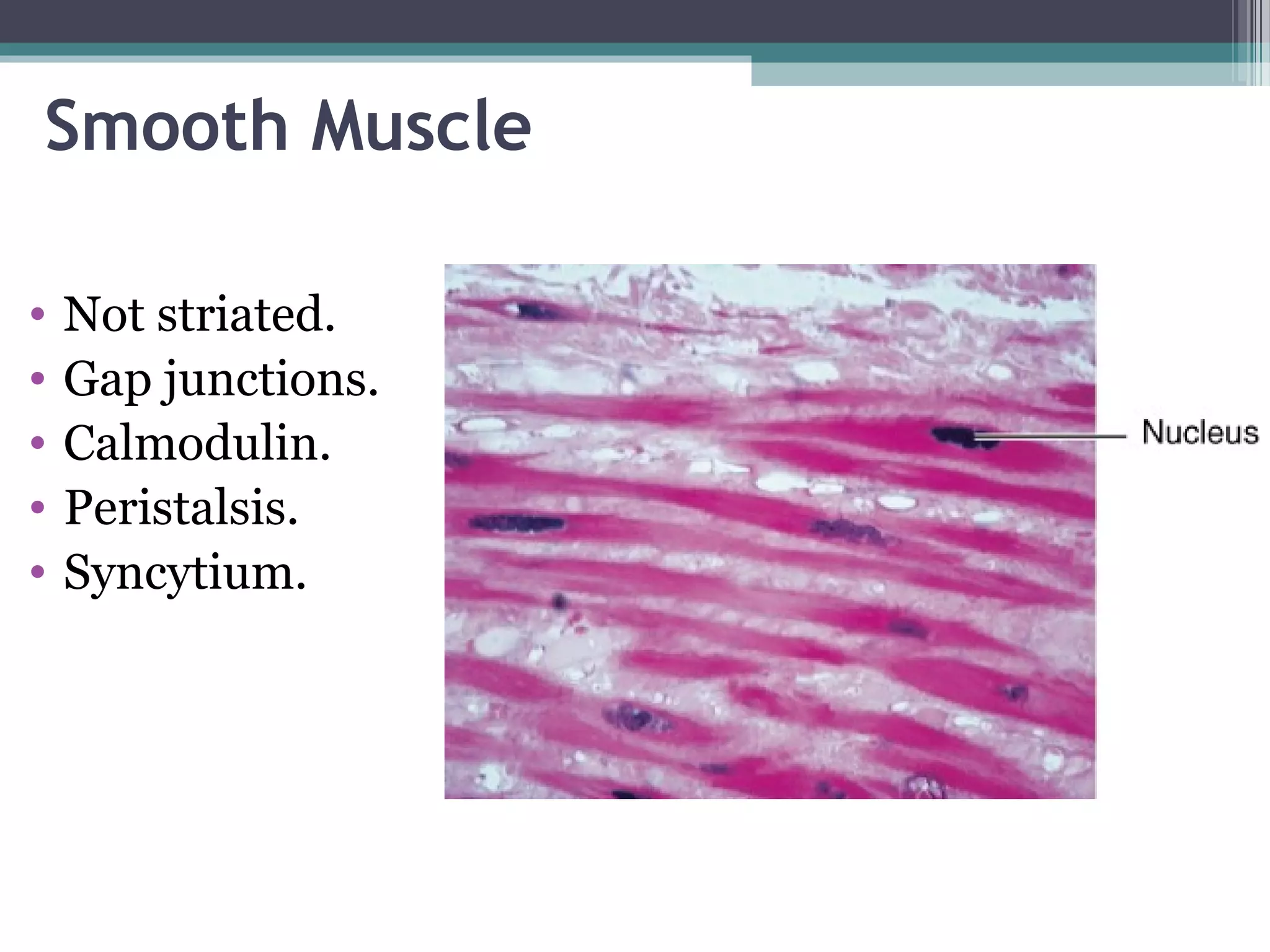
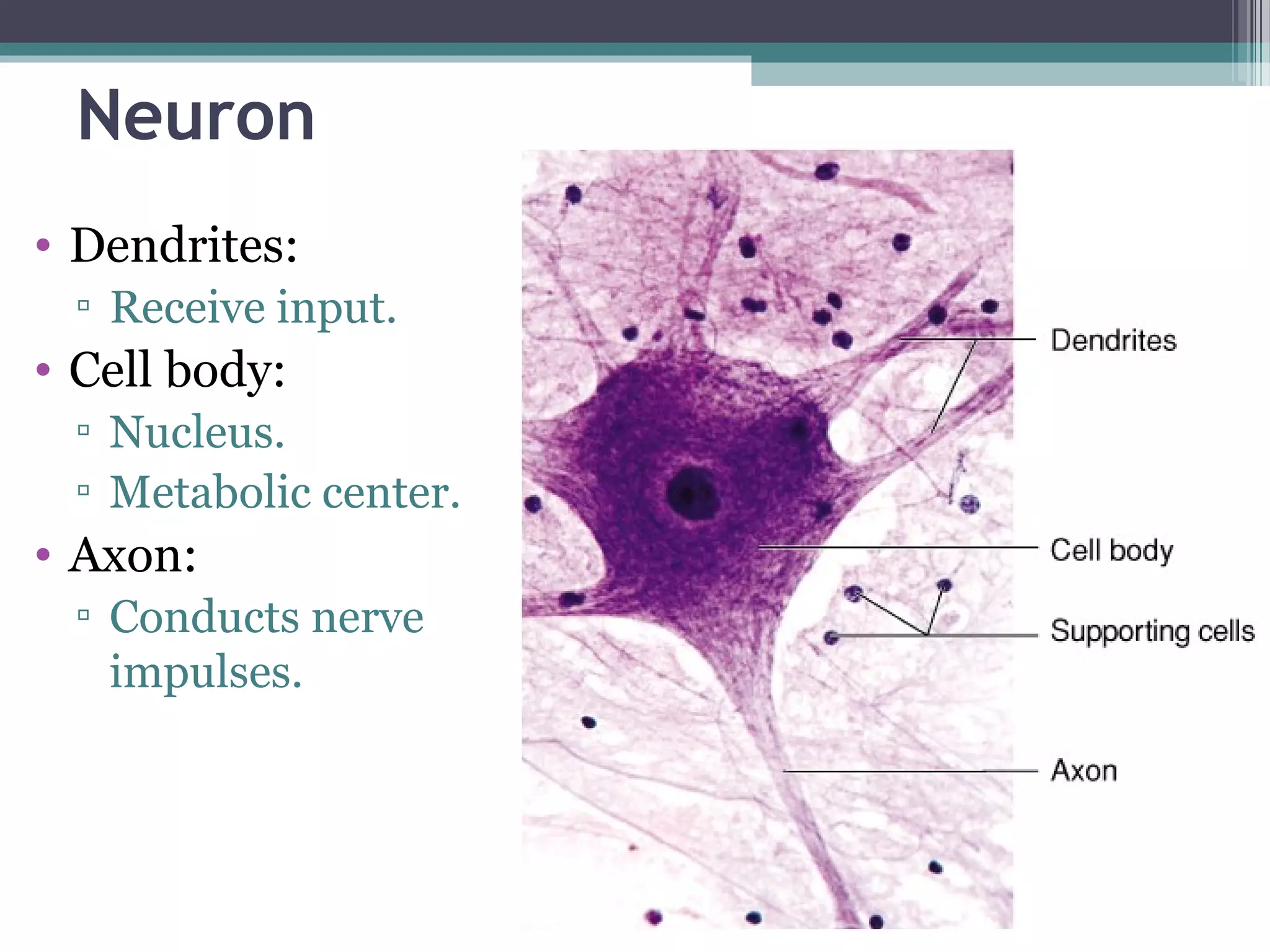
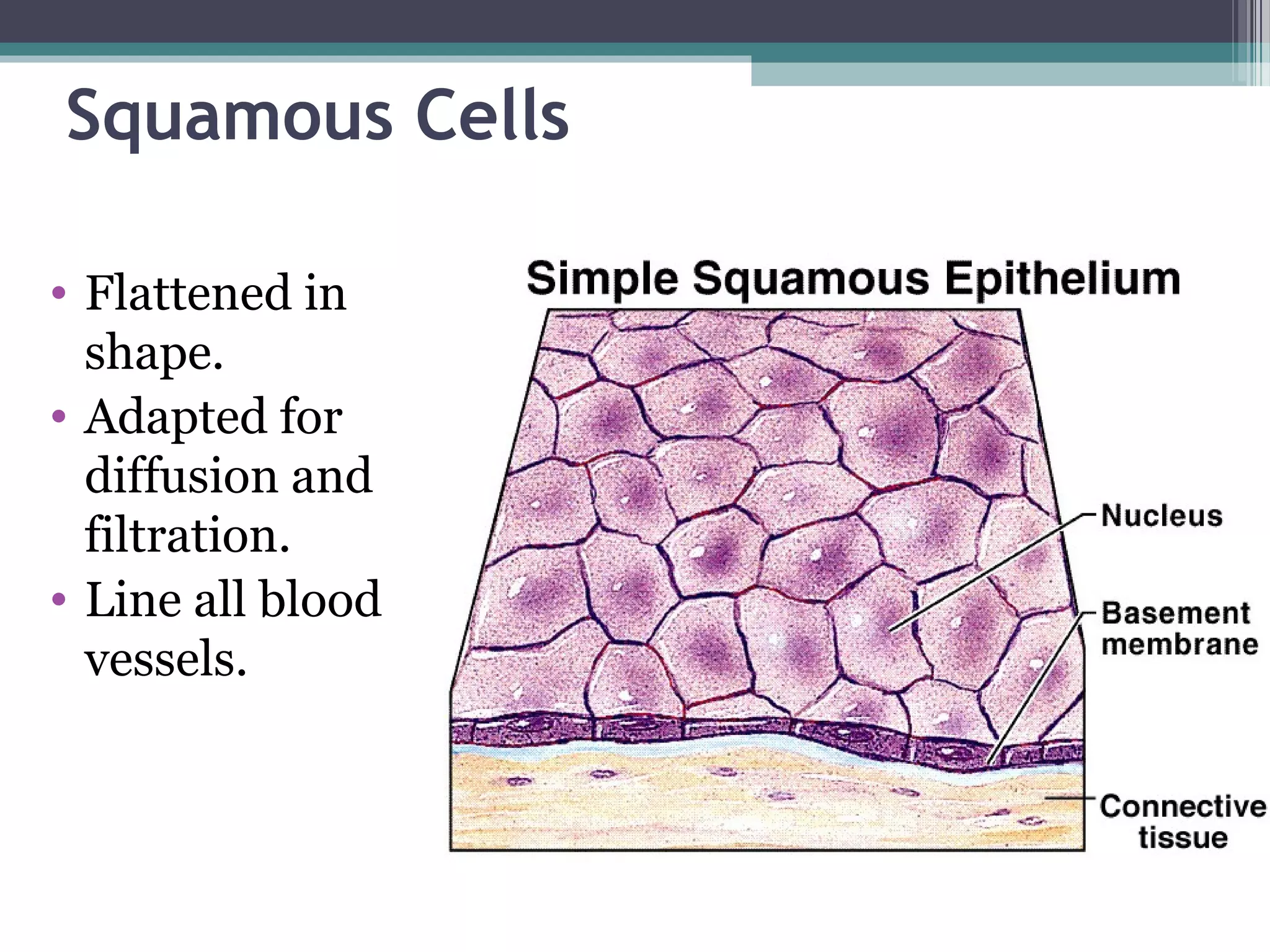
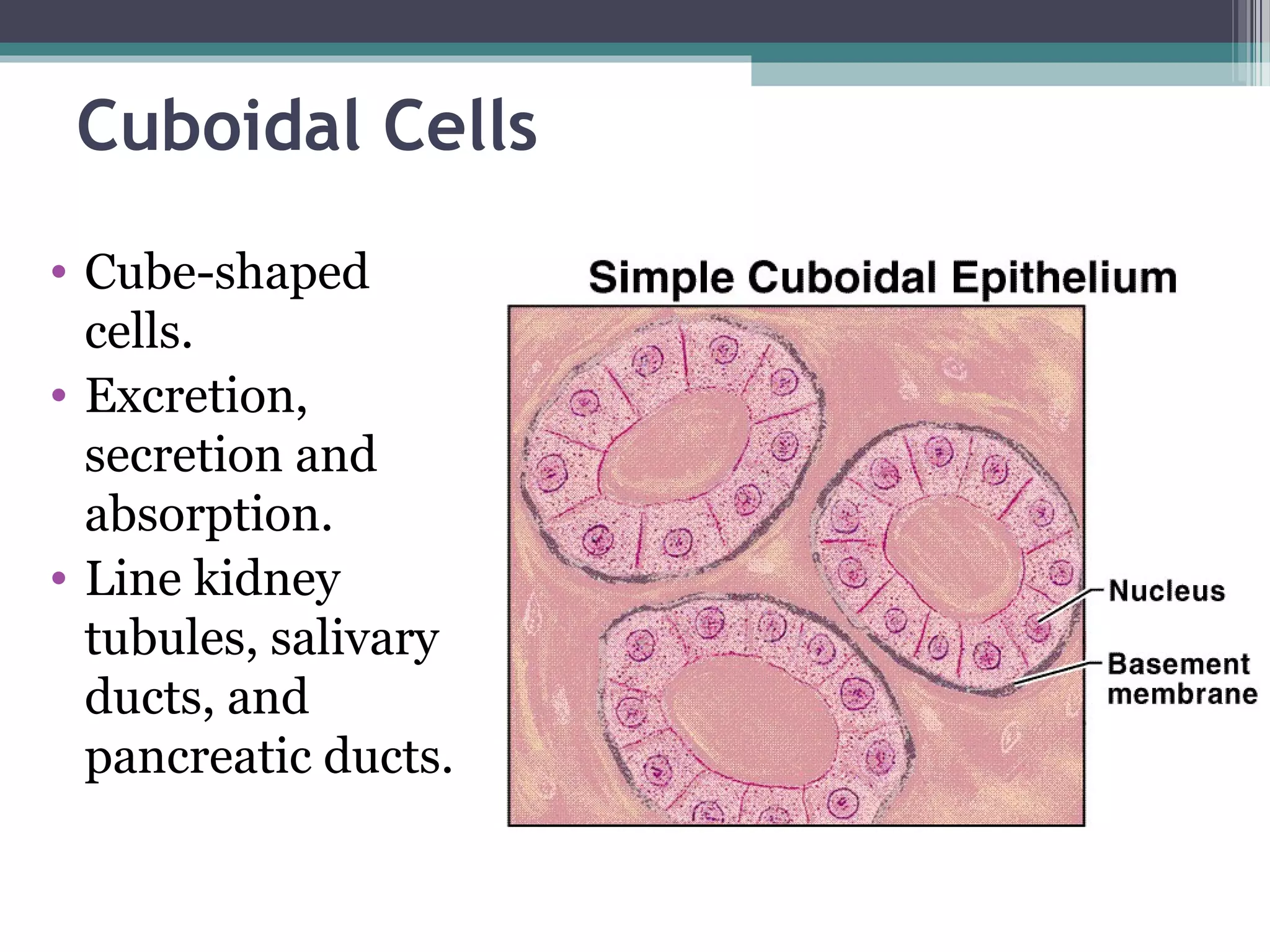
