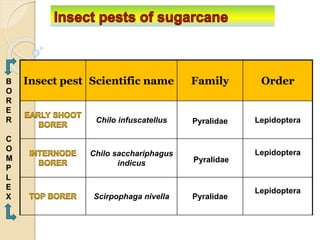
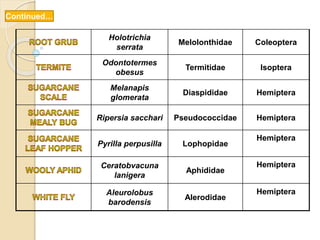
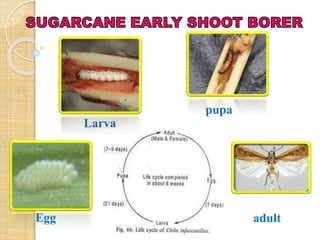
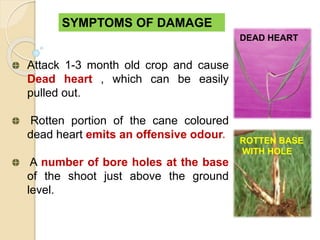
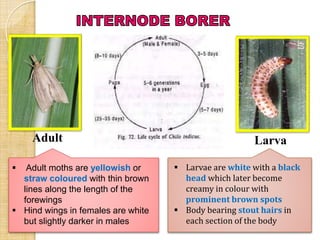
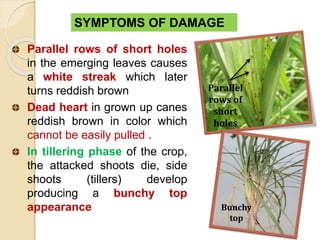
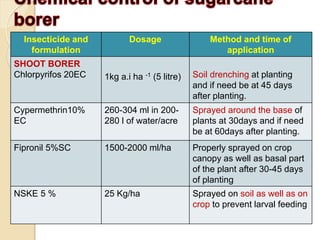
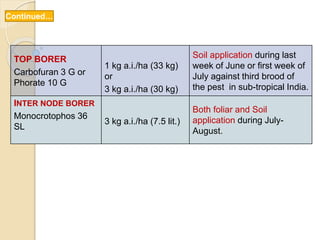
This document provides information on various insect pests that attack sugarcane crops. It describes the scientific names, symptoms of damage, life cycles and IPM strategies for borers like Chilo infuscatellus, Scirpophaga nivella, Holotrichia serrata, and Odontotermes obesus. It also discusses other pests like Melanapis glomerata, Ripersia sacchari, Pyrilla perpusilla, Ceratobvacuna lanigera, Aleurolobus barodensis and their management. The document lists cultural, biological and chemical control methods for effective management of sugarcane insect pests.