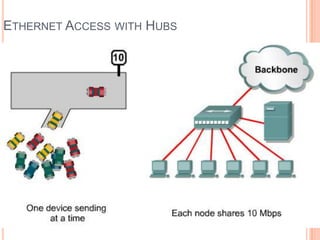
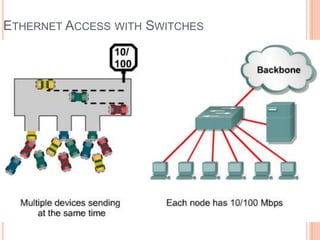
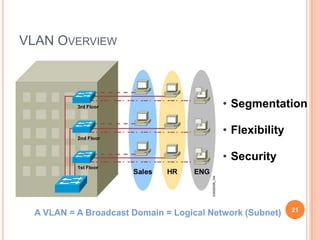
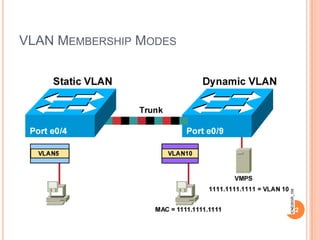
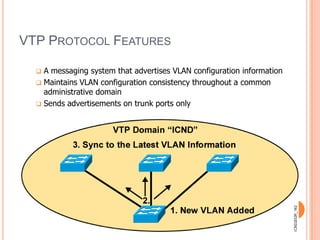
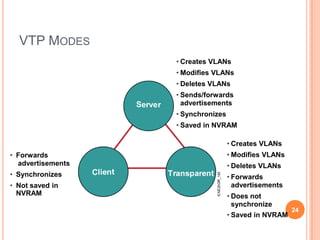
1. Layer 2 switches break up large collision domains into smaller ones by making each switch port its own collision domain, allowing a more efficient Ethernet LAN network than with hubs.
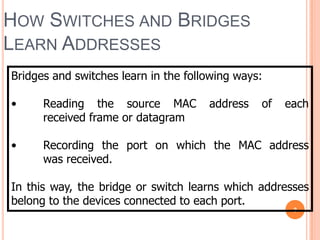
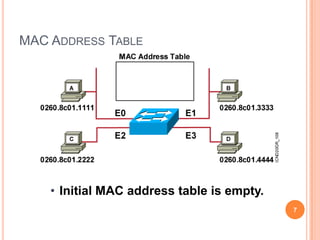
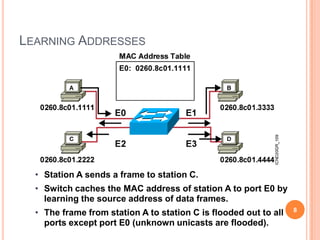
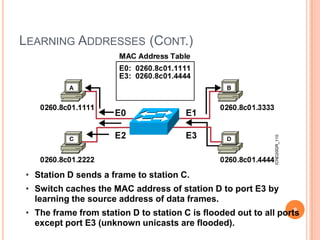
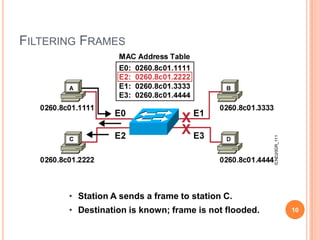
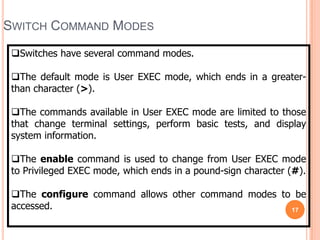
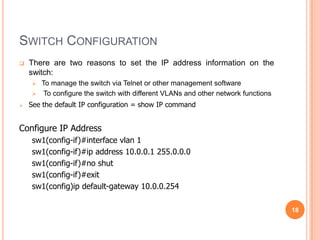
2. Bridges and switches learn MAC addresses and their associated ports by reading the source MAC address of each received frame and recording the port on which the MAC address was received.
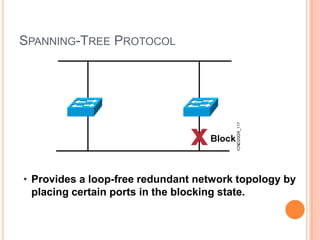
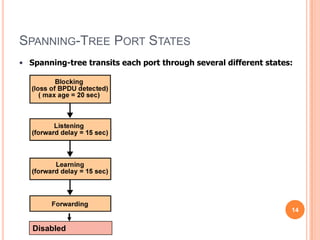
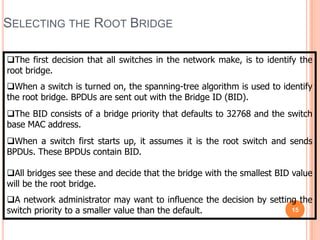
3. The Spanning Tree Protocol provides a loop-free redundant network topology by placing certain switch ports in the blocking state and identifying one switch as the root bridge using BPDUs.