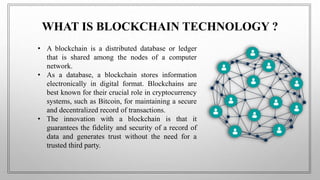
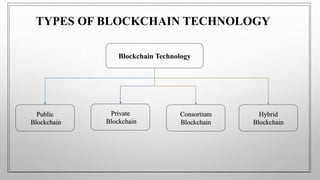
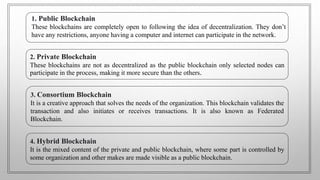
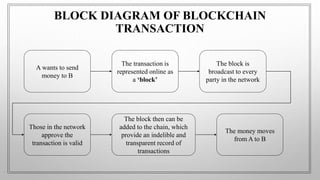
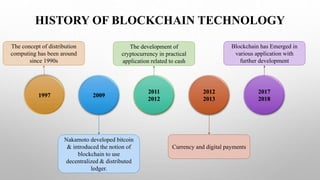
The document discusses blockchain technology. It begins by defining blockchain as a distributed database or ledger that is shared among computer networks to record transactions in a secure and decentralized manner. It then covers the fundamentals of blockchain including public distributed ledgers, encryption, proof of work, and mining. The document discusses different types of blockchain technologies and why decentralization is important. It outlines several applications of blockchain and covers the history and advantages/disadvantages. In conclusion, it discusses how blockchain is growing across many industries where trust is desired without a centralized authority.