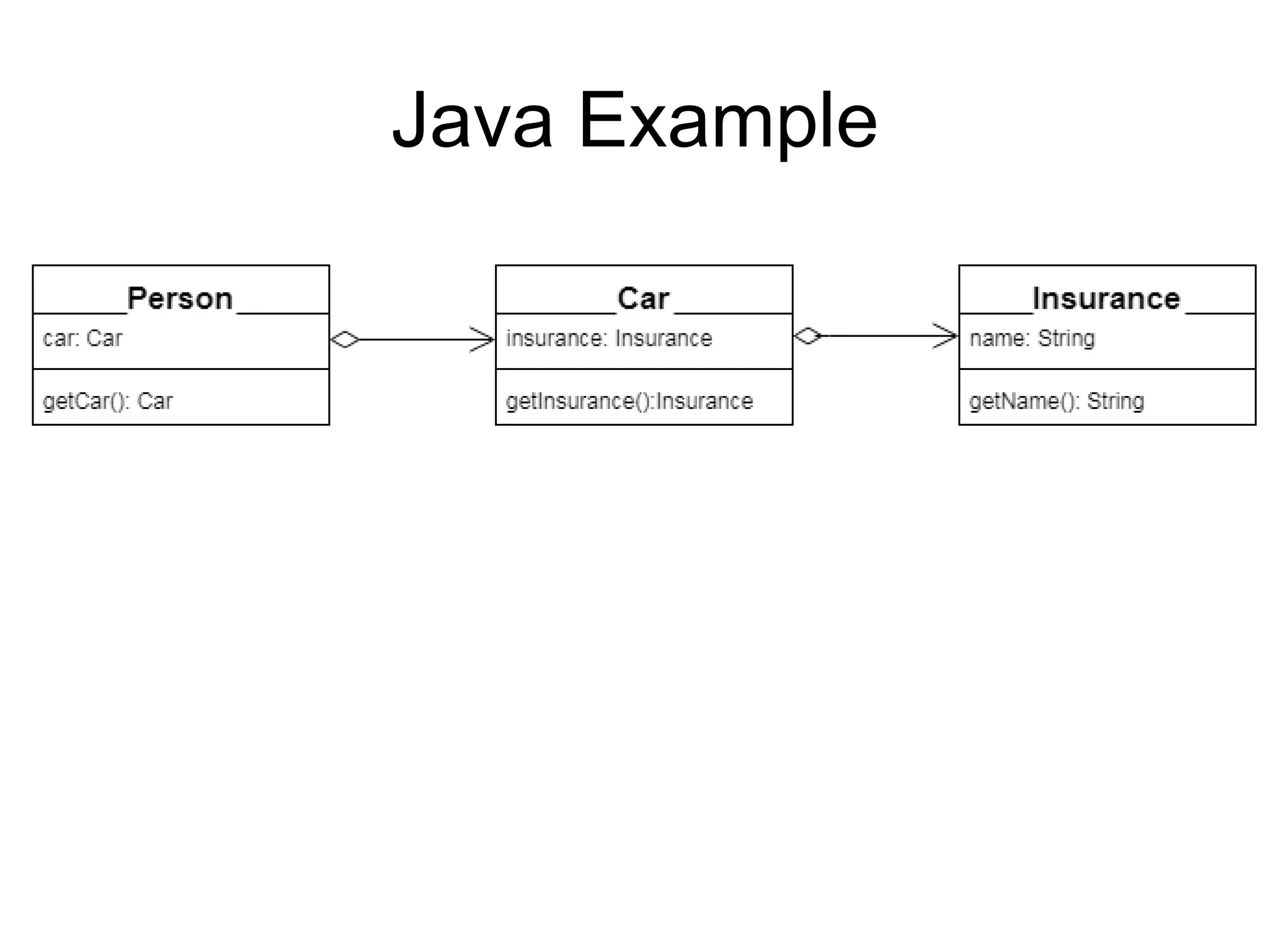
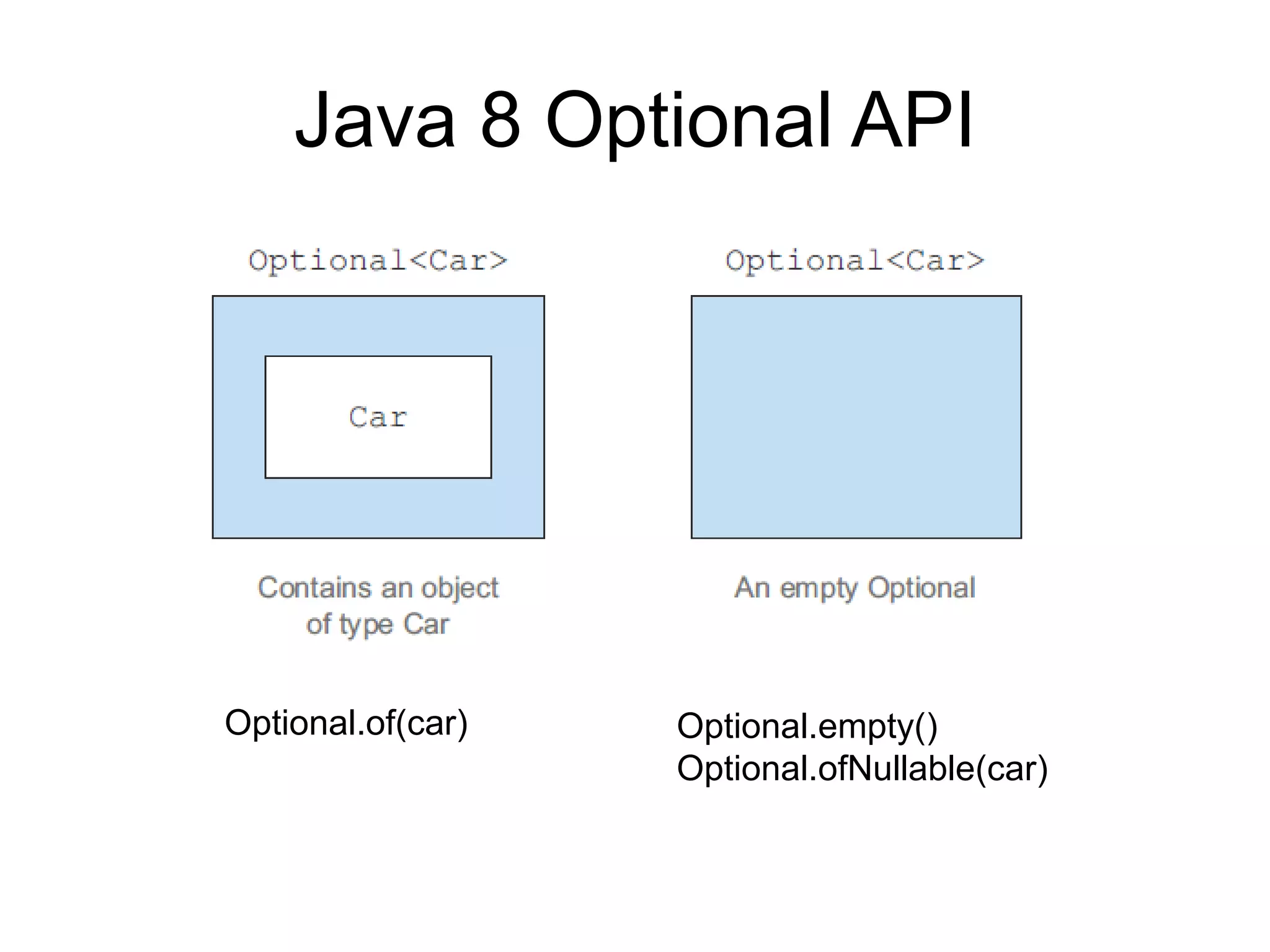
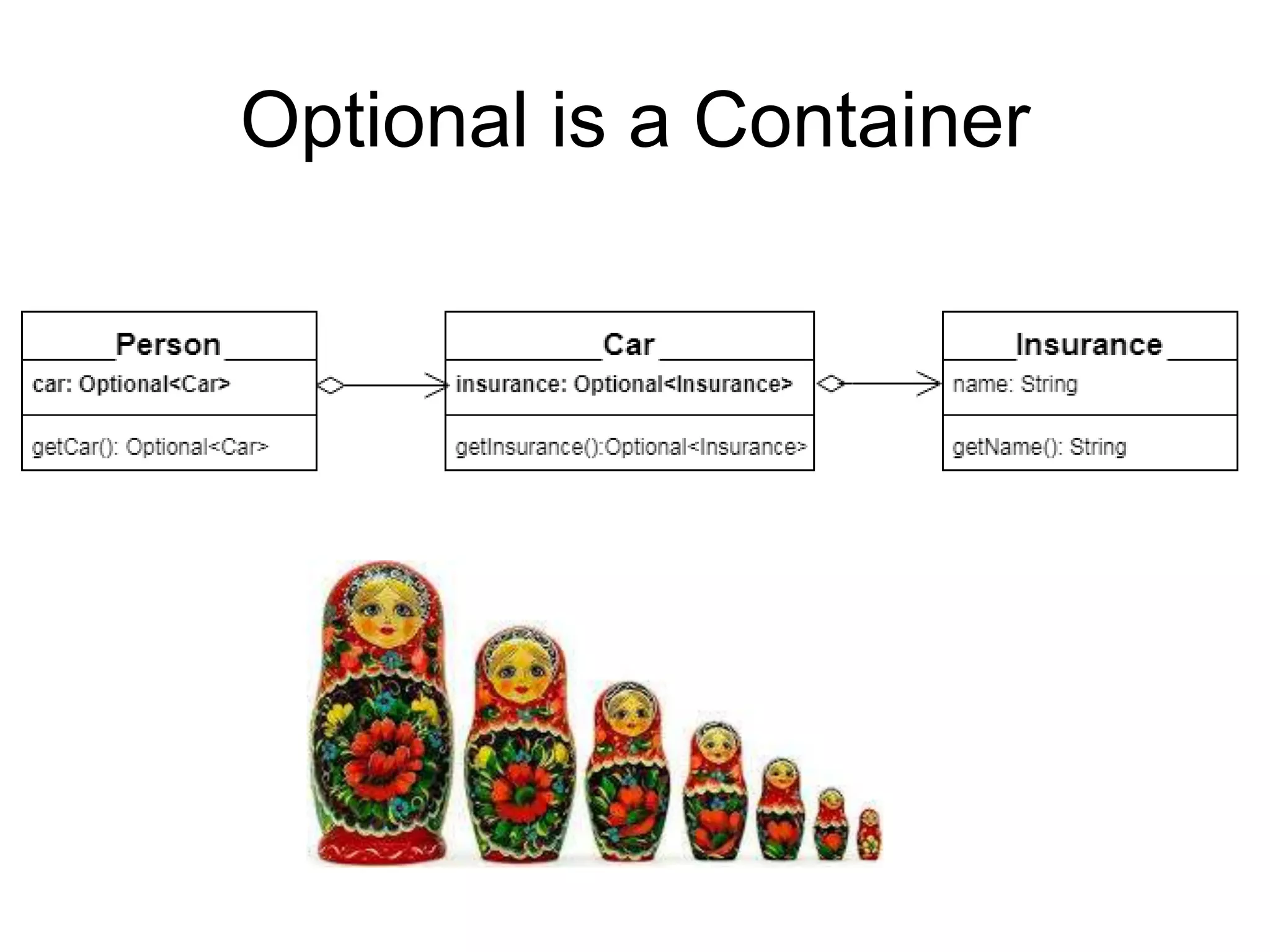
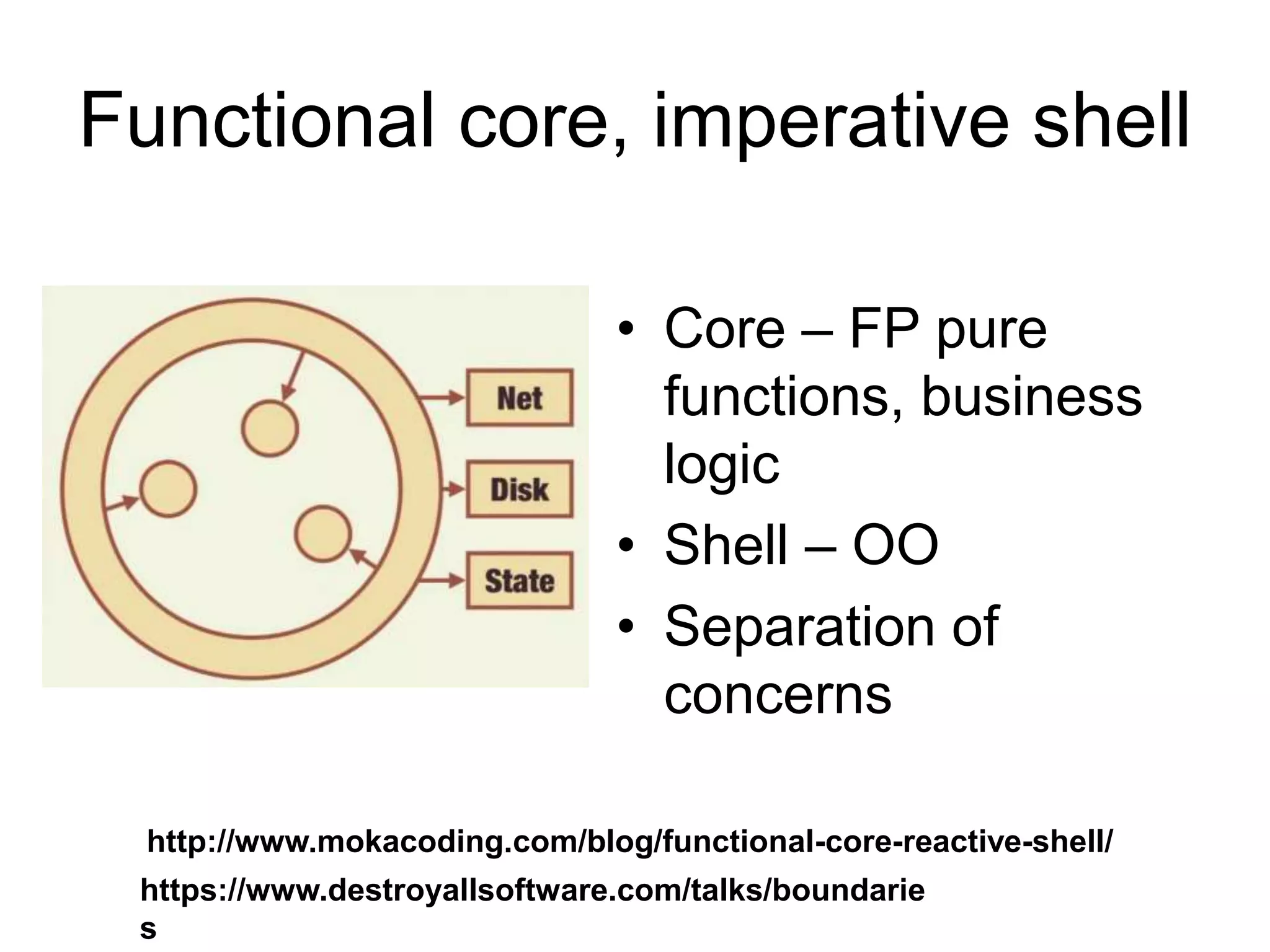
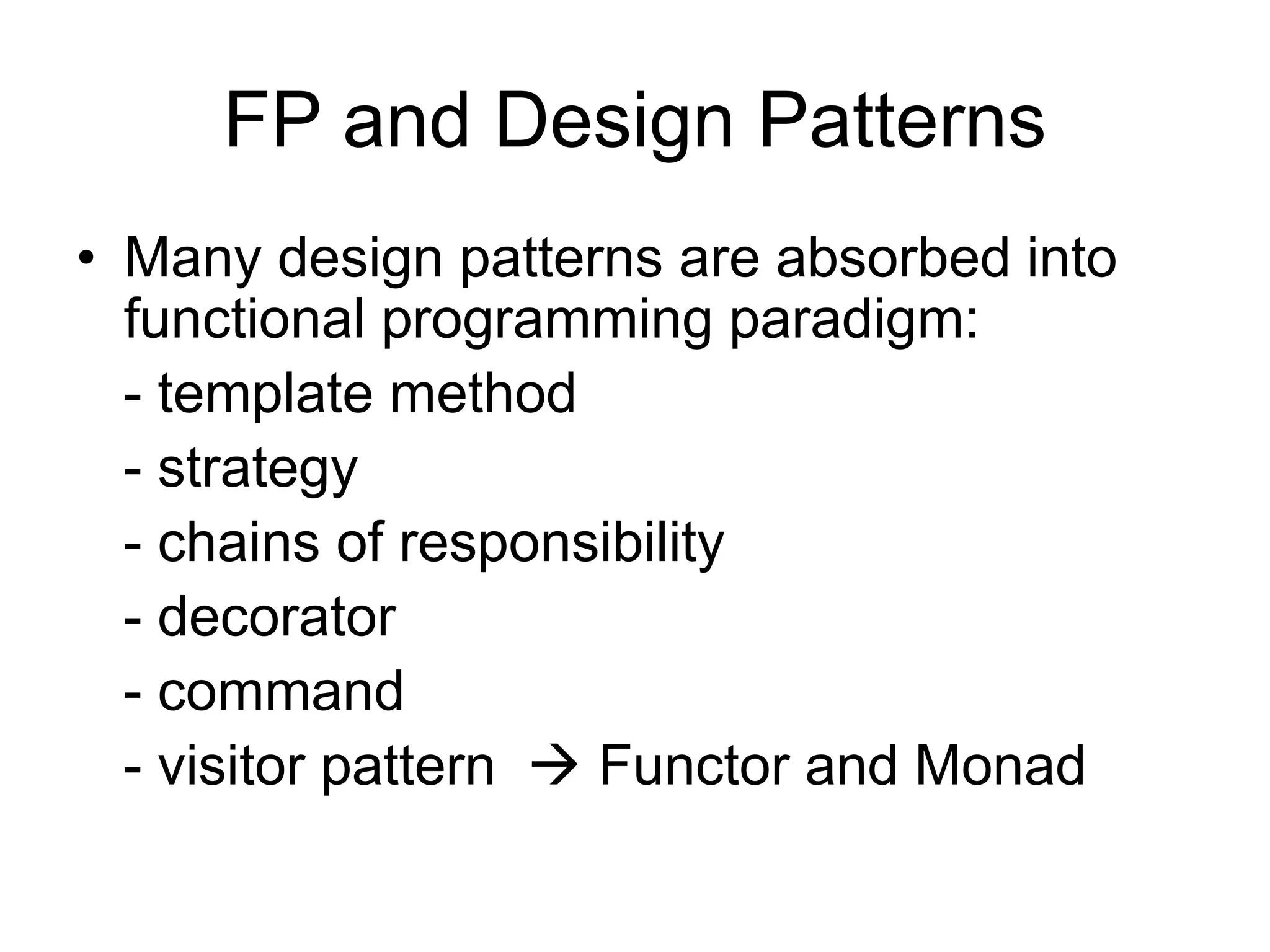
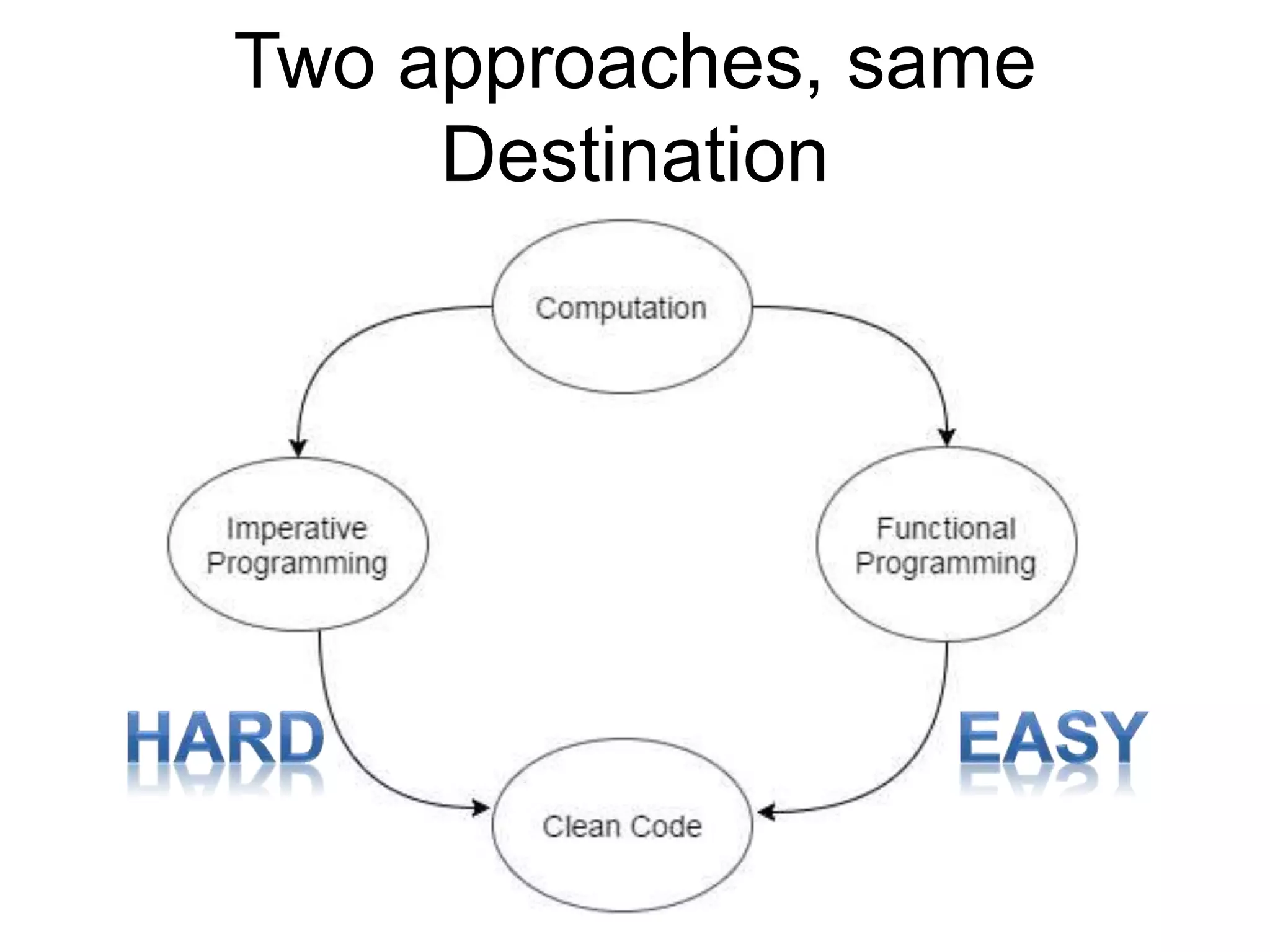
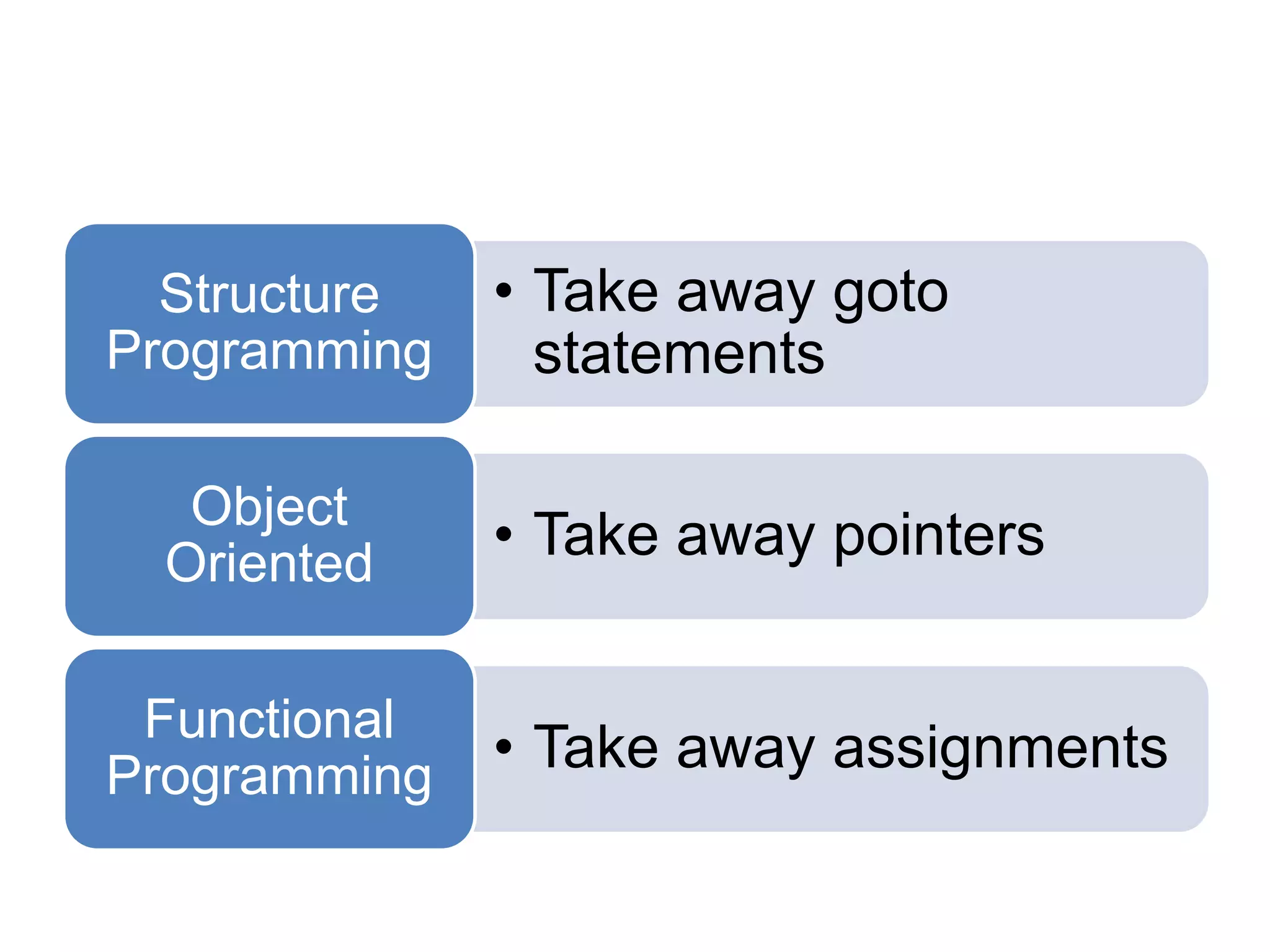
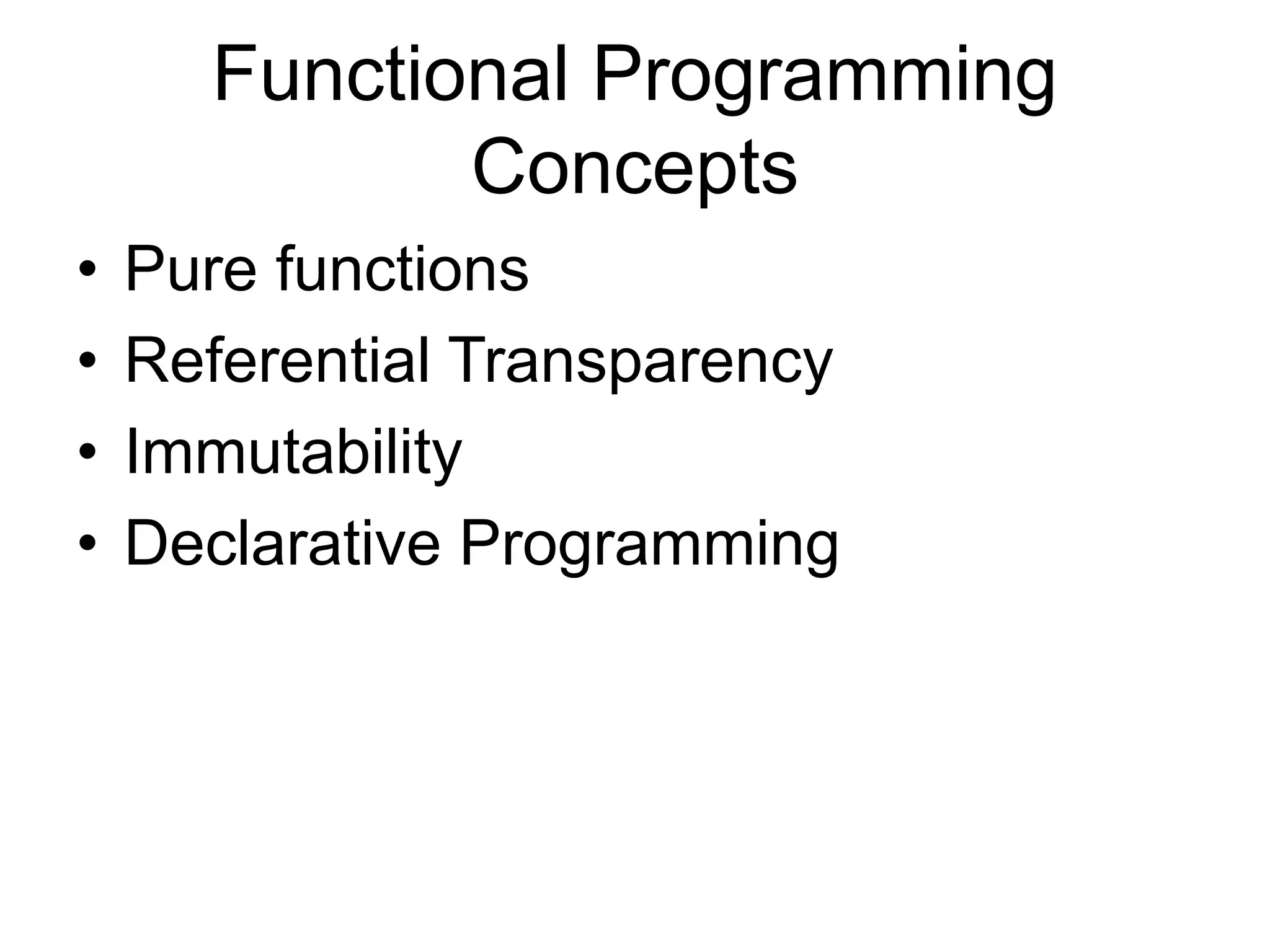
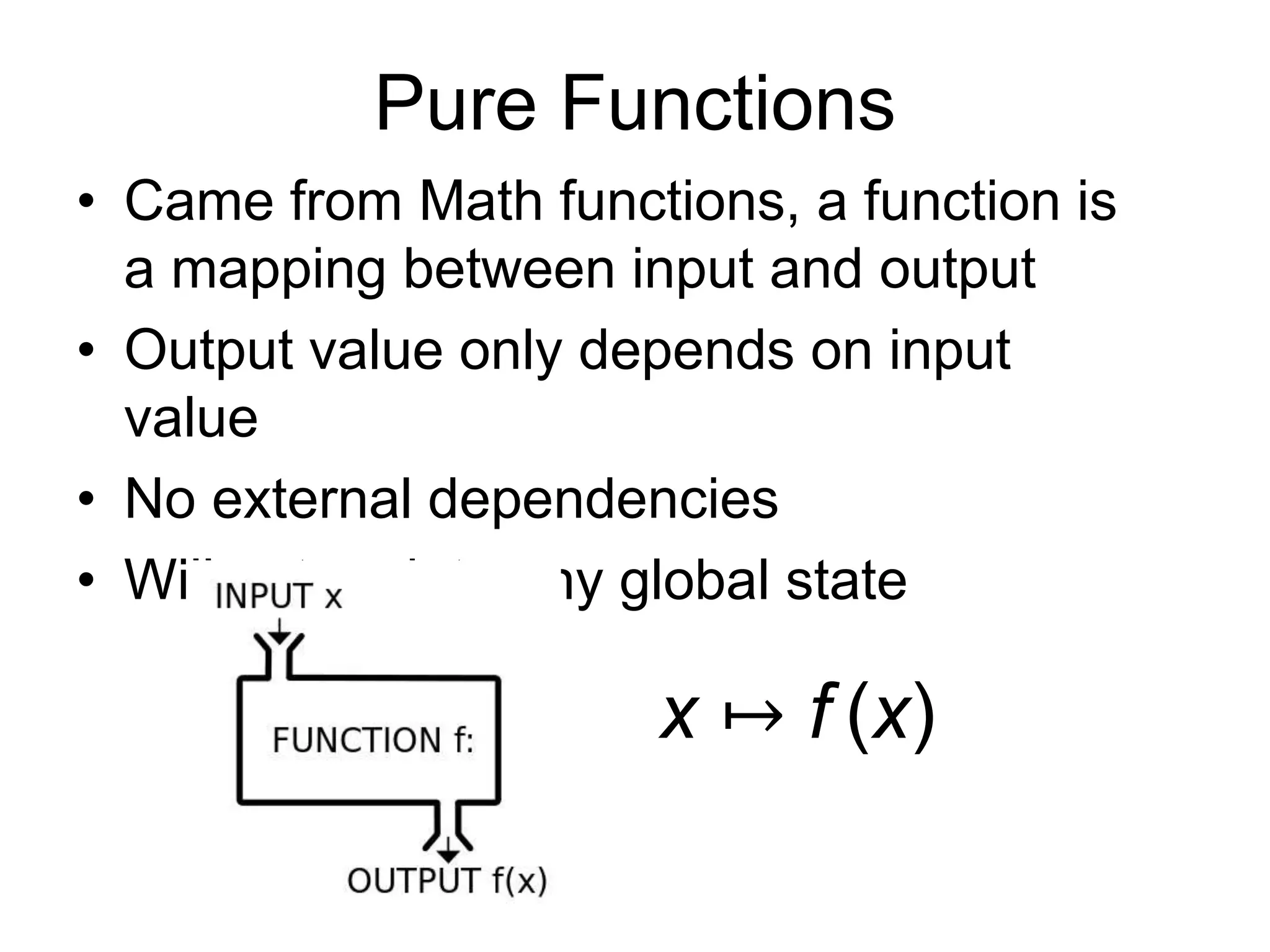
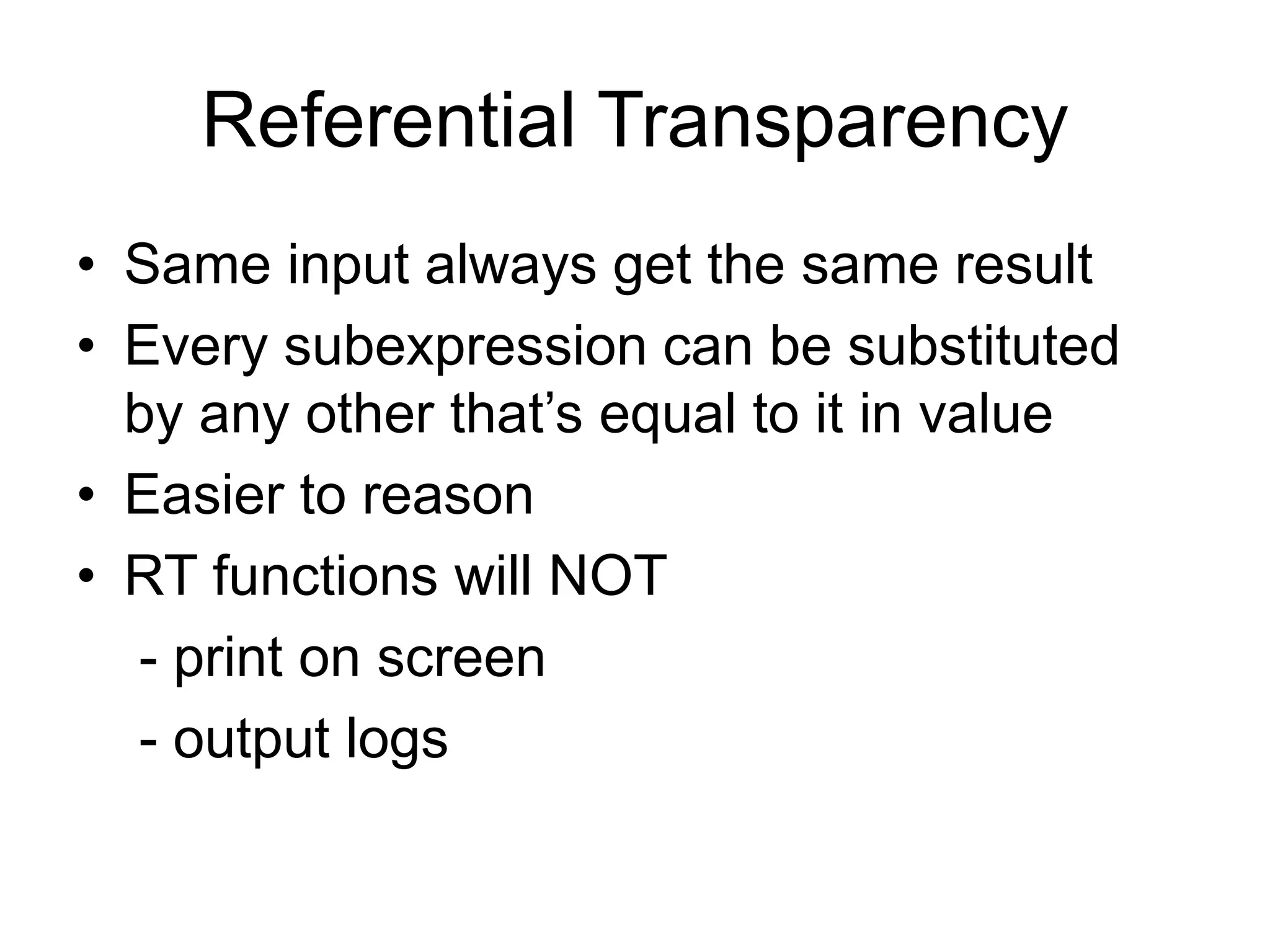
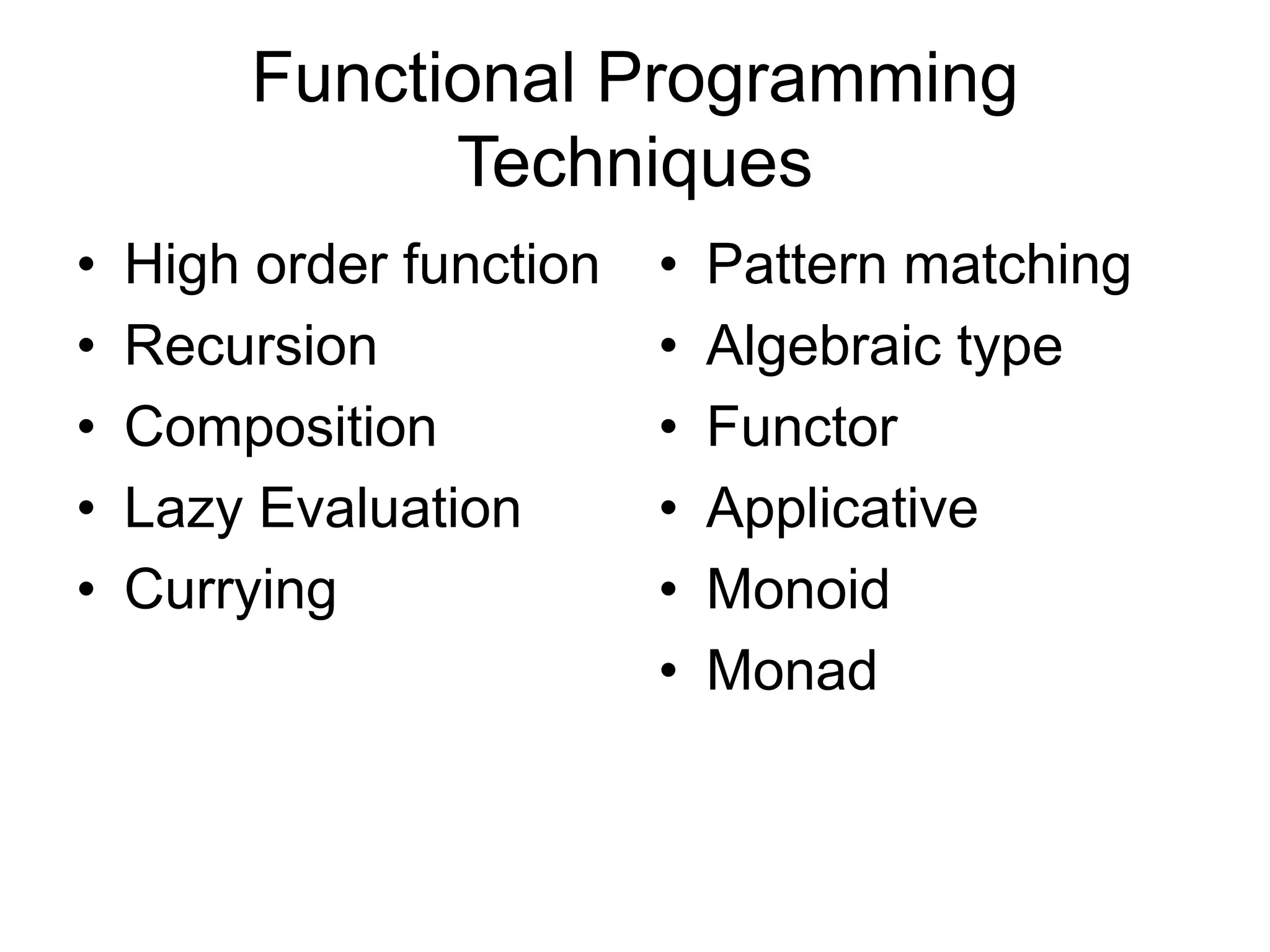
