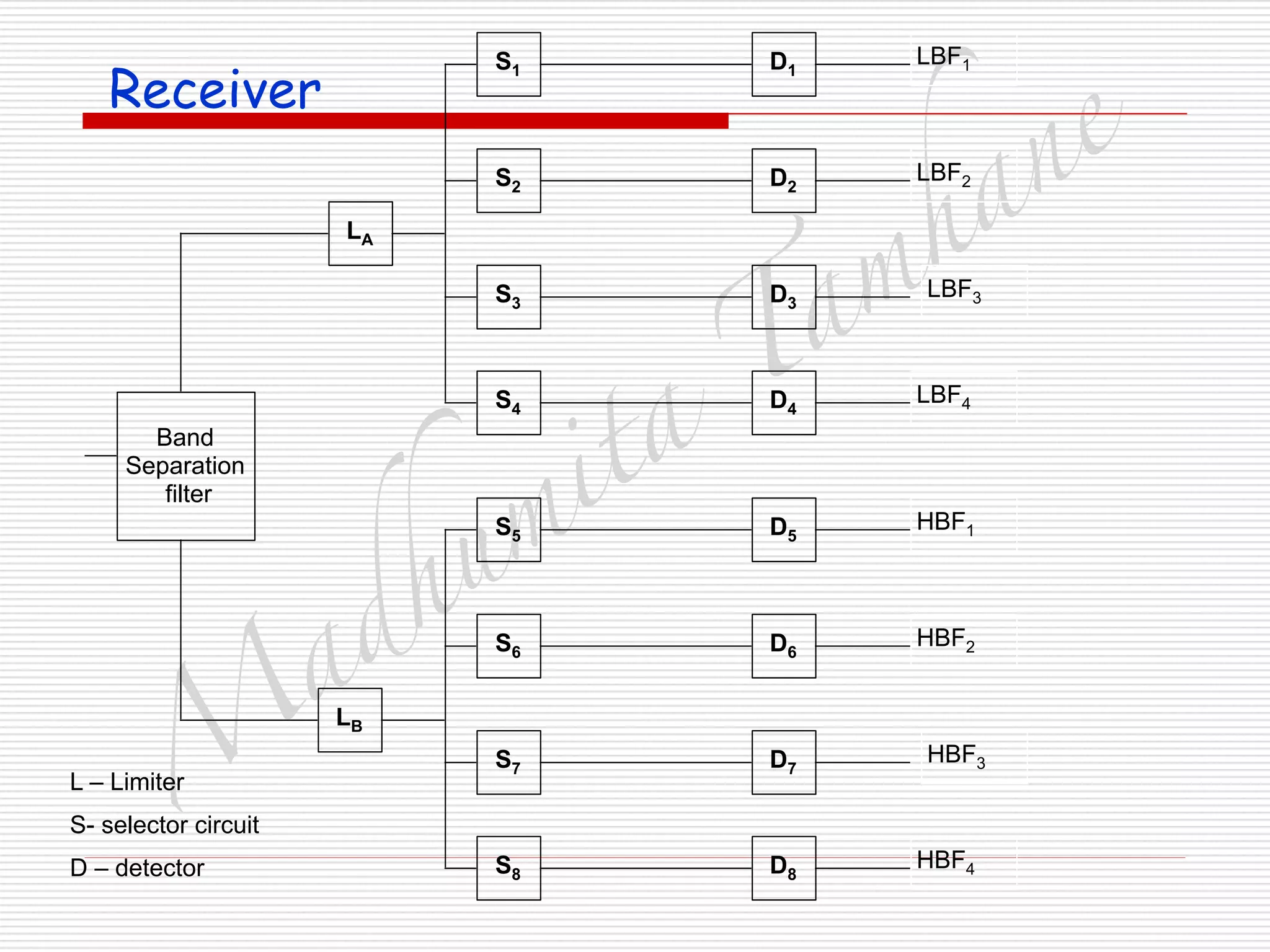
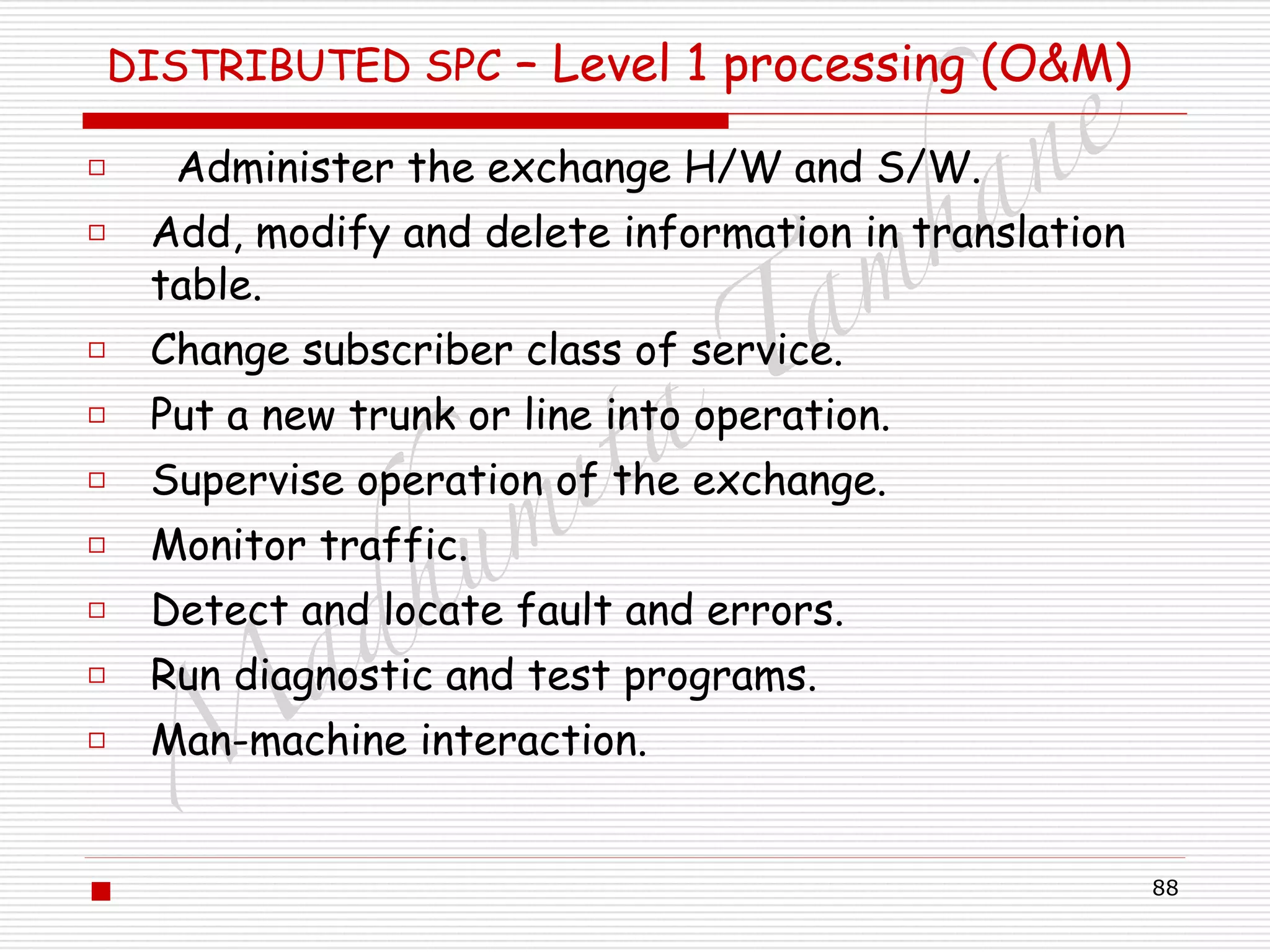
This document discusses simple telephone communication systems and their components. It describes how a carbon microphone works as an amplitude modulator to transmit sound signals along the line. An inductor allows DC current to flow while acting as a high impedance element for voice signals. At the receiver, an electromagnet converts the electrical signals back into sound waves. Early telephone systems used half duplex communication and included sidetone circuits to allow users to hear themselves. The document also covers the components and operation of local battery and central battery telephone exchanges.
















































