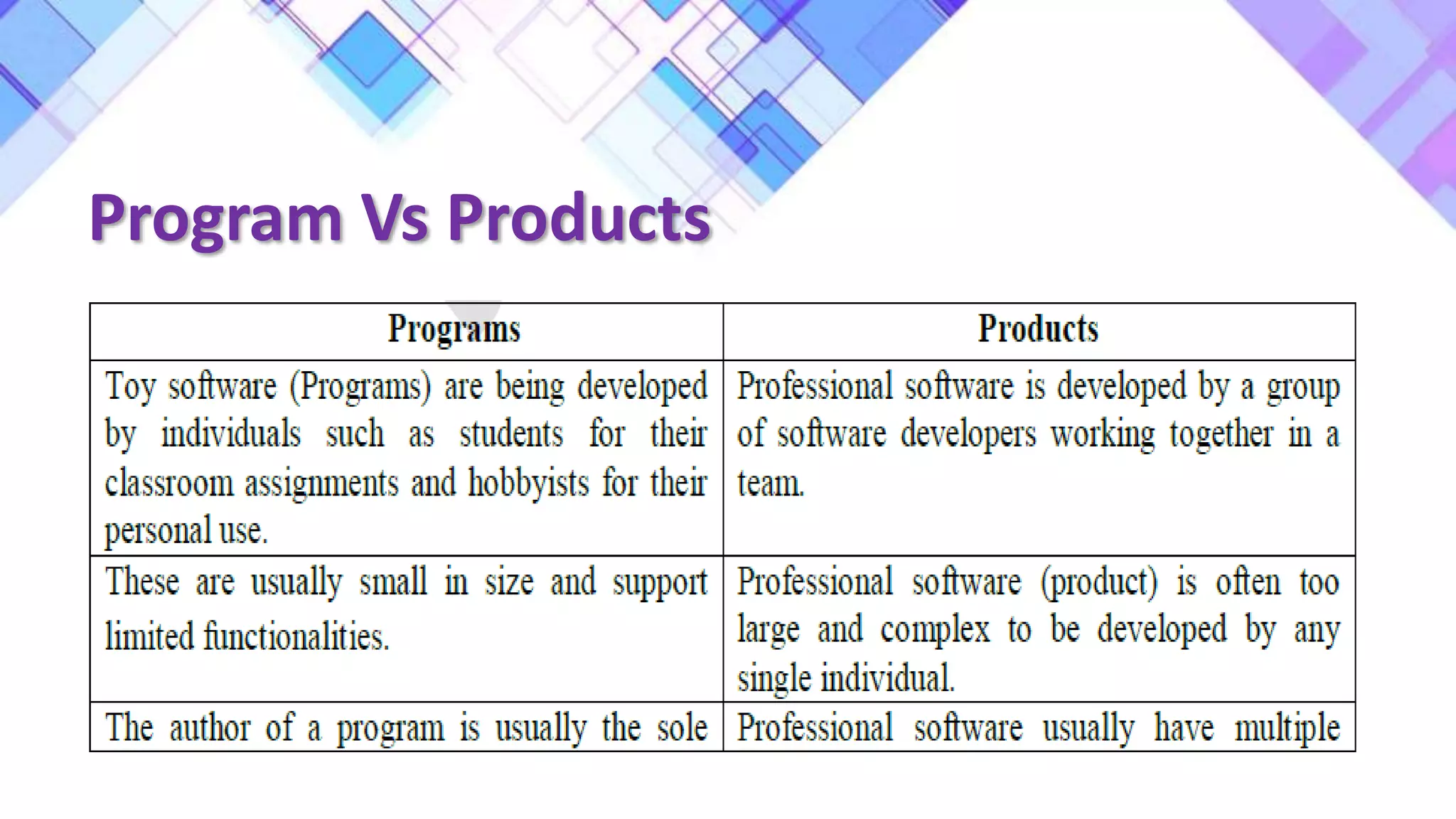
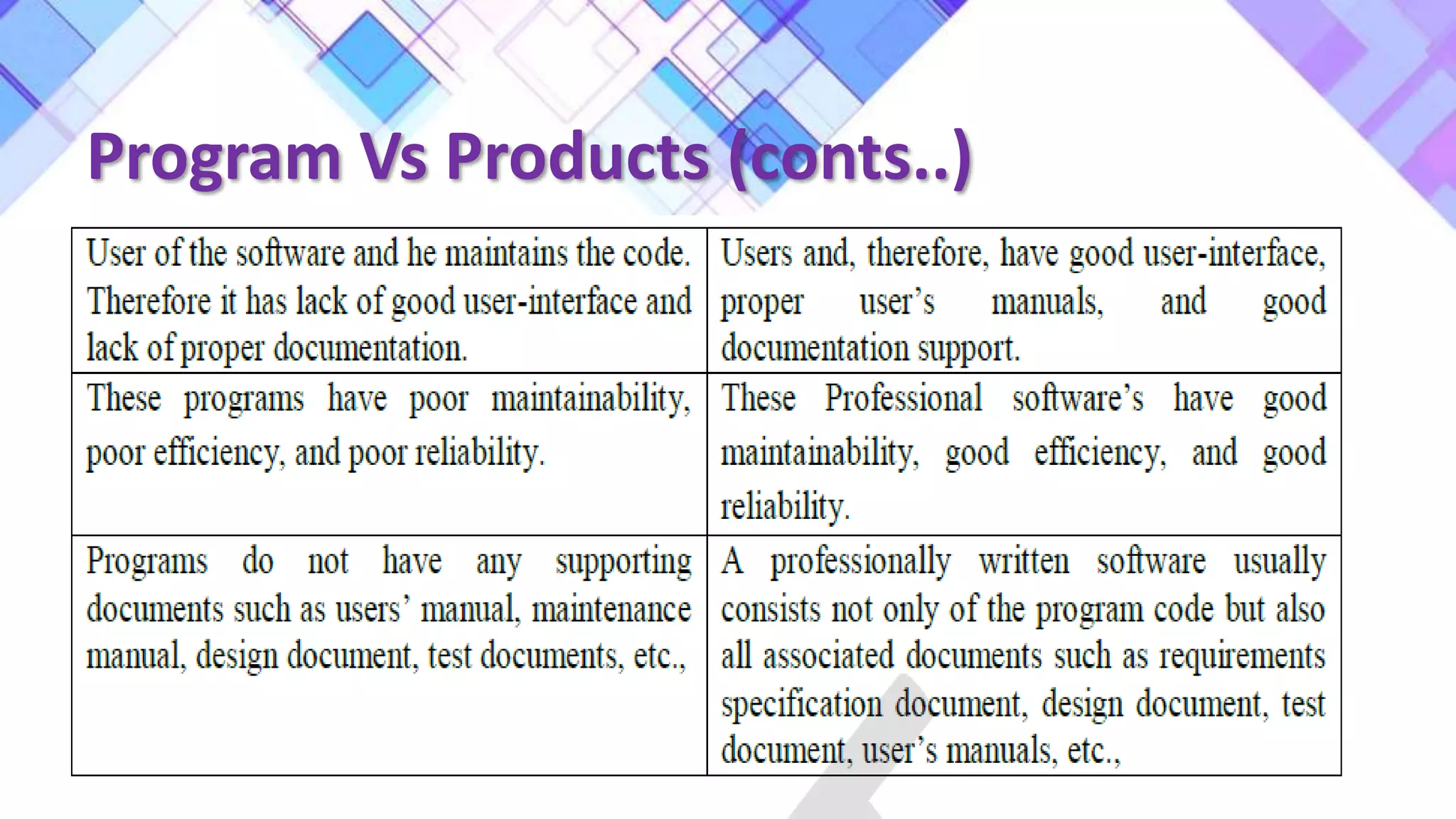
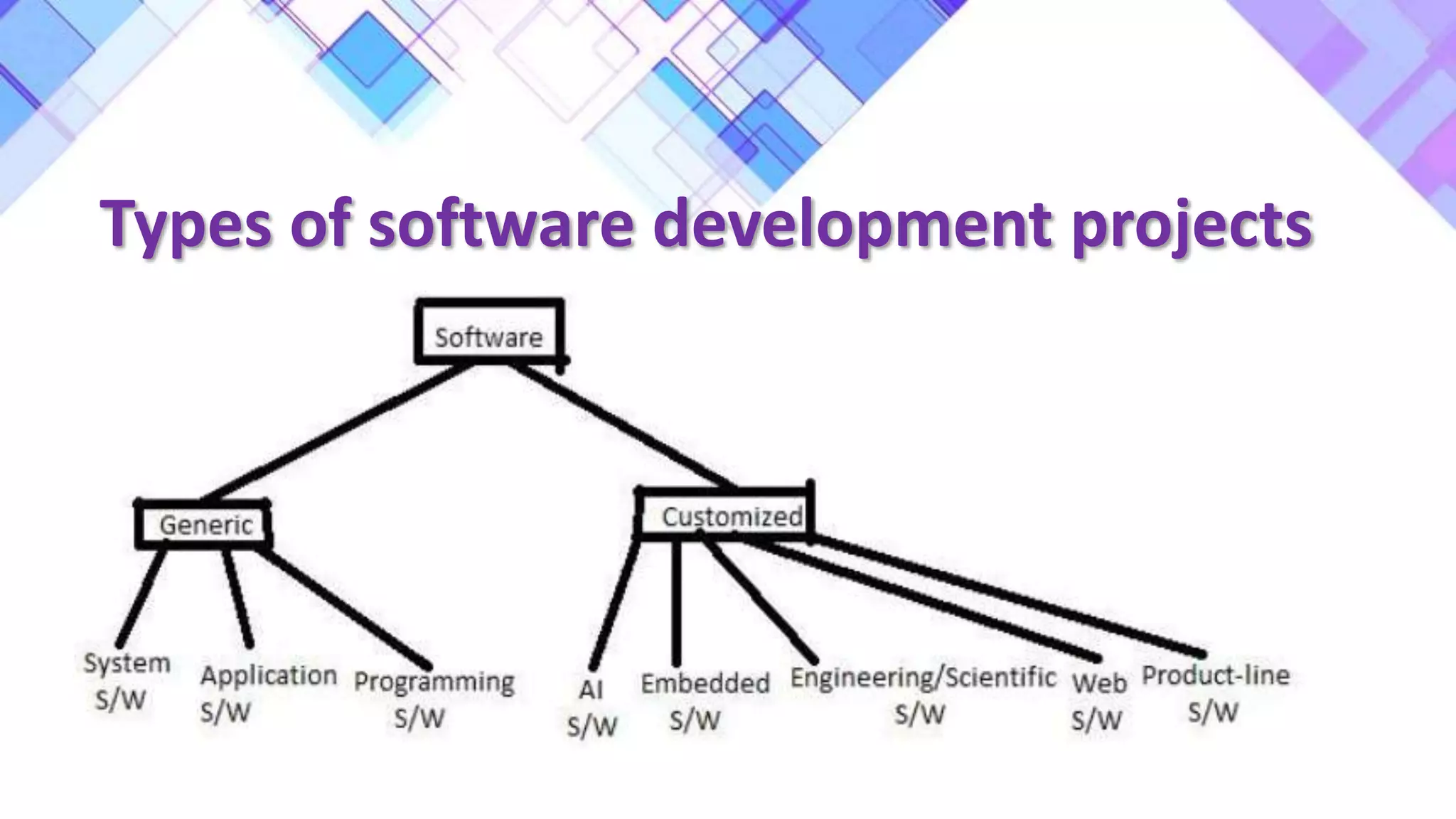