This document discusses functional programming and its benefits. It begins with an overview of functional programming concepts like pure functions, referential transparency, and immutability. It then covers functional programming techniques like higher order functions, recursion, composition, and pattern matching. Examples are given comparing imperative and functional implementations for quicksort and optional types. The document argues that functional programming leads to cleaner code by improving modularity, testability and adherence to SOLID principles. It recommends starting with functional features in existing languages and learning Haskell to fully embrace the functional paradigm.









![Quicksort In C
void quicksort(int *A, int len) {
if (len < 2) return;
int pivot = A[len / 2];
int i, j;
for (i = 0, j = len - 1; ; i++, j--) {
while (A[i] < pivot) i++;
while (A[j] > pivot) j--;
if (i >= j) break;
int temp = A[i];
A[i] = A[j];
A[j] = temp;
}
quicksort(A, i);
quicksort(A + i, len - i);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thejoyoffunctionalprogramming-170813045208/75/The-joy-of-functional-programming-19-2048.jpg)
![Quicksort in Haskell
quicksort :: Ord a => [a] -> [a]
quicksort [] = []
quicksort (p:xs) = (quicksort lesser) ++ [p] ++ (quicksort greater)
where
lesser = filter (< p) xs
greater = filter (>= p) xs](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thejoyoffunctionalprogramming-170813045208/75/The-joy-of-functional-programming-20-2048.jpg)


![Map
map (x -> x*x) [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
[1, 4, 9, 16, 25]
map _ [] = []
map f (x : xs) = f x : map f xs](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thejoyoffunctionalprogramming-170813045208/75/The-joy-of-functional-programming-24-2048.jpg)
![Filter
filter even [1..10] [2,4,6,8,10]