![M
adhum
ita
T
am
hane
72
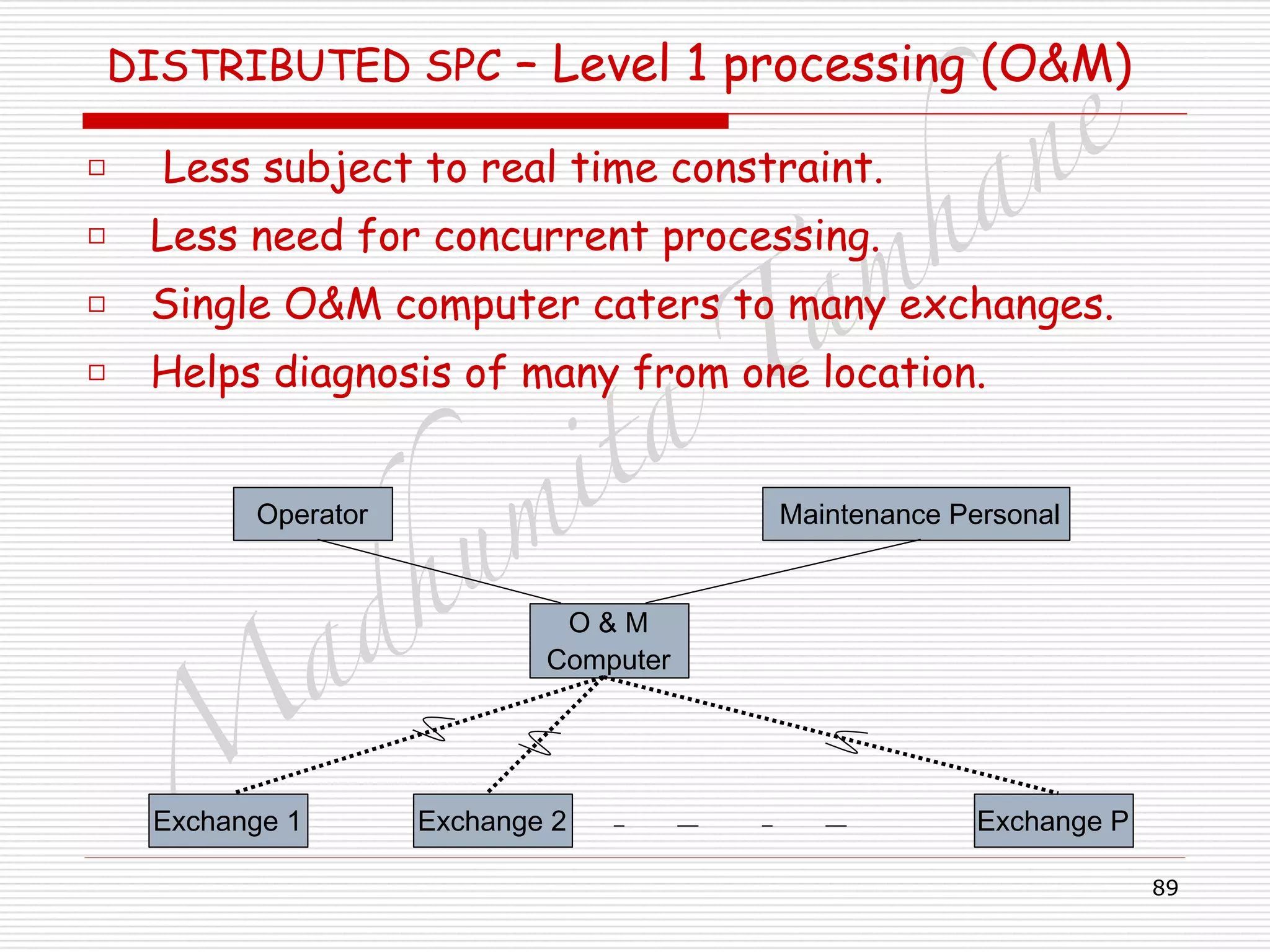
Availability of the Dual processor system
□ AD = MTBFD/ (MTBFD+ MTTR)
□ AD = (MTBF)2
/ [(MTBF)2
+ 2(MTTR)2
]
□ UD = 1- AD
□ = 2(MTTR)2
/ [(MTBF)2
+ 2(MTTR)2
]
