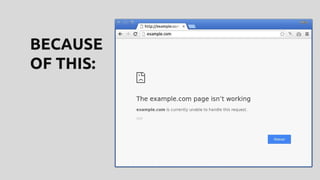
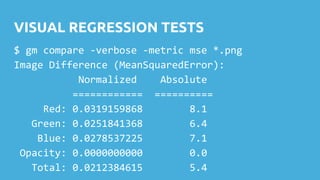
This document discusses techniques for safely updating WordPress core and plugins to avoid regressions. It recommends setting up a "shadow" test site to first update and thoroughly regression test plugins and themes before deploying updates to the production site. Integration tests can automate aspects of regression testing by programmatically interacting with and validating the site. Visual regression testing can additionally detect layout or design changes. While most updates can be safely automated, some human oversight is still important to determine if changes constitute failures.