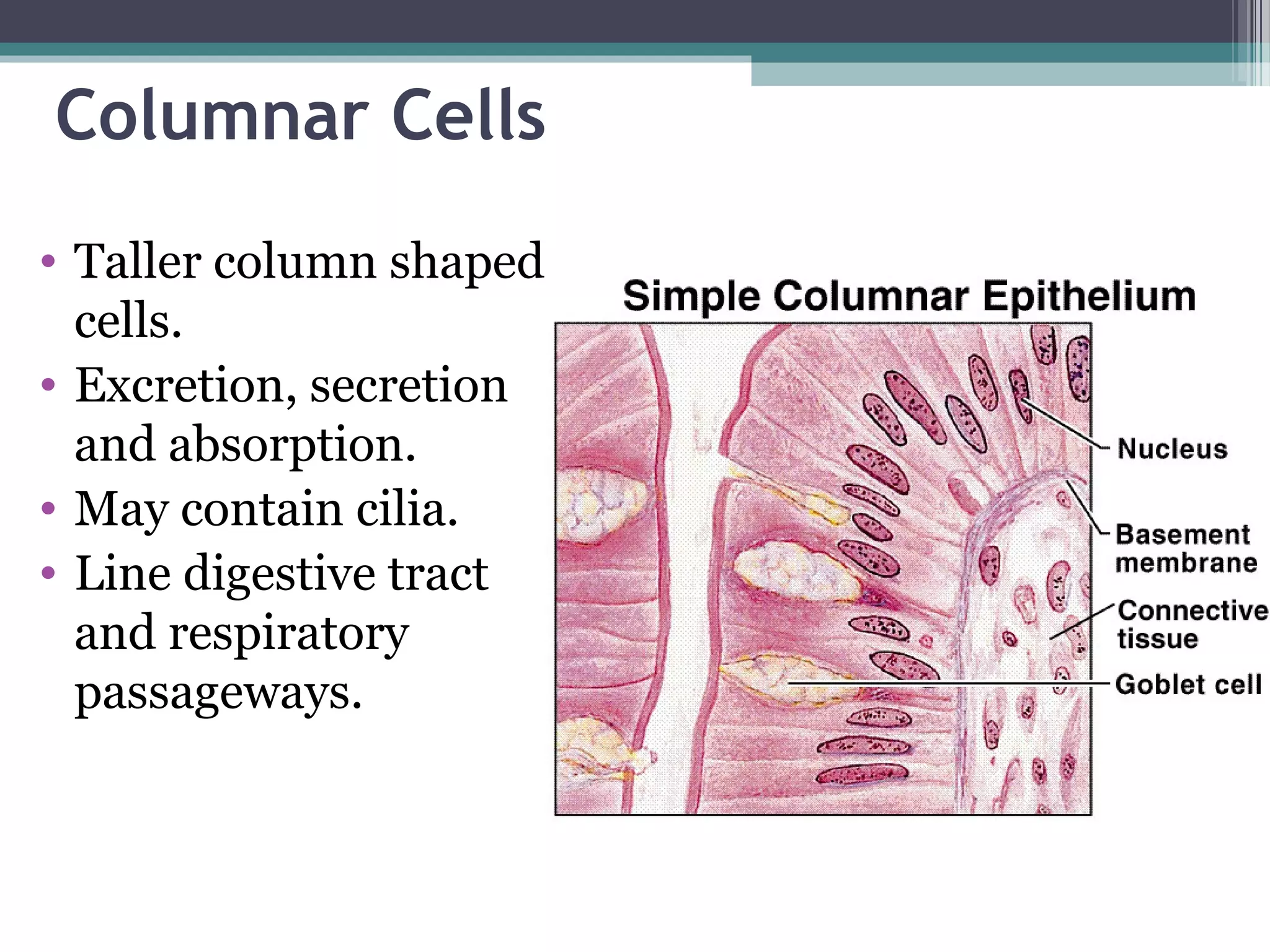
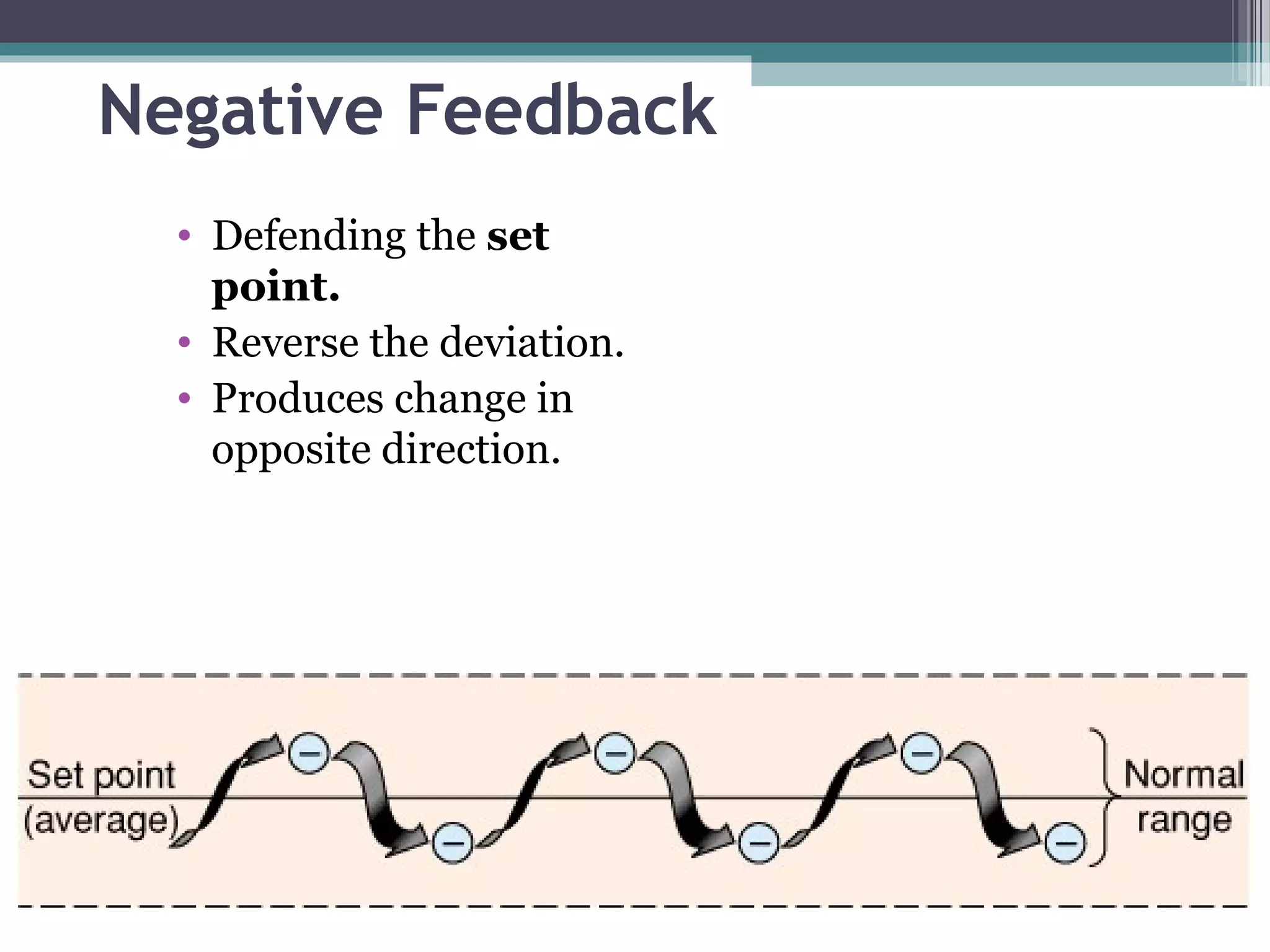
This document provides an overview of key