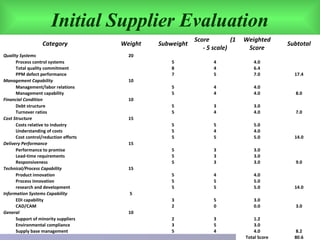
The document discusses supplier evaluation and selection. It provides an overview of the supplier evaluation and selection process, key criteria for evaluating suppliers, and developing surveys to aid in selection. Critical issues in supplier selection are also addressed. The presentation covers developing a multi-step process for evaluating suppliers on criteria like quality, cost, management capabilities, financial stability, and long-term relationship potential to select suppliers that minimize risk and maximize value.