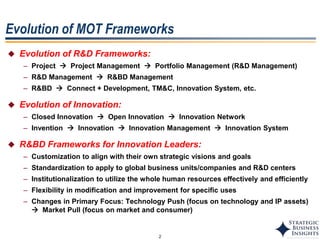
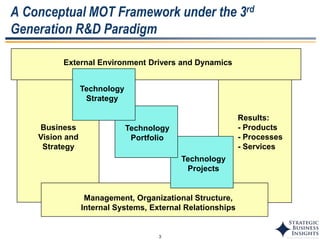
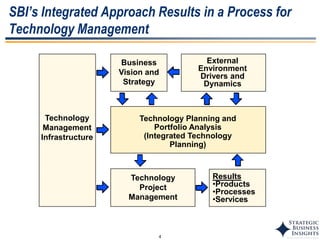
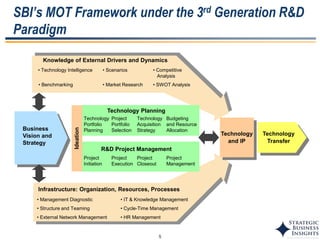
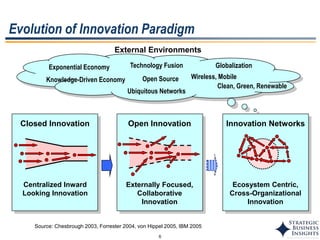
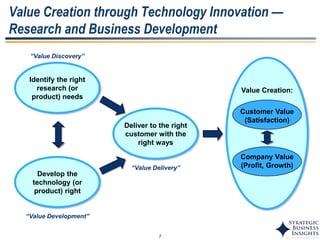
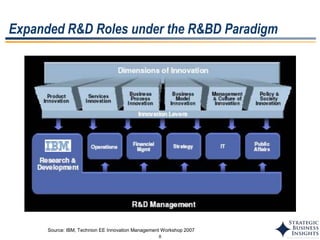
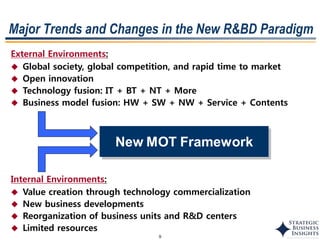
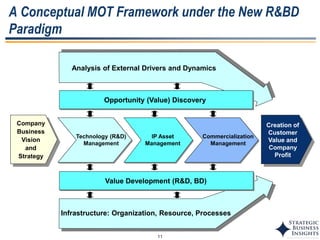
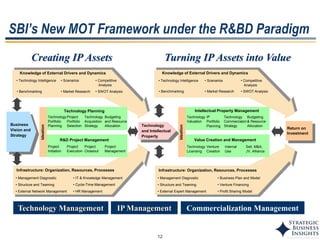
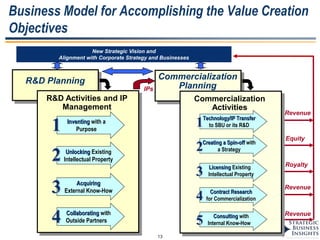
The document discusses the evolution of MOT (Management of Technology) frameworks from focusing solely on R&D projects to a more holistic approach integrating business strategy, commercialization, and intellectual property management. It proposes a new MOT framework to help organizations create value through technology innovation under the new "R&BD" (Research, Business Development) paradigm. The framework includes elements such as analyzing external drivers, infrastructure, technology planning, project management, commercialization management, and IP asset management. Key success factors for organizations adopting the new MOT framework include leadership commitment, institutionalizing the framework through training, creating an innovation culture, and diversifying technology commercialization paths.