concepts in human physiology. It discusses homeostasis and the use of feedback loops to maintain stable internal conditions. Negative feedback loops work to reverse deviations from the body's set points, while positive feedback loops amplify changes. The four primary tissues - muscle, nervous, epithelial and connective tissue - are introduced. Key cell and tissue types within each primary tissue are defined, including their structures and functions. The chapter concludes with definitions of organs, organ systems, and the body's fluid compartments.





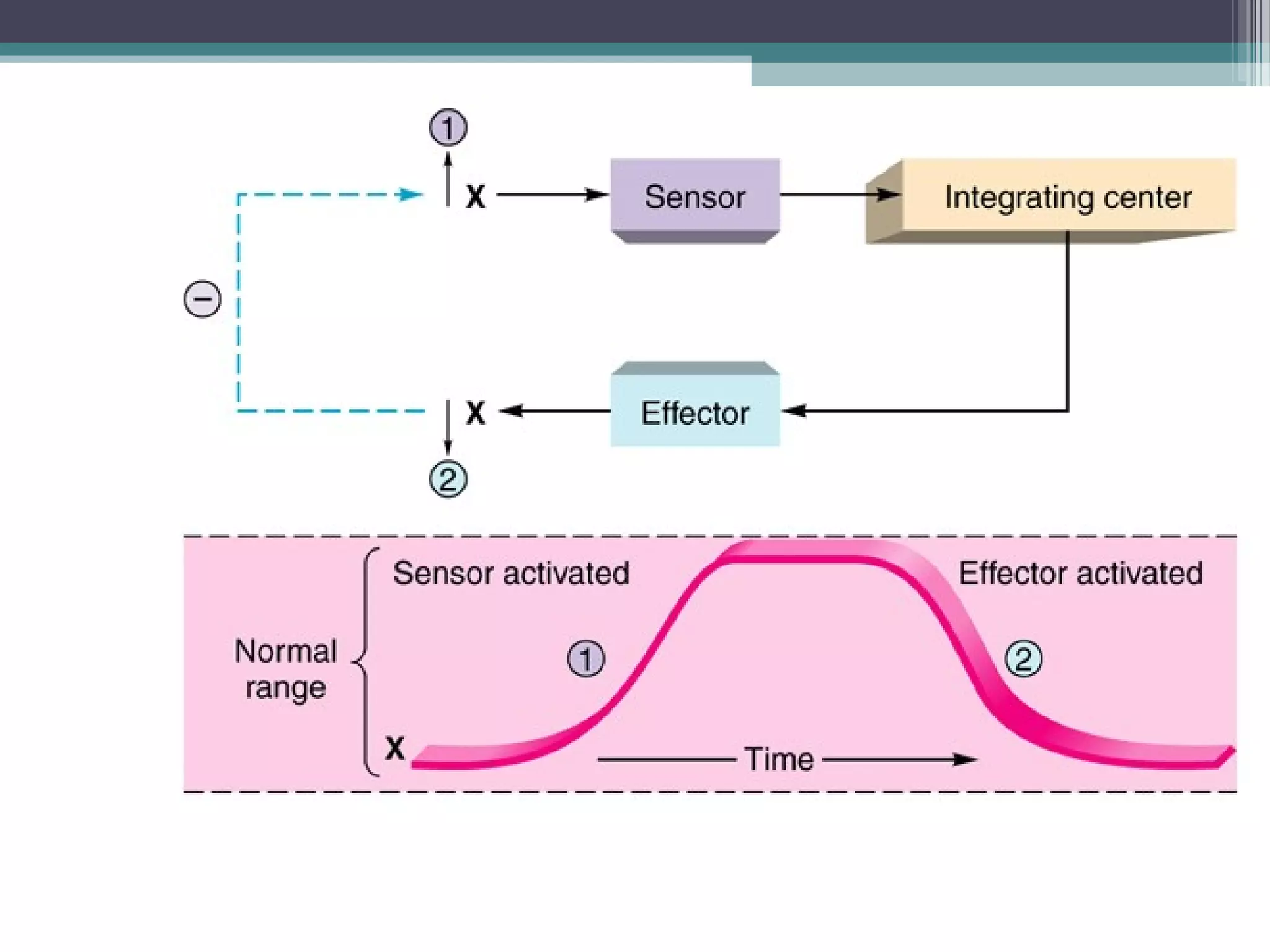
