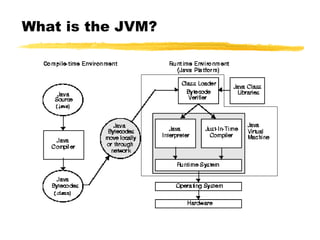
The document provides an overview of the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) from multiple perspectives:
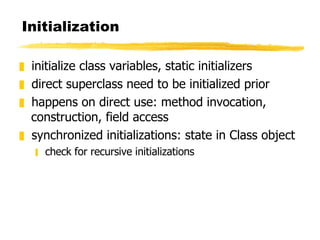
- It discusses the operational view of how the JVM loads, links, executes and exits from a Java program. This includes class loading, linking, initialization and object lifetime.
- It also presents the structural view of the JVM specification versus implementation and key distinctions like object layout and garbage collection being outside the specification.
- Examples are provided to illustrate static initialization order and object creation on the JVM.








![Example class Super { static { System.out.print(“Super “); } class One { static { System.out.print(“One “); } class Two extends Super { static { System.out.print(“Two “); } class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { One o = null; Two t = new Two(); System.out.println((Object)o == (Object)t); } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/testing-ppt2448/85/testing-ppt-12-320.jpg)
![Example class Super { static int taxi = 1729; } class Sub extends Super { static { System.out.print(“Sub “); } class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(Sub.taxi); } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/testing-ppt2448/85/testing-ppt-13-320.jpg)


