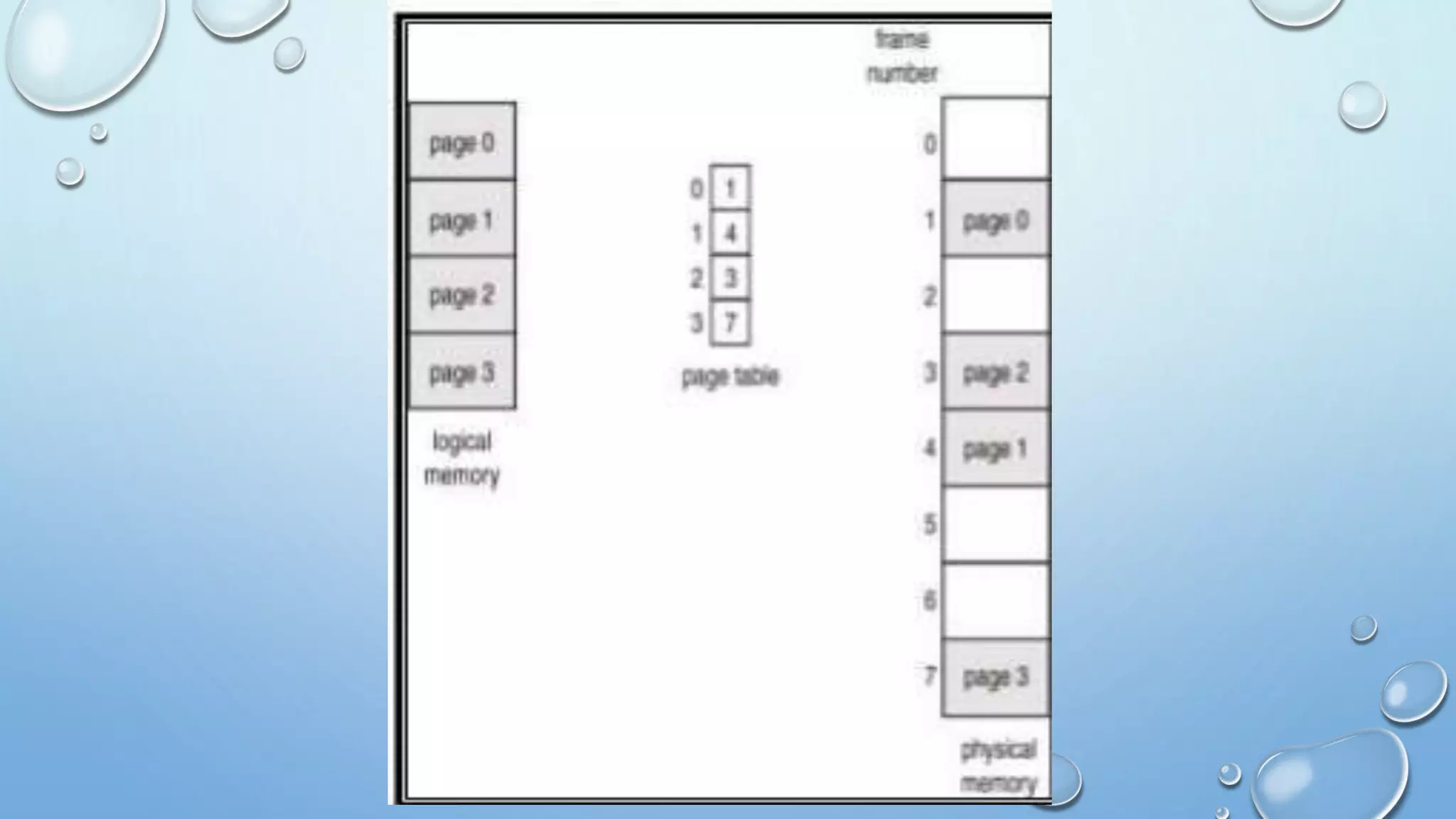
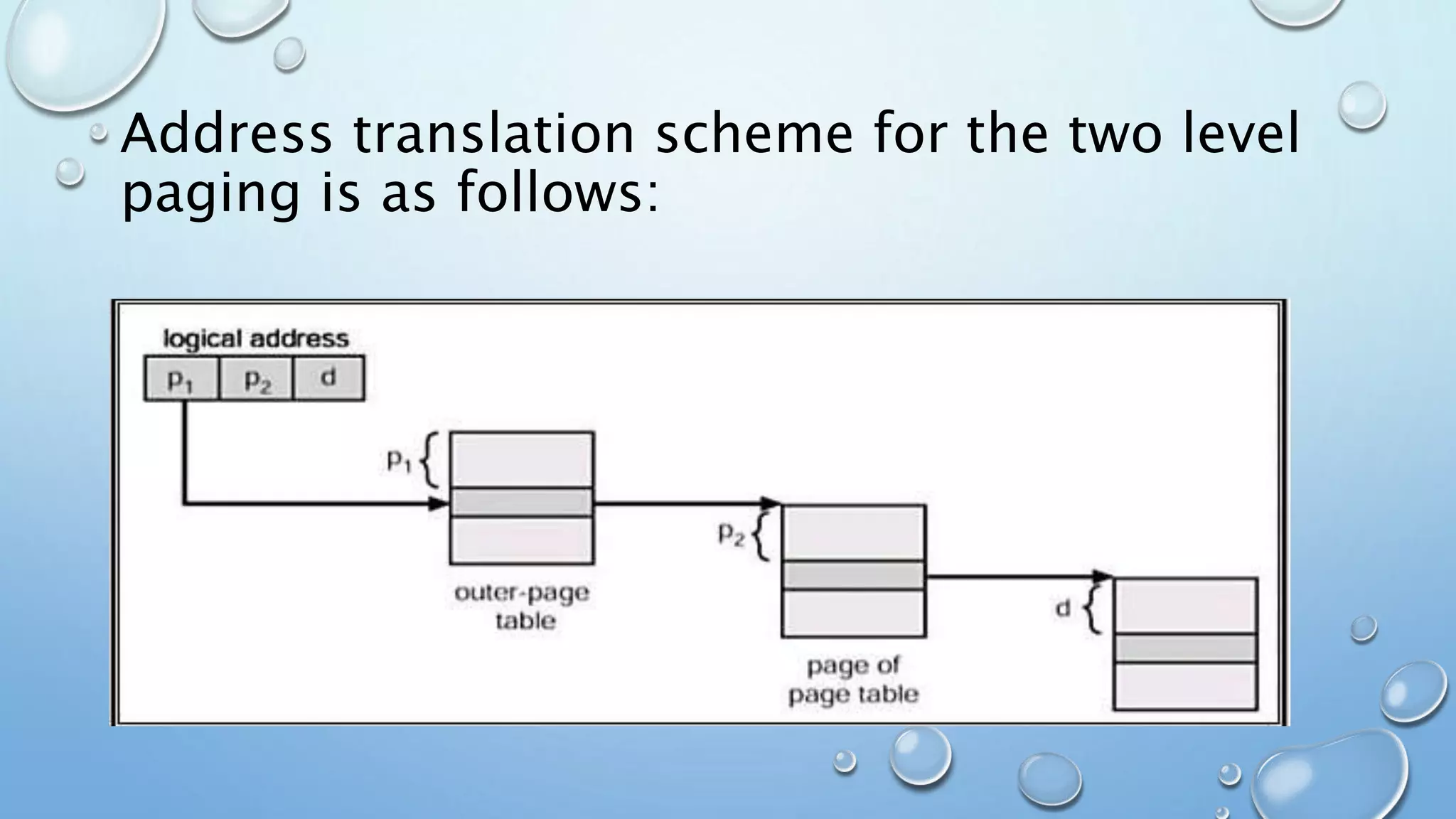
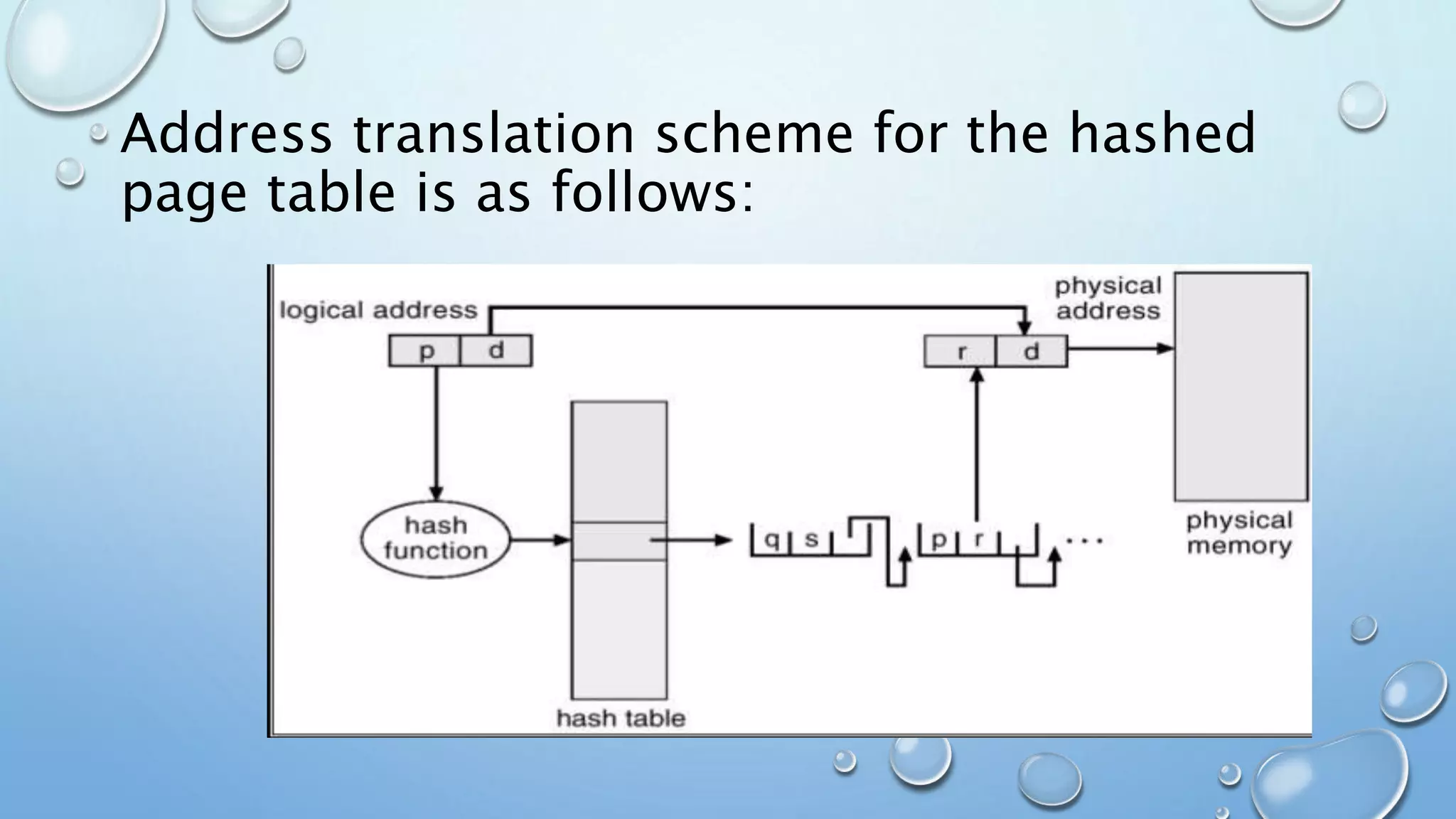
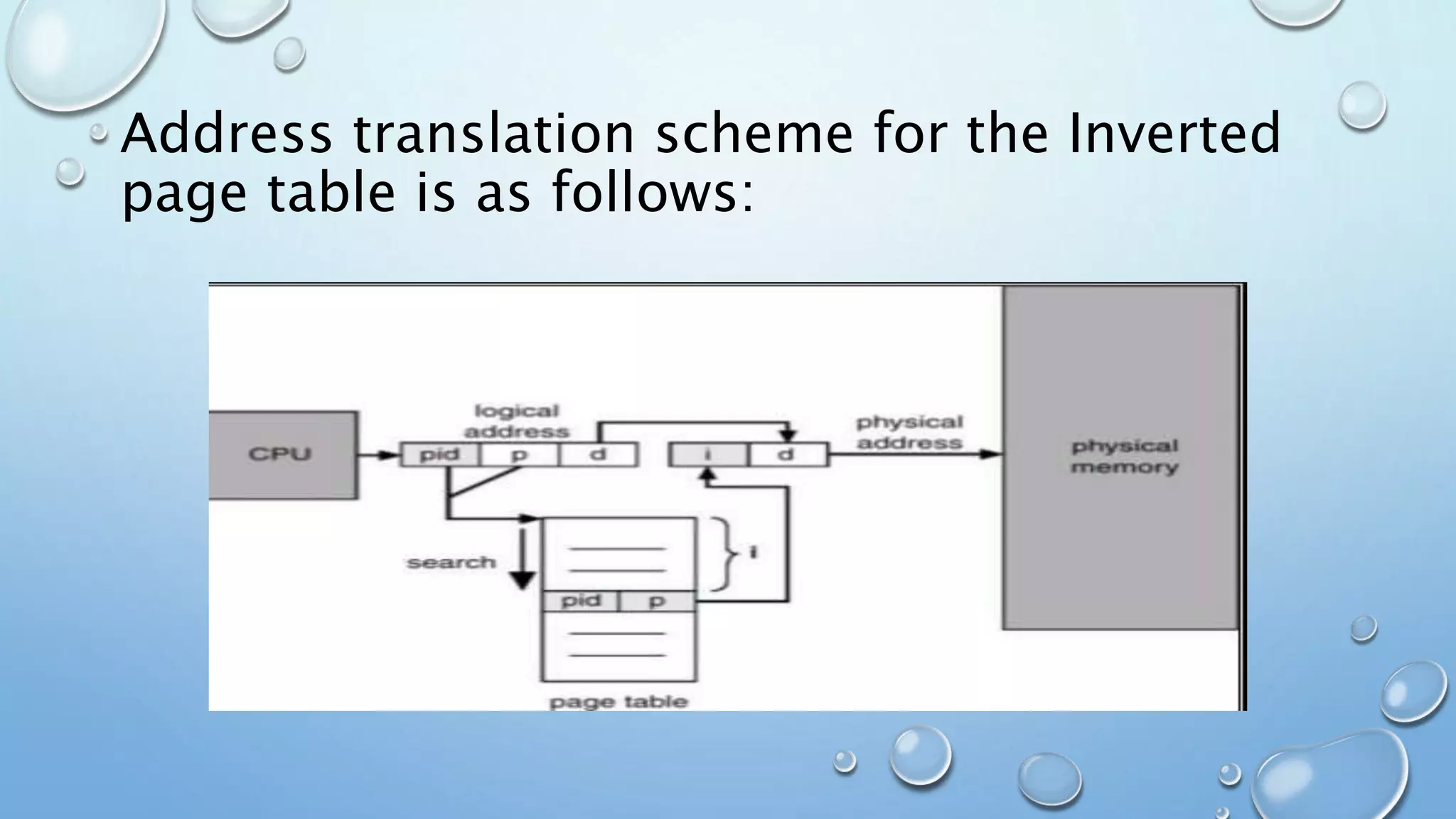
A page table is a data structure used in virtual memory systems to map virtual addresses to physical addresses. Common techniques for structuring page tables include hierarchical paging, hashed page tables, and inverted page tables. Hierarchical paging breaks up the logical address space into multiple page tables, such as a two-level or three-level structure. Hashed page tables use hashing to map virtual page numbers to chained elements in a page table. Inverted page tables combine a page table and frame table into one structure with an entry for each virtual and physical page mapping.