□ If MTBF>>MTTR
□ UD = 2(MTTR)2
/ (MTBF)2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/telecommunicationswitchingsystem-160420152411/75/Telecommunication-switching-system-72-2048.jpg)










![M
adhum
ita
T
am
hane
96
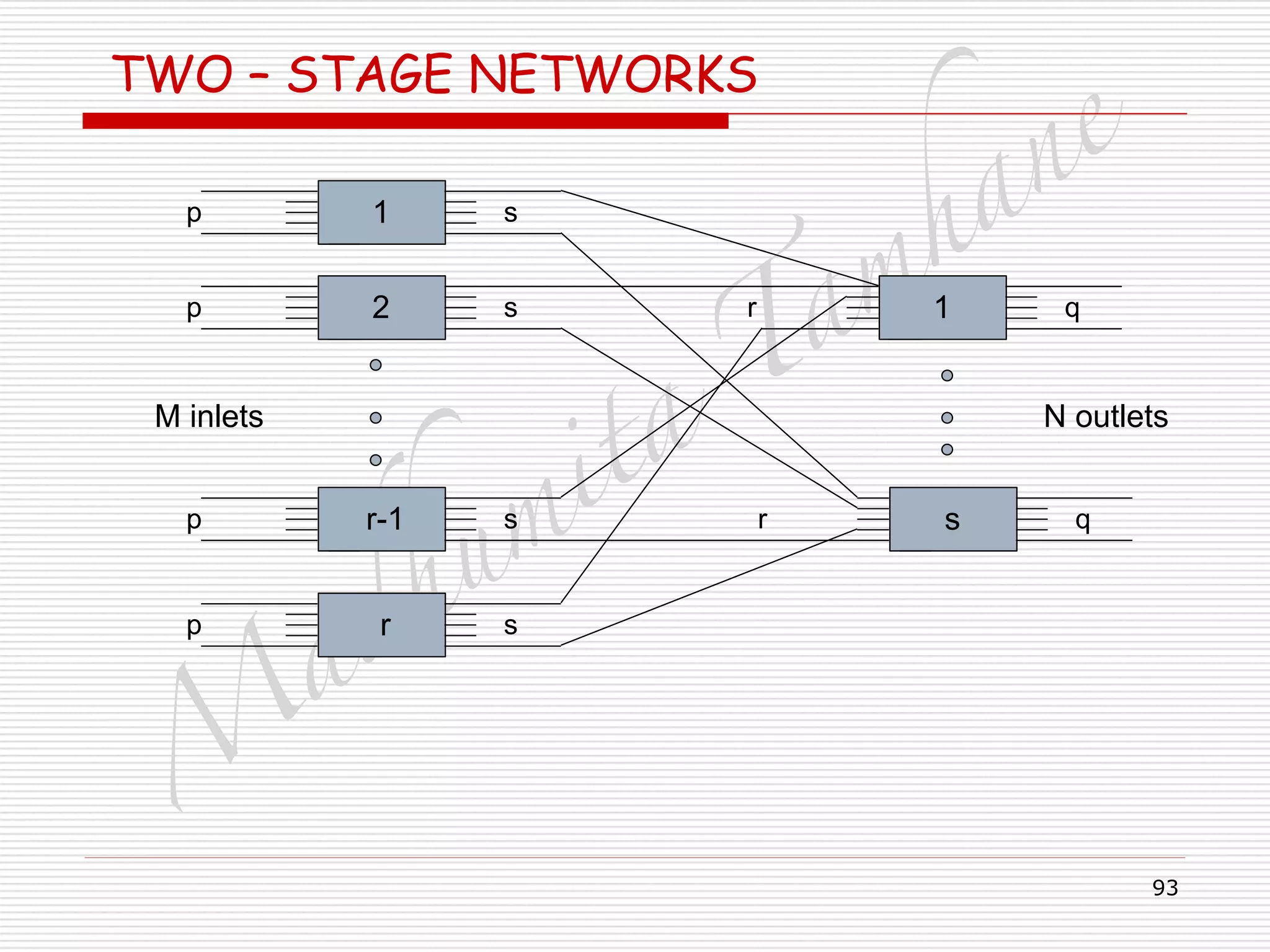