filter _ [] = []
filter p (x:xs)
| p x = x : filter p xs
| otherwise = filter p xs](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thejoyoffunctionalprogramming-170813045208/75/The-joy-of-functional-programming-25-2048.jpg)
![Fold (Reduce)
• sum [1, 5, 10] 16
• product [2,3,4] 24](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thejoyoffunctionalprogramming-170813045208/75/The-joy-of-functional-programming-26-2048.jpg)
![sum [] = 0
sum (x:xs) = x + sum xs
product [] = 1
product (x:xs) = x * product xs
concat [] = []
concat (x:xs) = x ++ concat xs
Identify the
similar structure,
abstract the
common pattern](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thejoyoffunctionalprogramming-170813045208/75/The-joy-of-functional-programming-27-2048.jpg)
![foldr
foldr f z [] = z
foldr f z (x:xs) = f x (foldr f z xs)
sum = foldr (+) 0
product = foldr (*) 1
concat = foldr (++) []](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thejoyoffunctionalprogramming-170813045208/75/The-joy-of-functional-programming-28-2048.jpg)

![Function composition
(f . g) x = f (g x)
( sum . take 5 . filter even ) [1..100]
ls -l | grep key | less
functions are Lego bricks, they are easily
assembled](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thejoyoffunctionalprogramming-170813045208/75/The-joy-of-functional-programming-30-2048.jpg)