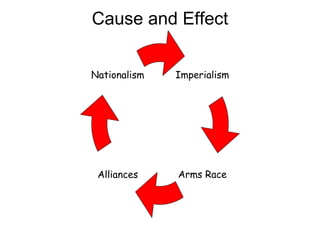
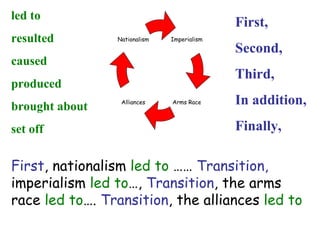
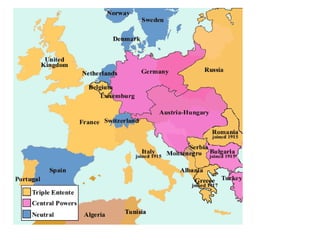
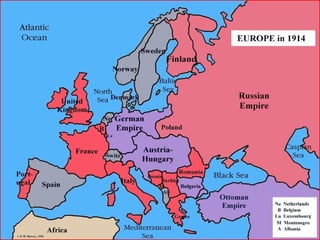
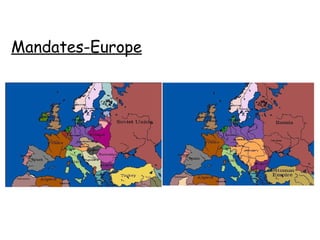
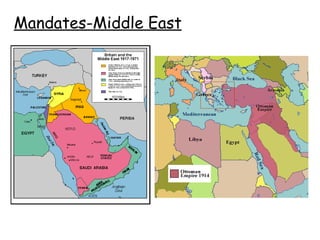
1. Multiple long-term factors contributed to the outbreak of World War 1, including nationalism, imperialism, militarism, and a web of alliances across Europe.
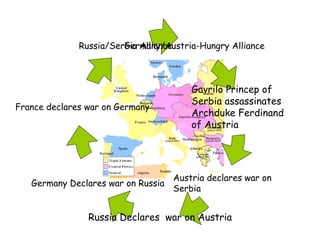
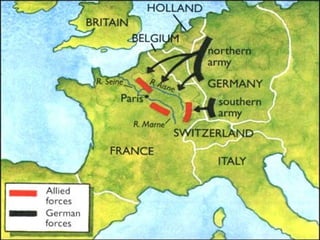
2. When Archduke Ferdinand of Austria-Hungary was assassinated by a Serbian nationalist in 1914, this triggered a series of escalating events and declarations of war as countries were pulled into conflict through their alliance systems.
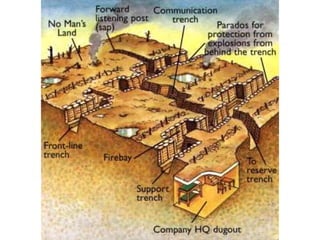
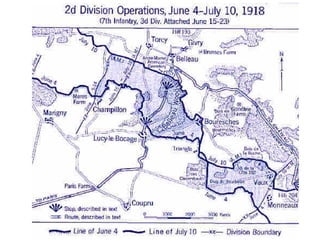
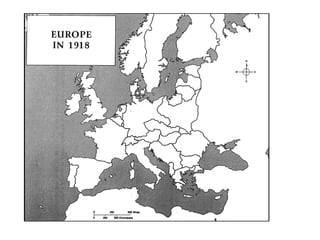
3. The war quickly evolved into a bloody stalemate as armies engaged in trench warfare along the Western Front, resulting in massive casualties with little territorial gain over the next four years until the Allied powers were eventually able to break the stalemate and force Germany's surrender in November 1918.