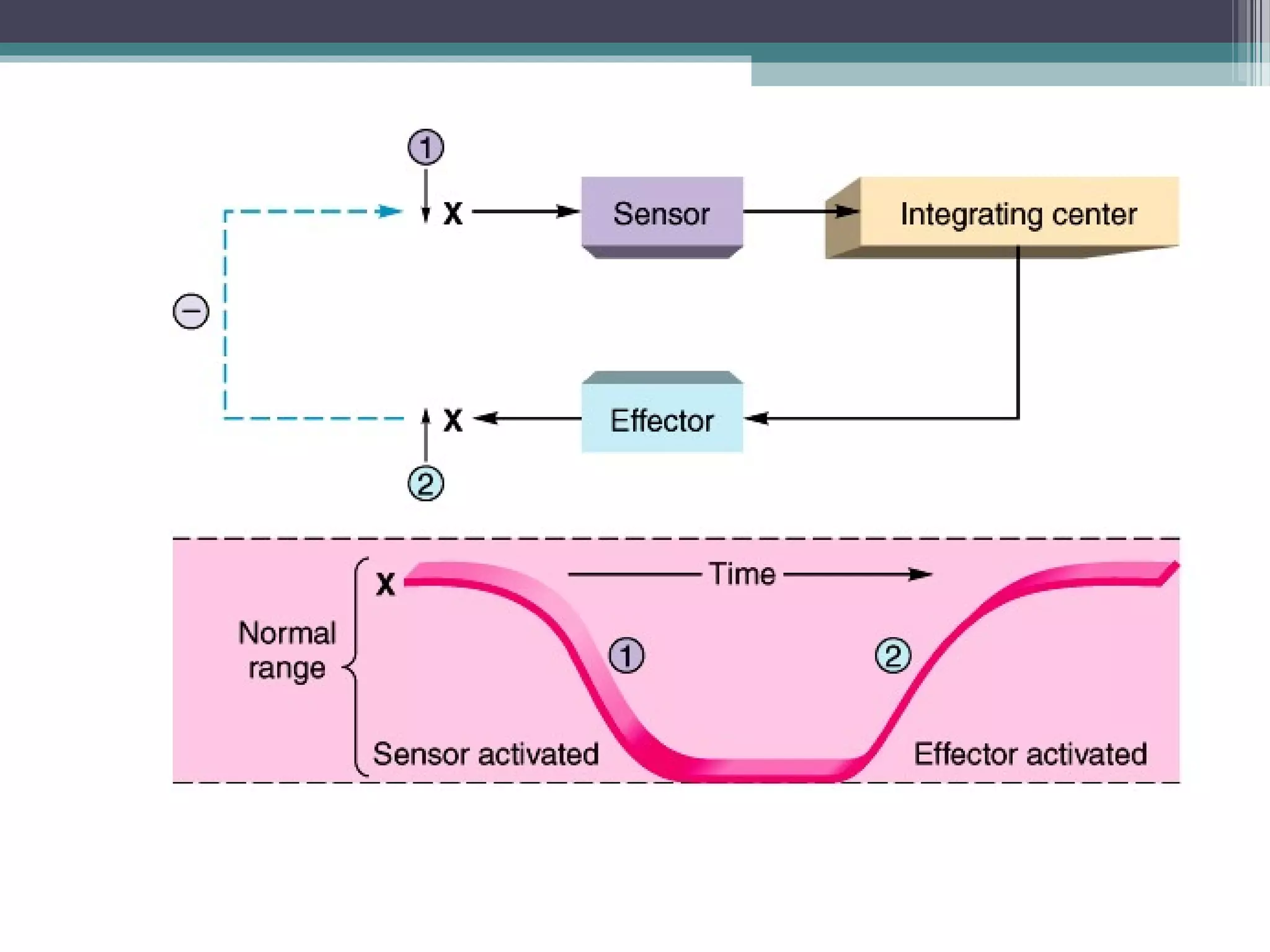
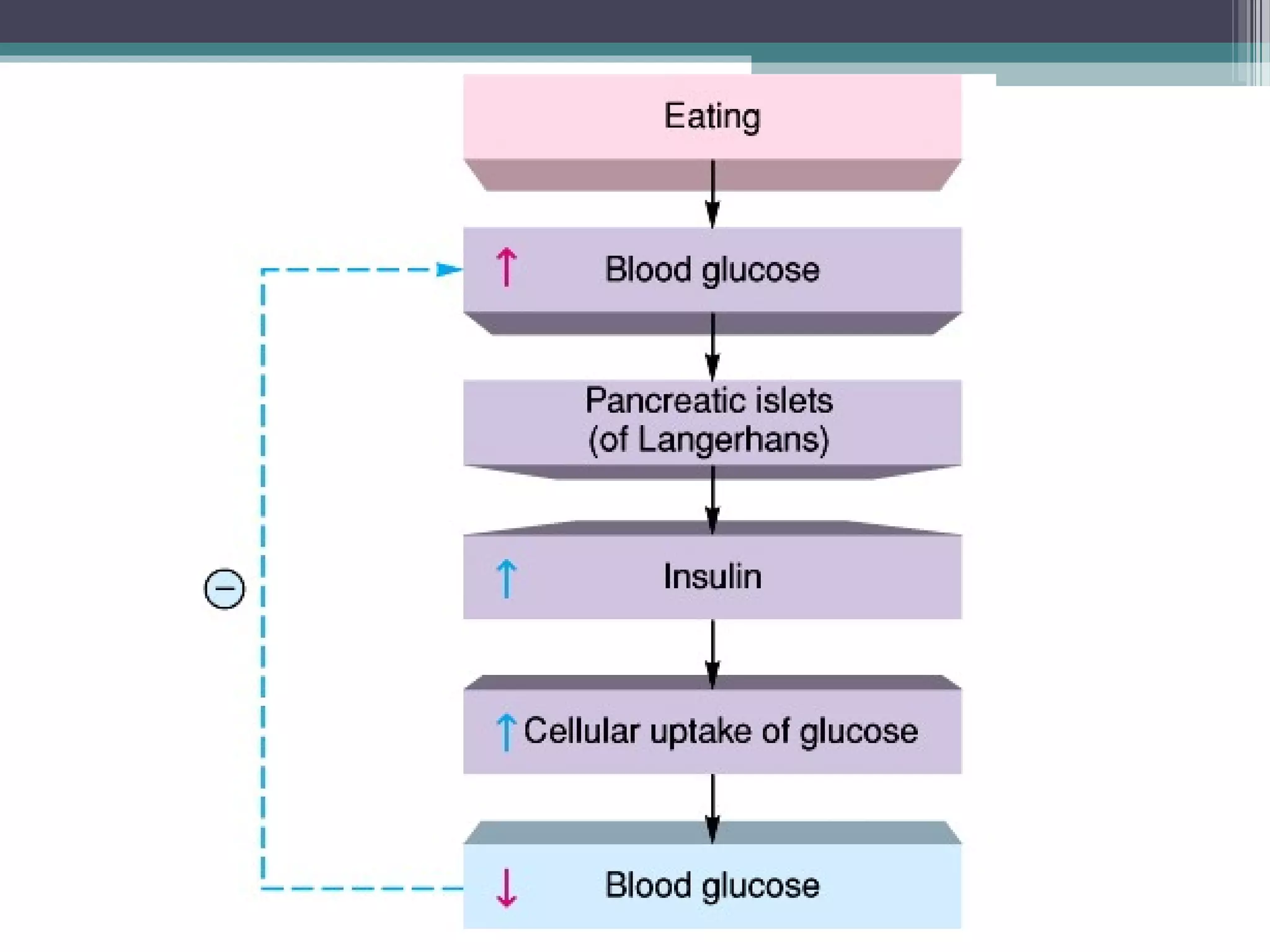
![Hormone insulin restores plasma [glucose].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chp1thestudyofbodyfunction-151007031558-lva1-app6891/75/The-study-of-body-function-9-2048.jpg)