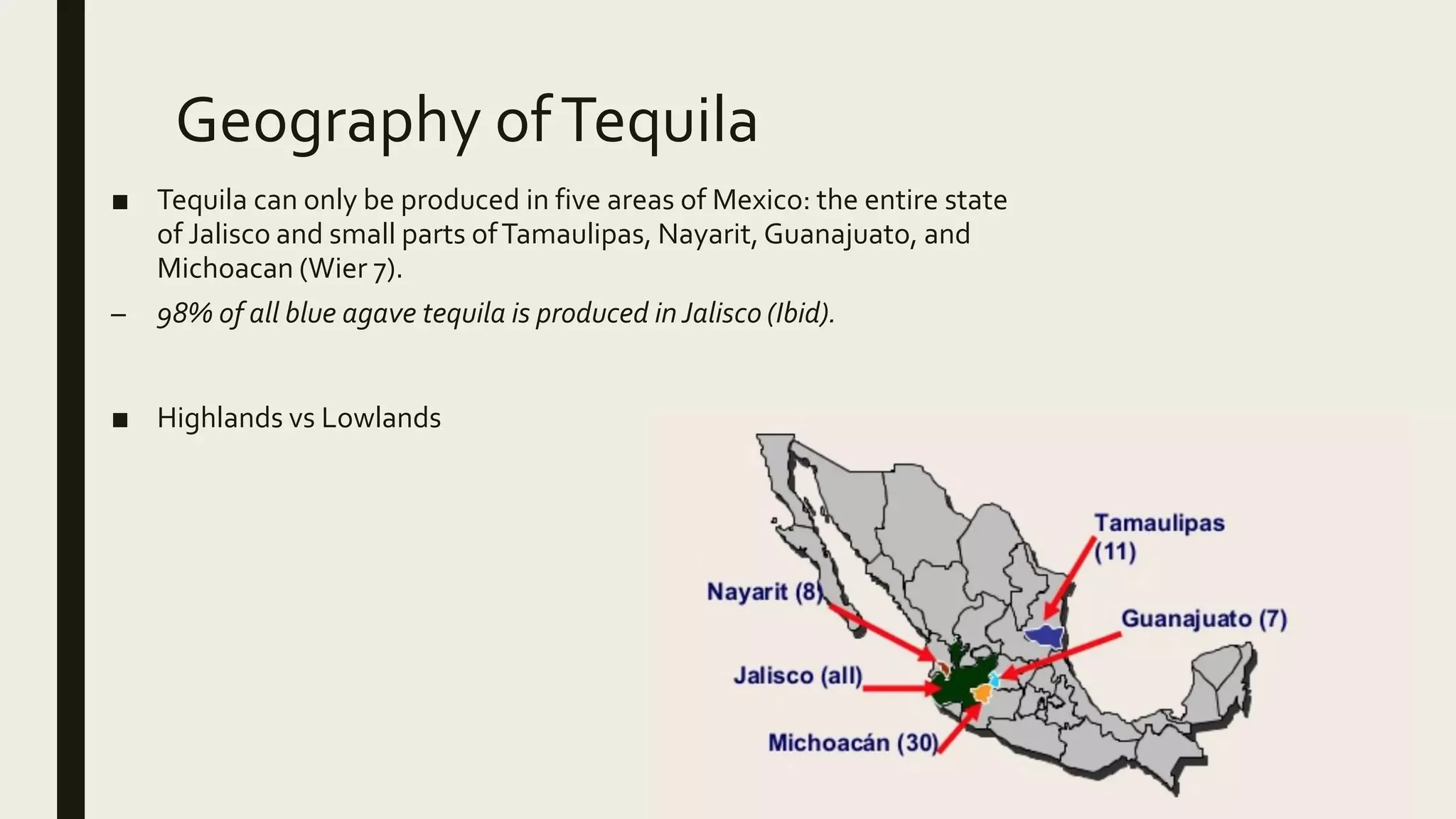
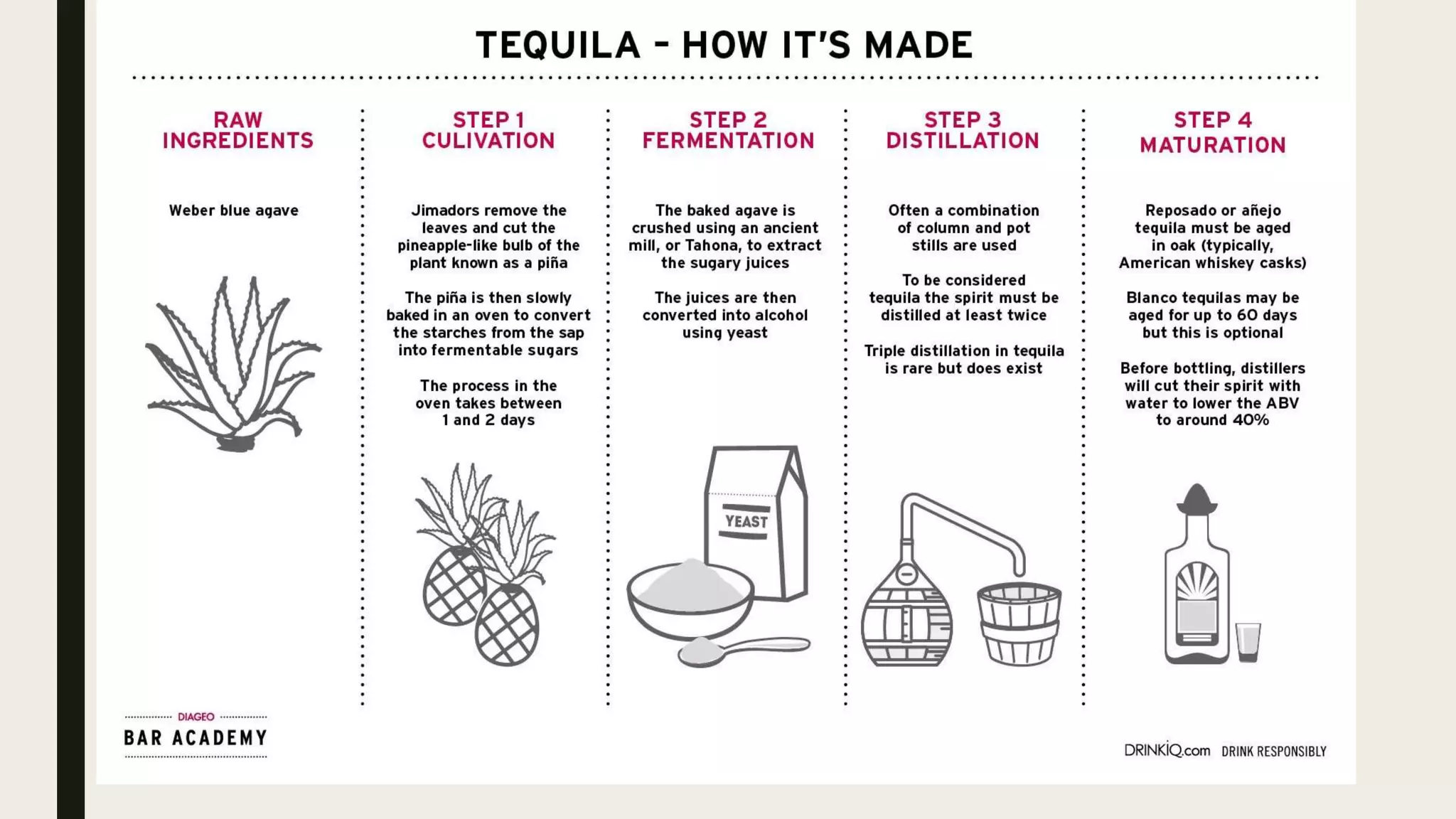
Tequila can only be produced from the blue agave plant, which grows in specific regions of Mexico. The plant's core, or pina, is cooked, crushed, fermented and distilled. Tequila must contain at least 60% blue agave according to Mexican regulations established in the 1970s. There are several types of tequila defined by aging periods - blanco/silver is bottled immediately, reposado is aged under a year, anejo 1-3 years, and extra anejo over 3 years. Tequila adds distinctive flavors from its production process and aging.