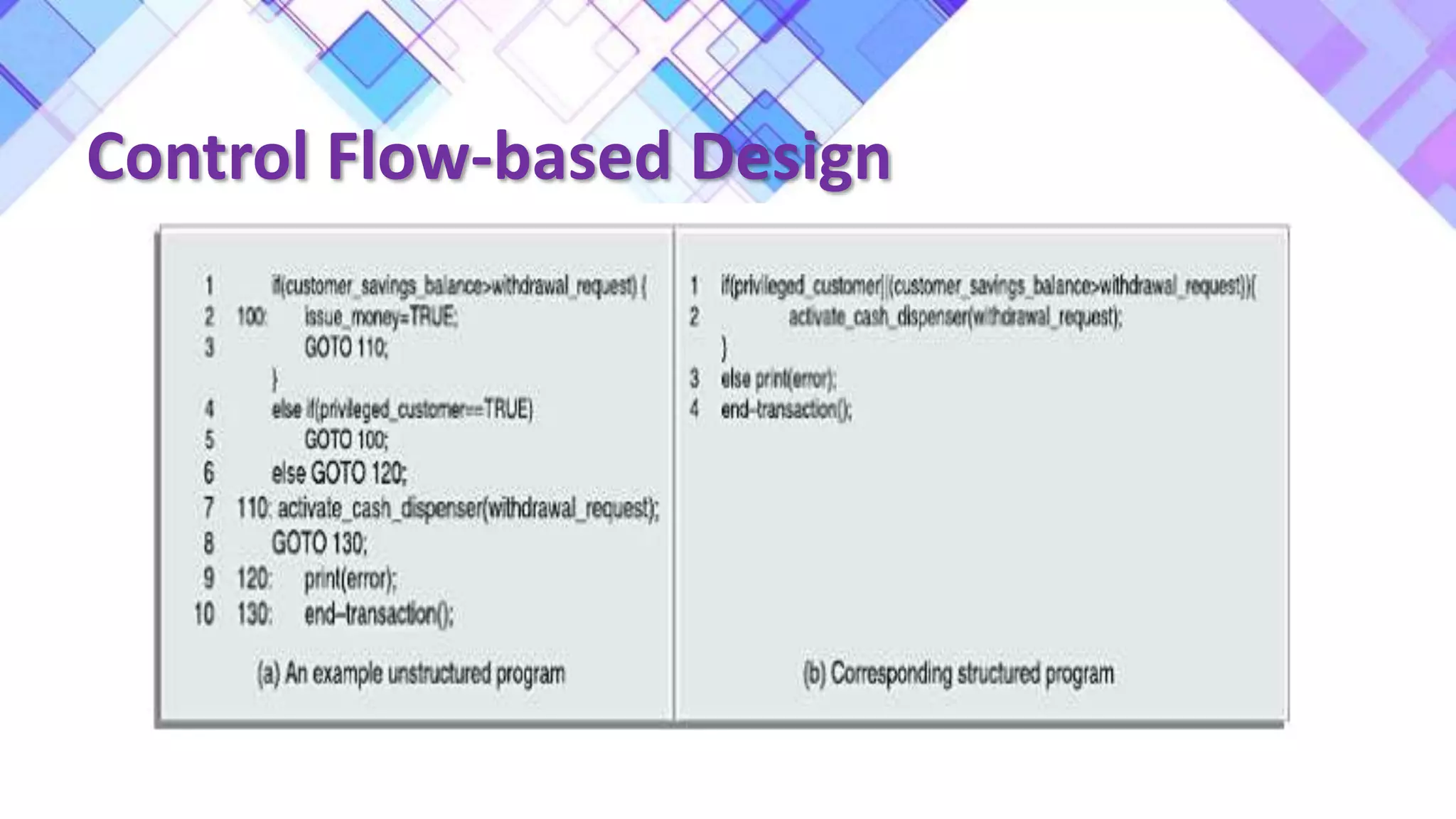
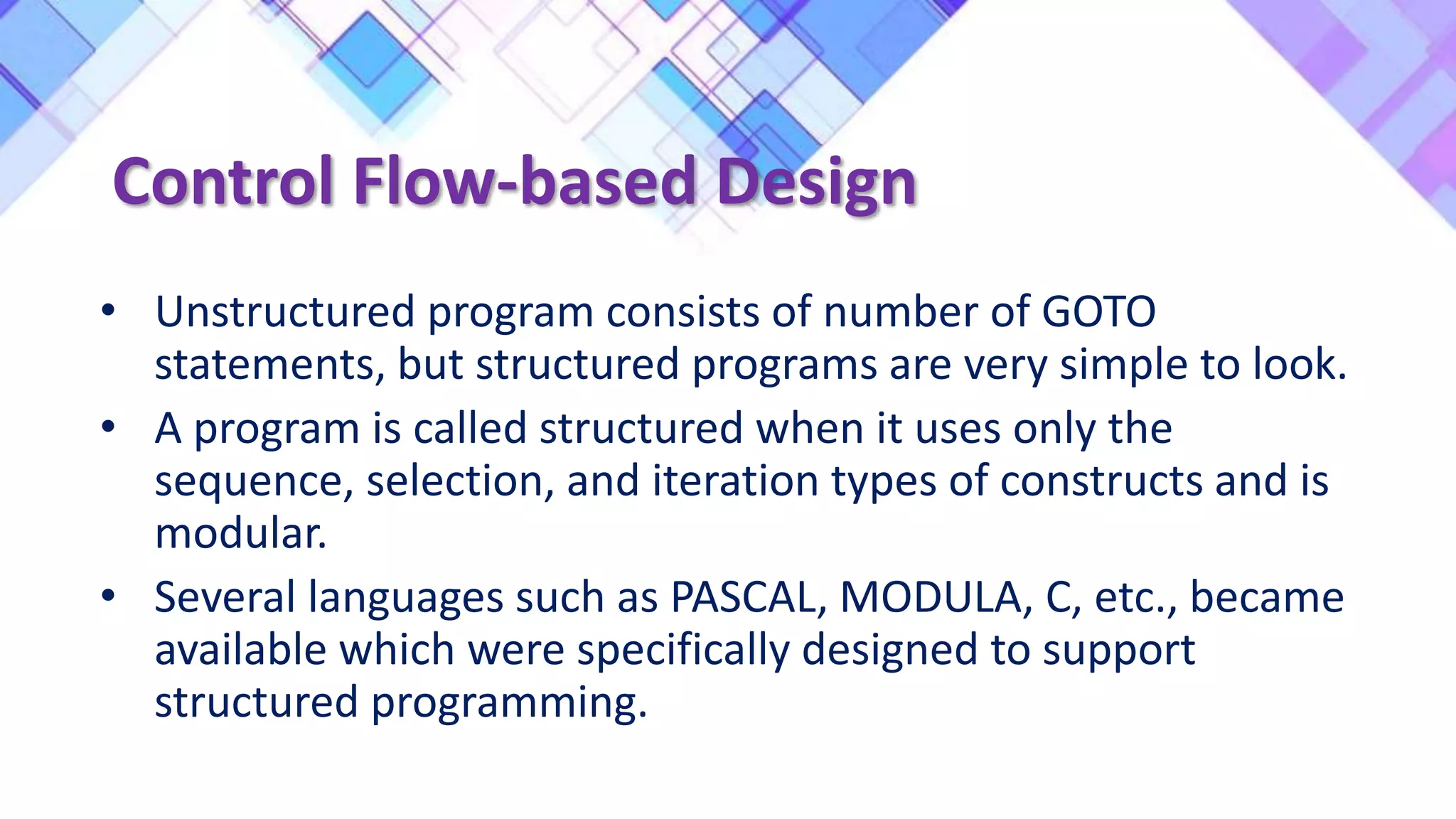