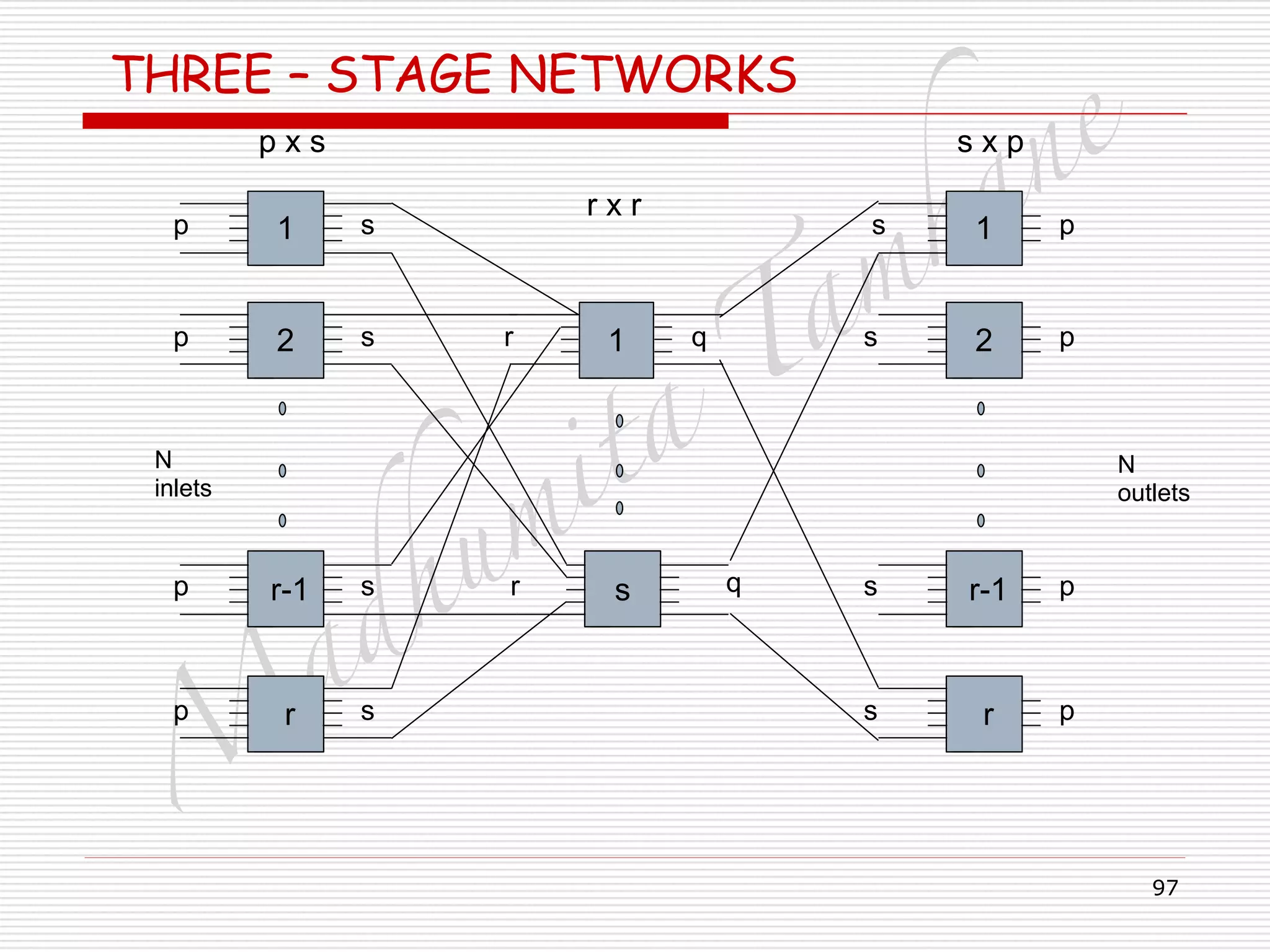
TWO – STAGE NETWORKS
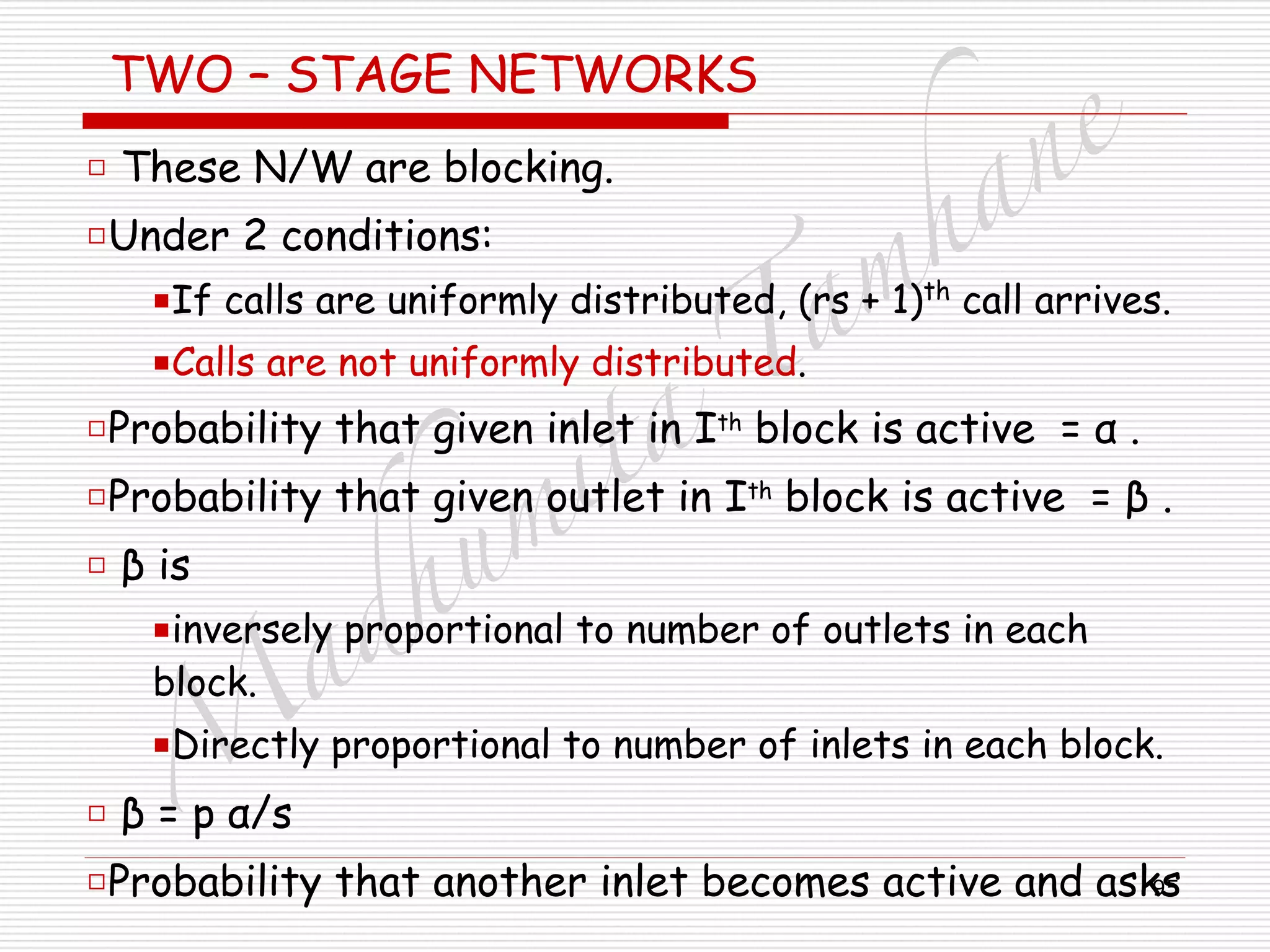
□ Blocking means –
□ All outlets are already active, and no free outlets.
□ The probability that an already active outlet is sought =
□ = probability that the particular outlet is active AND
