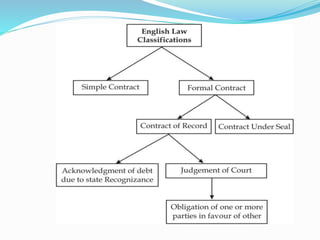
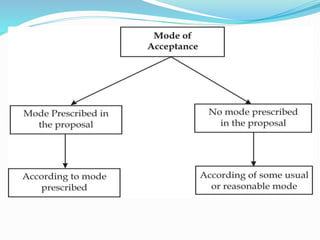
This document provides an introduction to Indian contract law. It summarizes that a contract requires an agreement between two parties that creates a legal obligation. The key elements of a valid contract are offer and acceptance, intention to create legal relations, lawful consideration, capacity of the parties, free consent, lawful object, and certainty of terms. It outlines the main principles of contract law in India as defined in the Indian Contract Act of 1872, including defining a contract, the essential elements, and specific types of contracts such as indemnity, guarantee, bailment, and agency.