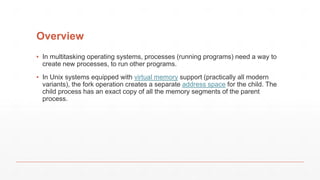
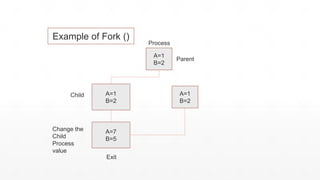
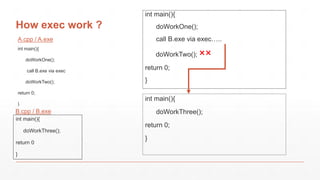
Fork() is a system call that creates a new process by duplicating the calling process. The child process created by fork() is an exact duplicate of the parent process, having the same memory space and file descriptors. Exec() is another system call that replaces the current process with a new executable, keeping the same process ID. It is commonly used along with fork() to launch new programs from within a process. Fork() alone does not replace the process image - it is used to create a new process while exec() replaces the current process image with a new program.











![C language prototypes
int execl(char const *path, char const *arg0, ...);
int execle(char const *path, char const *arg0, ..., char const *envp[]);
int execlp(char const *file, char const *arg0, ...);
int execv(char const *path, char const *argv[]);
int execve(char const *path, char const *argv[], char const *envp[]);
int execvp(char const *file, char const *argv[]);
“ l ” is specified as a list of arguments.
“ v “ is specified as a vector (array of character pointers).
“ e “ environment is specified as an array of character pointers.
“ p “ user's PATH is searched for command, and command can be a shell program
If exec return value<0 then Error occurred in “exec” call .
Else successfully call the “exec”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/systemcall-160107132802/85/System-call-Fork-Exec-15-320.jpg)