□ other outlets are not sought.
□ PB = p α/s[1-{(p-1) α/(s-1)}]
□ If p = M/r
!
□ PB = {M α(s-1) – ((M/r) –1) α} / {rs(s-1)}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/telecommunicationswitchingsystem-160420152411/75/Telecommunication-switching-system-96-2048.jpg)








![M
adhum
ita
T
am
hane
110
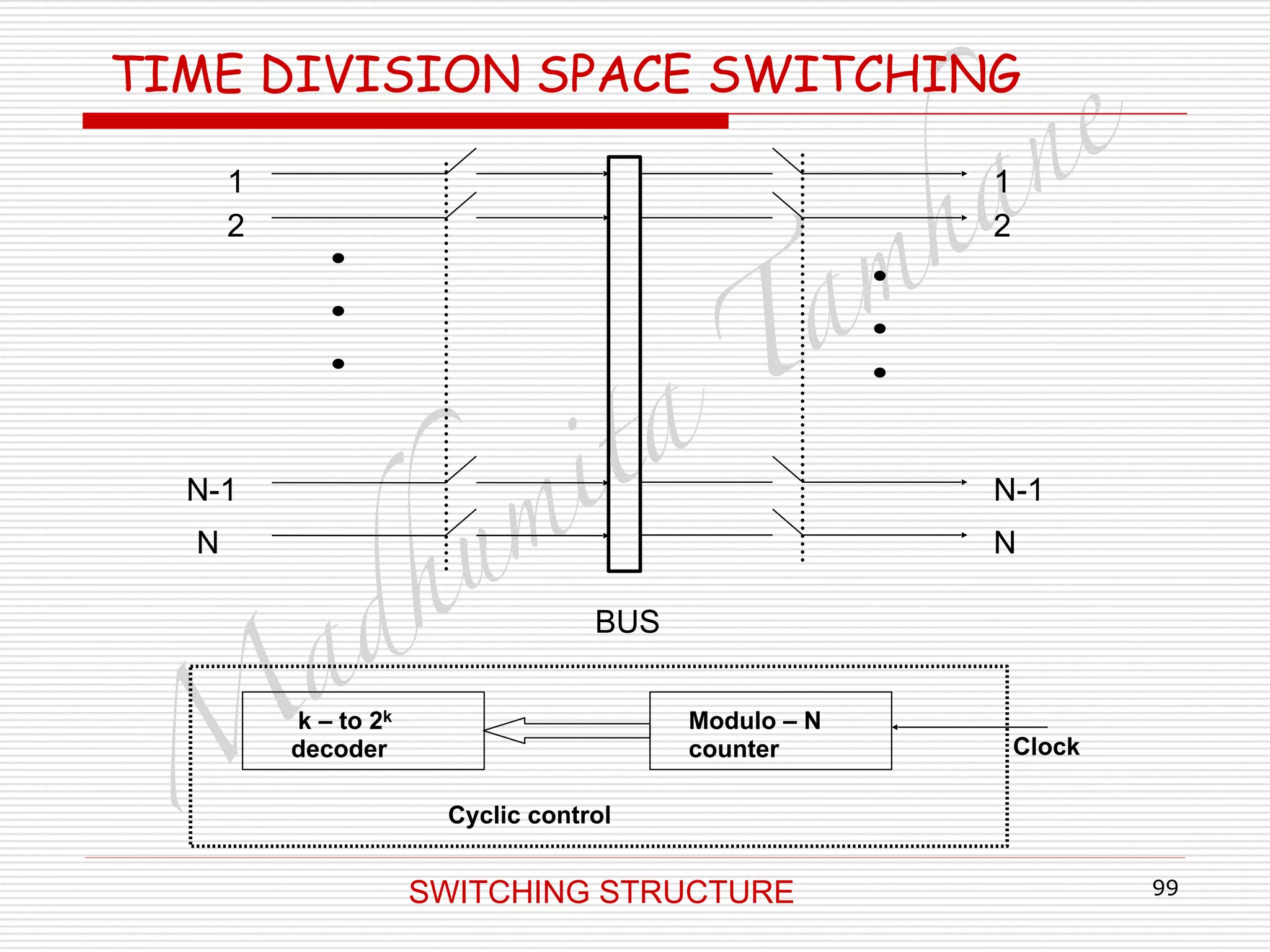
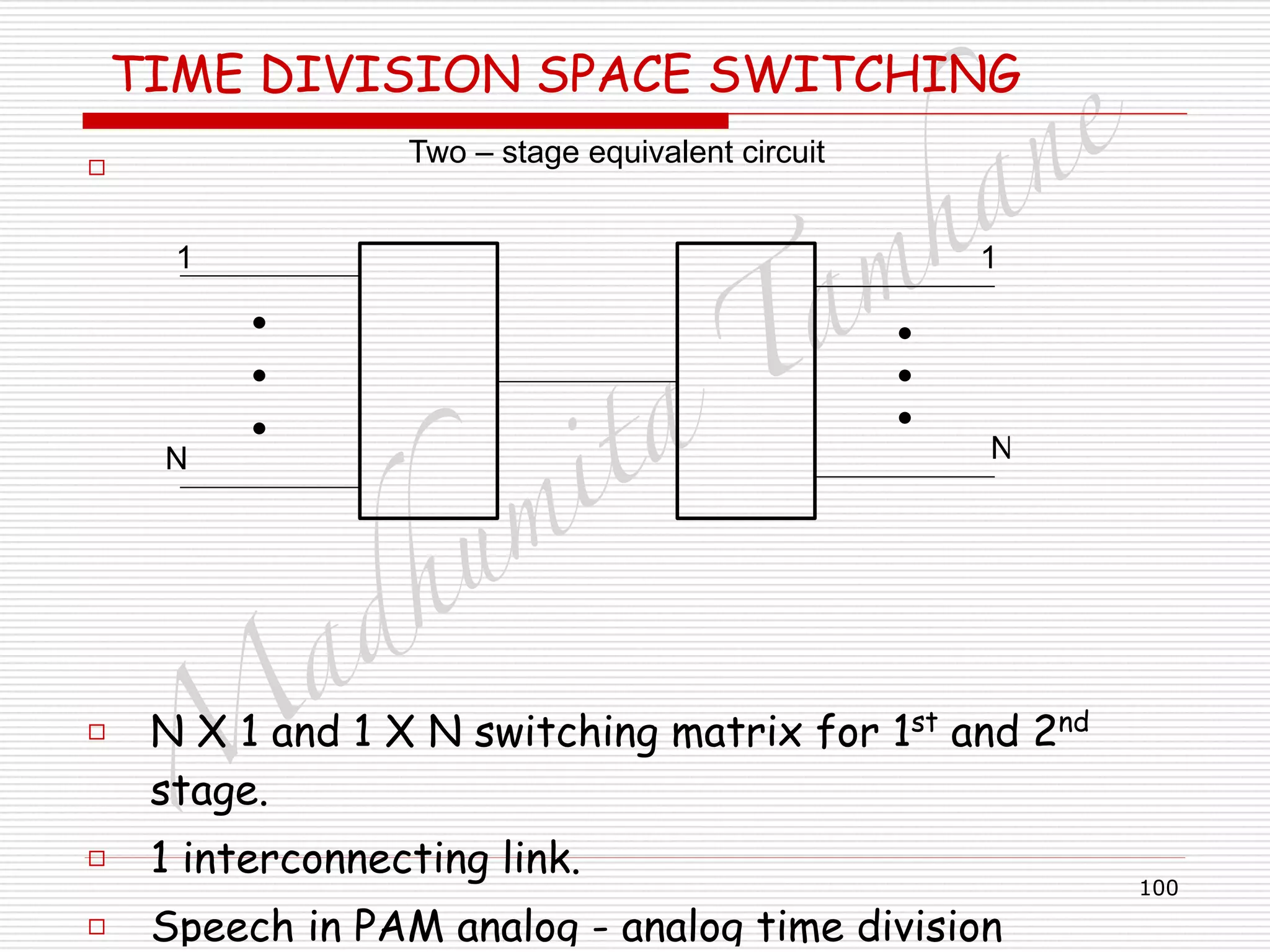
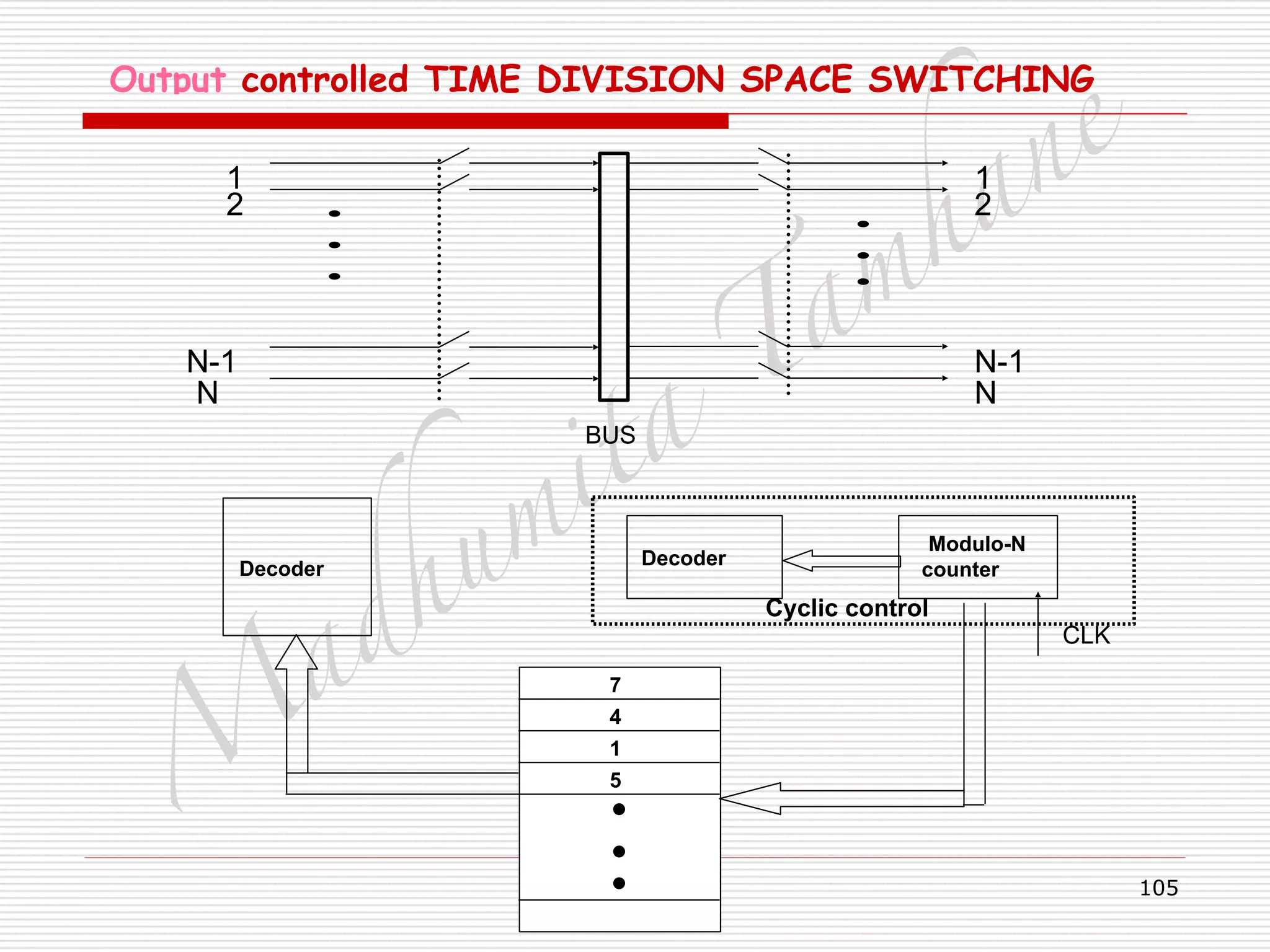
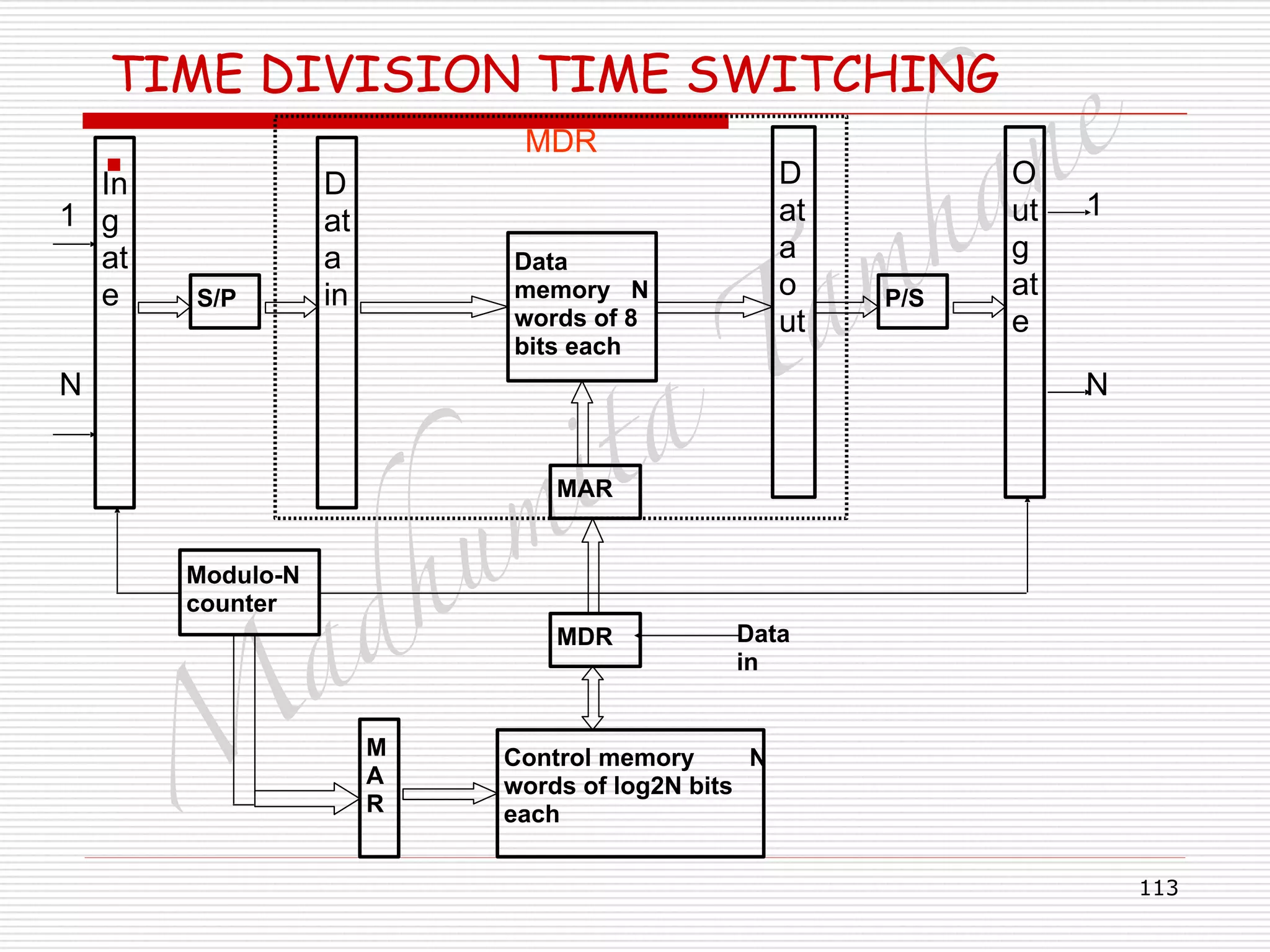
Generalised TIME DIVISION SPACE SWITCHING
□ Control memory word has two address.