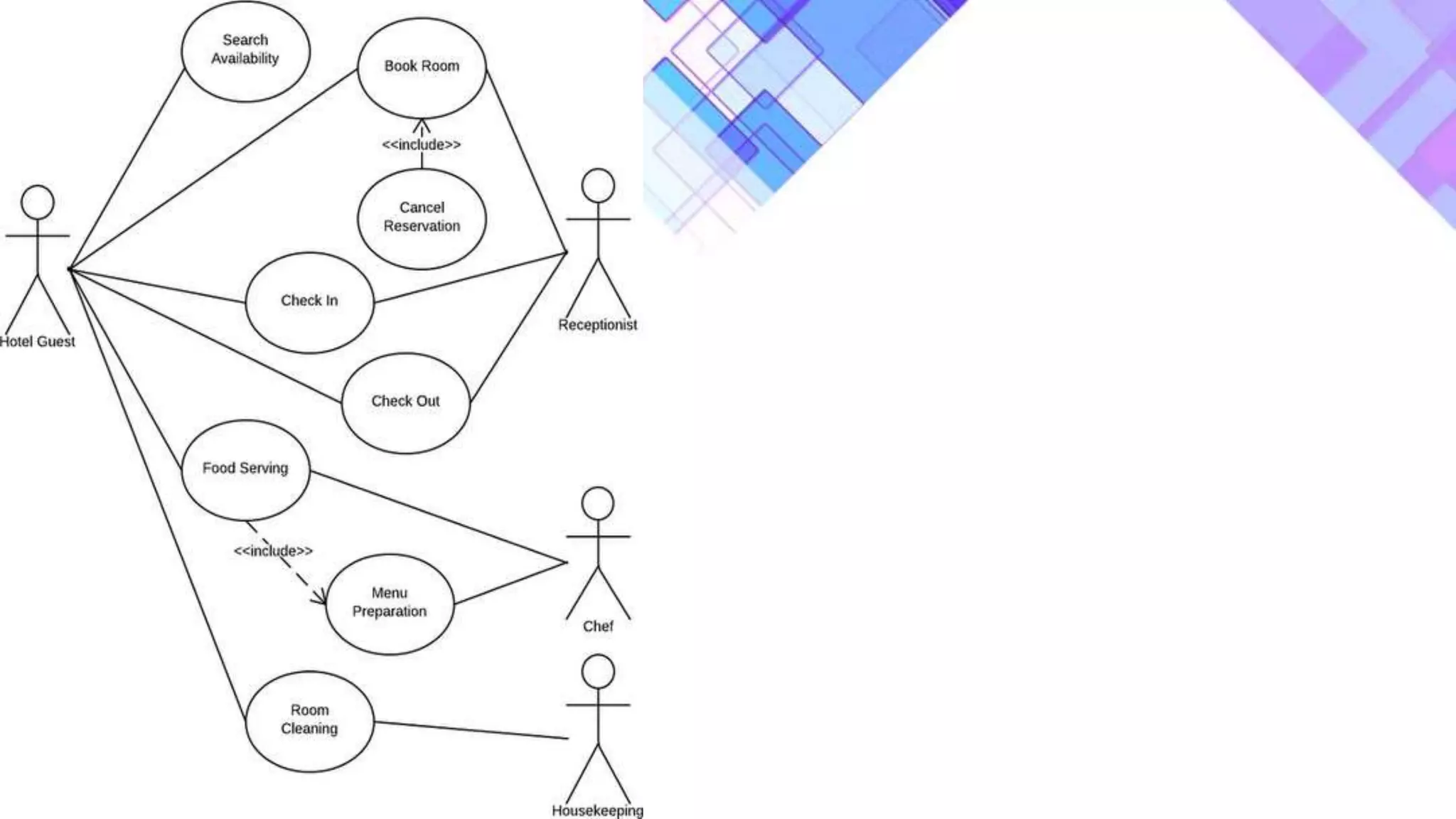
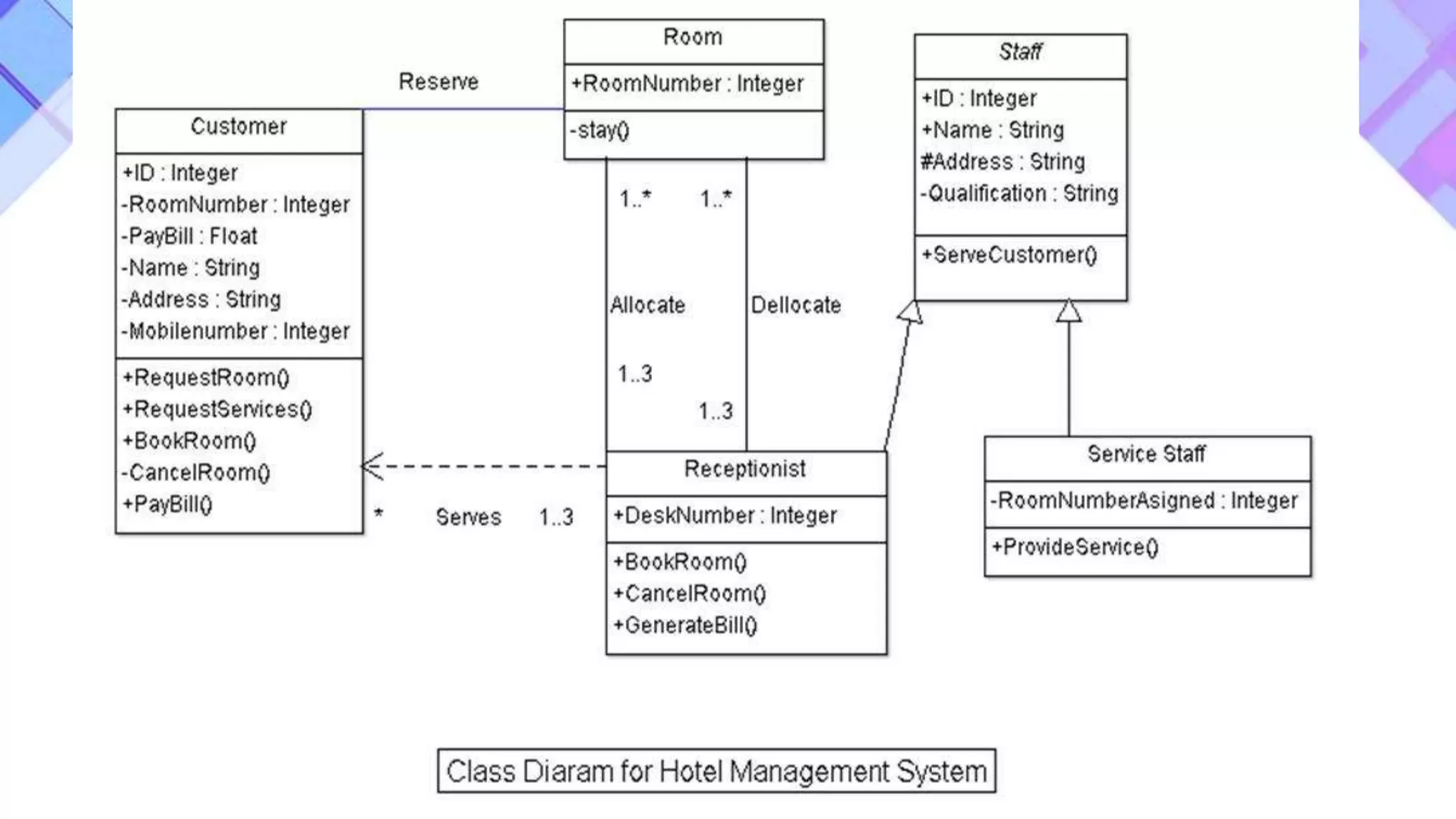
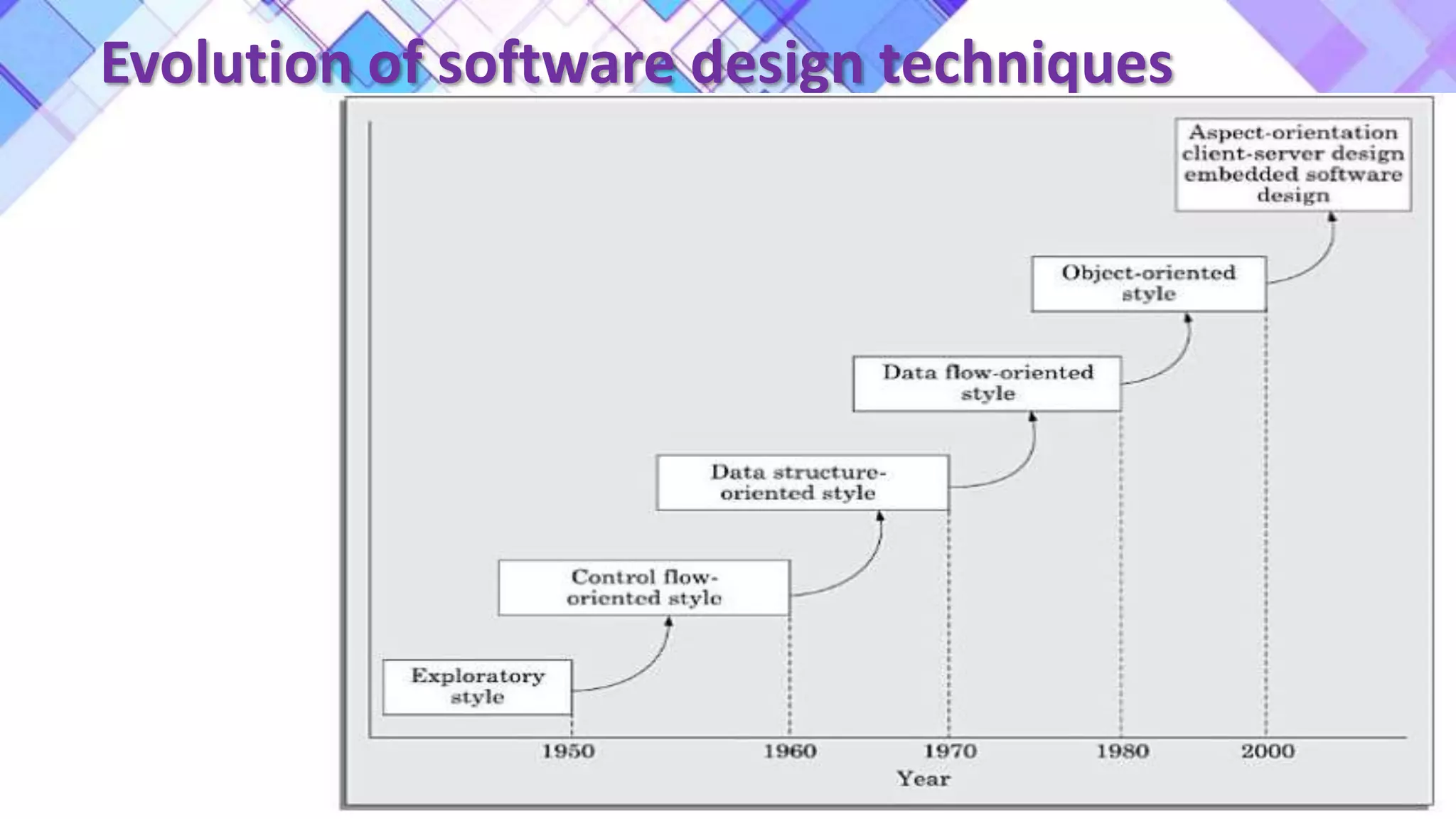
This document discusses the evolution of software engineering methodologies from early computer programming to modern object-oriented design. It describes five stages of evolution: 1) Early programming used exploratory coding without formal design. 2) High-level languages improved abstraction but design was still ad hoc. 3) Structured programming introduced control flow design with flowcharts. 4) Data structure design became important for large programs. 5) Data flow design and object-oriented design improved abstraction through information hiding and reuse.