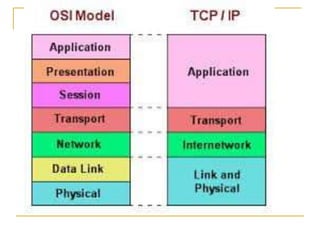
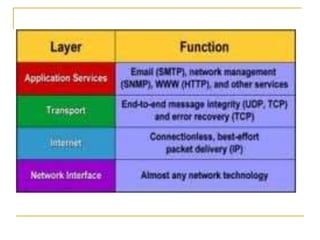
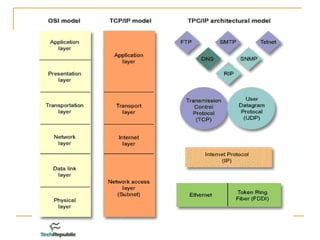
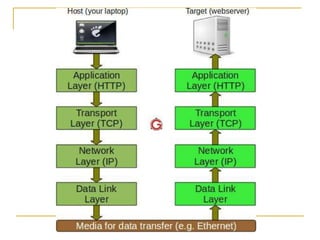
The TCP/IP model is composed of four layers: Application, Transport, Internet, and Network. The two most important protocols are TCP and IP, which operate at the Transport and Internet layers, respectively. TCP provides reliable data transmission with error checking and UDP provides a simpler transmission method without these checks. Common protocols like HTTP, SMTP, and TFTP reside at the Application layer and utilize either TCP or UDP depending on their reliability needs. The Network layer handles physical addressing and routing of data between devices using protocols like ARP, PPP, and Ethernet.