□ Inlet and out let address.
□ Word width is 2[log2N] bits.
□ Operation:
□ Inlet k and outlet j addresses entered into free
location of control memory via data input.
□ The Location then marked busy.
□ Modulo – SC counter updated at clock rate.
□ Control memory word read out one by one.
□ Addresses are used to connect respective inlet and
outlet.
□ Sample transferred from inlet to outlet.
□ Clock updates counter.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/telecommunicationswitchingsystem-160420152411/75/Telecommunication-switching-system-110-2048.jpg)








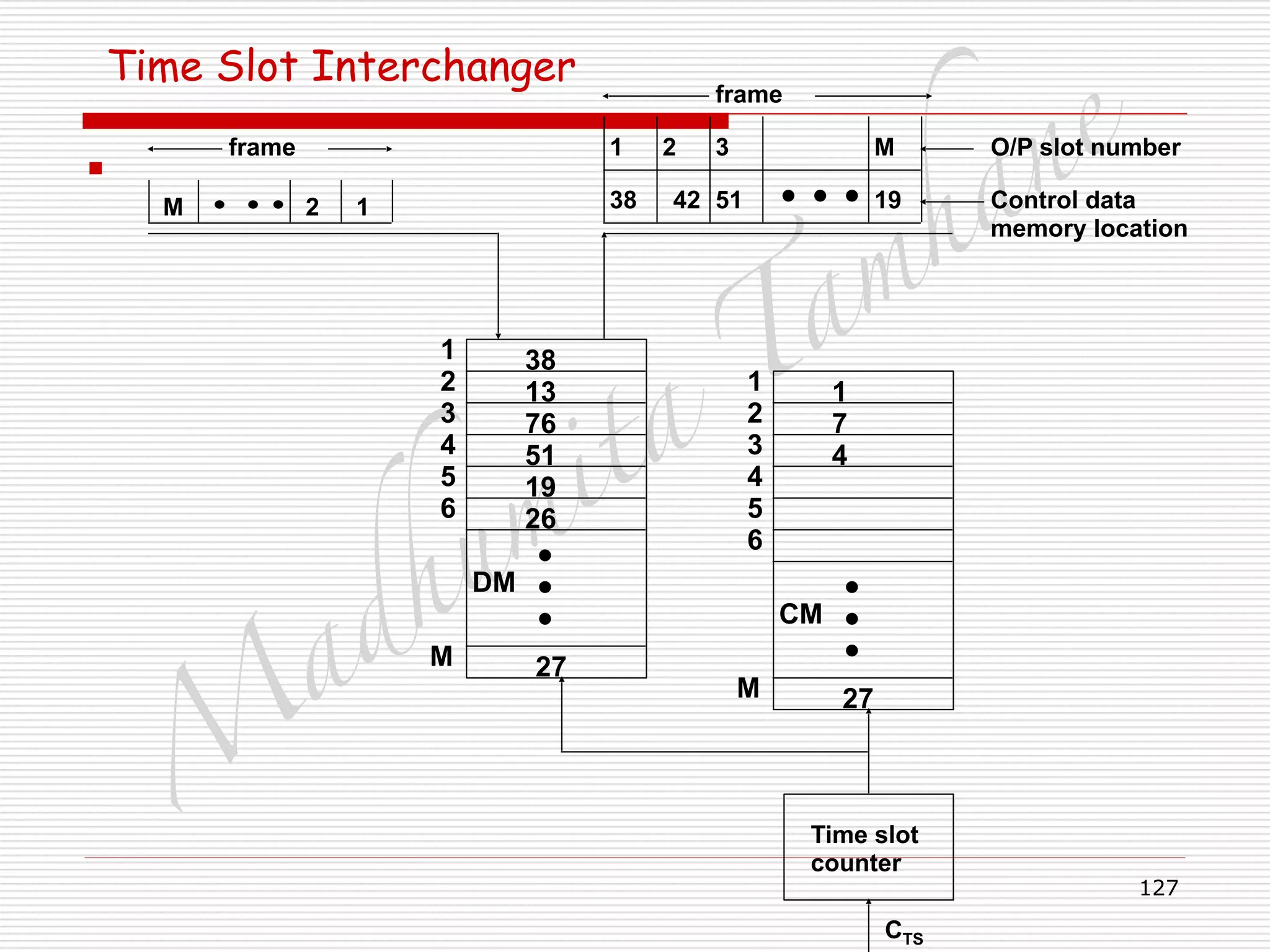
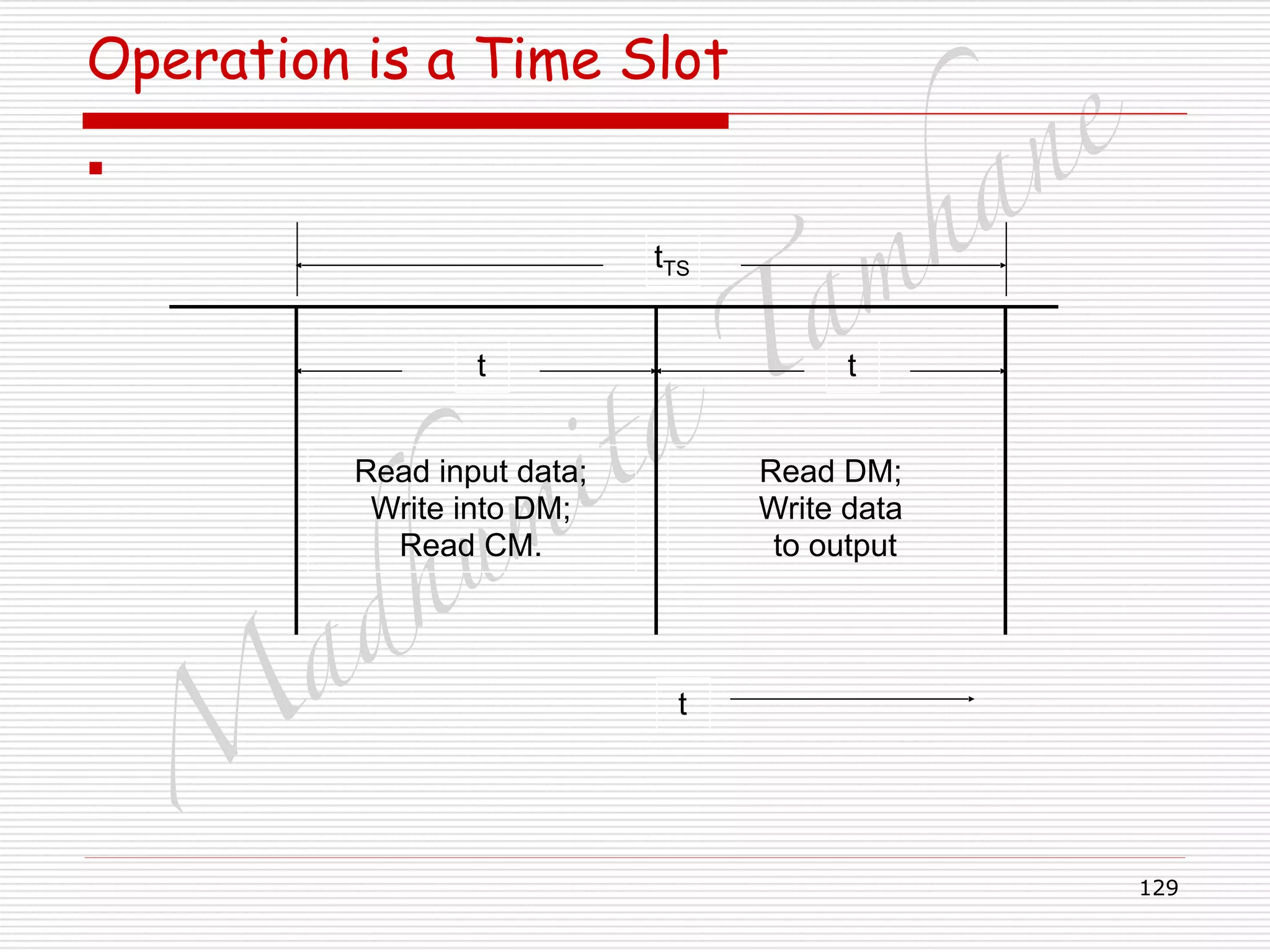

![M
adhum
ita
T
am
hane
131
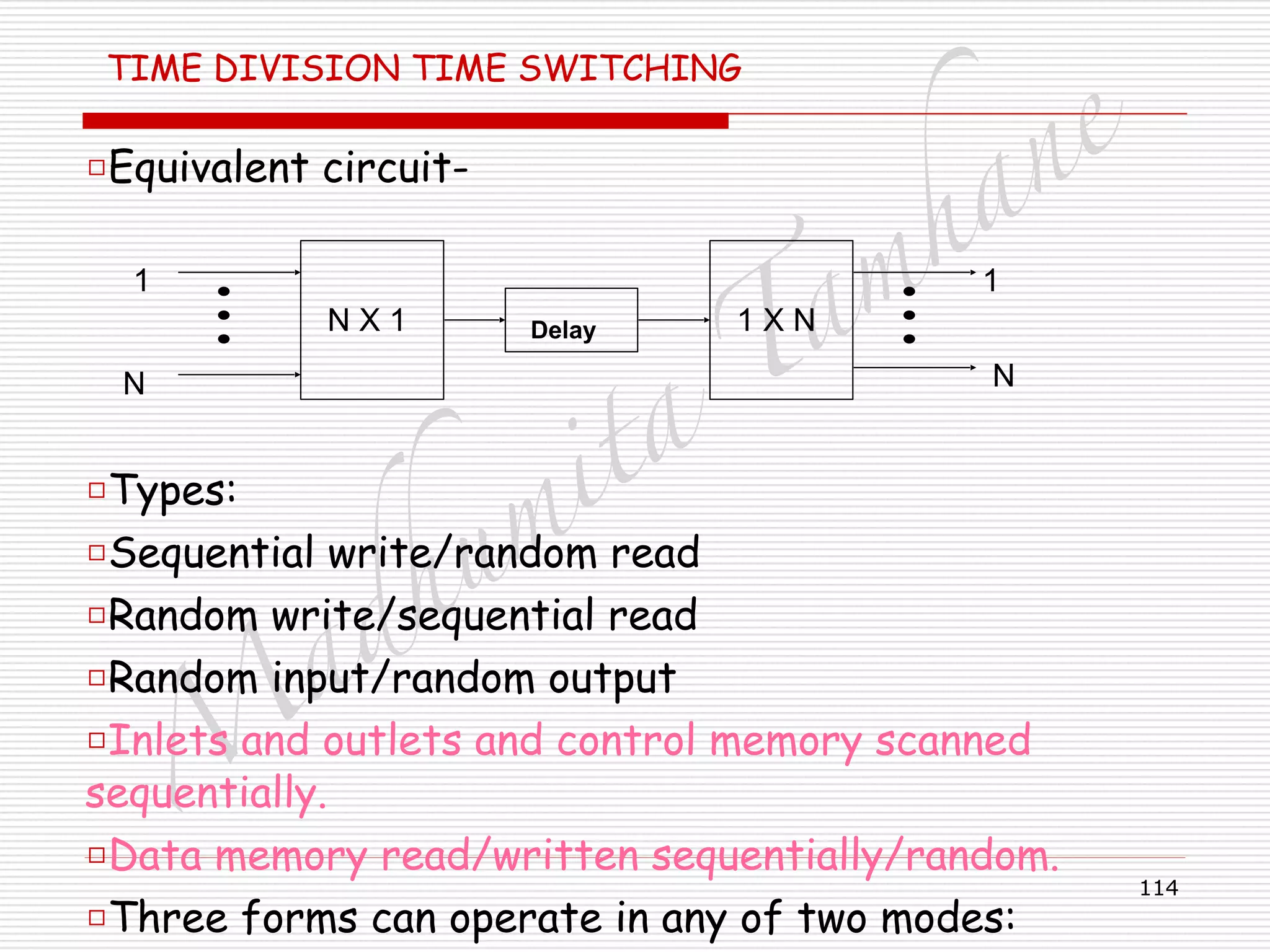
Time Slot Interchanger
□ Delay depends on to which output slot, input slot is
switched.
□ Previous cycle, all DM is filled/ written in.
□ In current cycle, CM is read for DM address.
□ CM1 =1, contents of DM1 switched to O/P1.
□ Current contents can be switched only in this case.
□ Delay tTS microseconds.
□ CM2=7, contents of DM7 switched to O/P 2.
□ Delay = [(M-7)+2+1] tTS = (M-4) tTS microseconds.
□ CM3=4, contents of DM4 switched to O/P 3.
□ Delay = [(M-4)+3+1] tTS = M tTS microseconds.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/telecommunicationswitchingsystem-160420152411/75/Telecommunication-switching-system-131-2048.jpg)